Oral
Electro-Magnetic Properties of Tissues
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:15 |
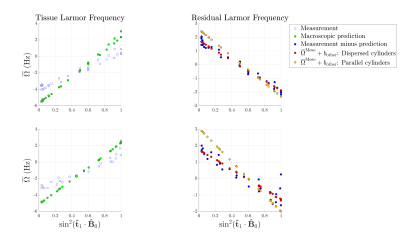 |
1263. Predicting
Mesoscopic Larmor Frequency Shifts with Diffusion MRI in Ex Vivo
Pig Optic Nerve

A. Sandgaard, A. Pampel, R. Müller, N. Wallstein, T.
Mildner, A. Alstrup, C. Jäger, H. Möller, S. Jespersen
Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
Impact: This study elucidates the nature of Larmor
frequency shifts in coherent white matter, enhancing our
understanding of its microstructural origin. These insights
have the potential to improve QSM techniques by achieving
better estimation of tissue magnetic susceptibility.
|
| 13:27 |
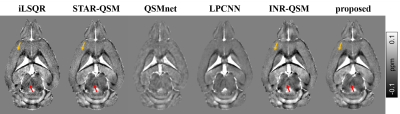 |
1264. A
robust deep learning method for quantitative susceptibility
mapping using diffusion model with a time-travel and resampling
refinement module

M. Zhang, H. Wei
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: We introduce a diffusion model-based method for
QSM reconstruction by enforcing hard data consistency during
inference. We also present a time-travel and
resampling refinement module in the latter steps to enhance
performance. Our approach enables robust and high-quality
QSM reconstruction.
|
| 13:39 |
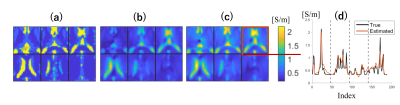 |
1265. Boundary
value estimation for electrical properties tomography based on
Helmholtz decomposition for the electric and magnetic fields
T. Nara, N. Eda
The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Impact: The estimated boundary EP values can be used in
the conventional partial-differential-equation-based and
integral-equation based methods for reconstructing
non-homogeneous EPs in the ROI, which eliminates the
necessity of assuming the boundary EPs.
|
| 13:51 |
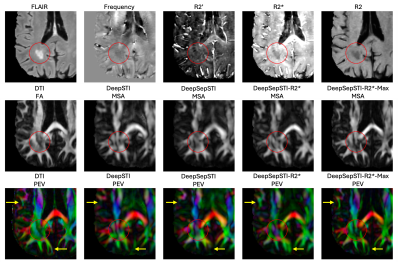 |
1266. DeepSepSTI-R2*:
R2-Free Anisotropic Susceptibility Source Separation in
Susceptibility Tensor Imaging with Deep Learning
Z. Fang, H-G Shin, B. Dewey, P. Calabresi, P. van Zijl, J.
Sulam, X. Li
The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, United States
Impact: DeepSepSTI-R2* enhances anisotropic
susceptibility source separation by eliminating the need for
extra R2 measurement, i.e., using only R2* and phase maps
derived solely from gradient echo data, thereby
significantly reducing scan time.
|
| 14:03 |
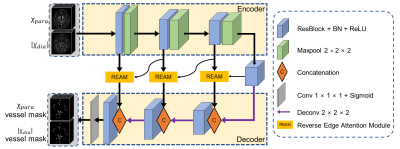 |
1267. Vessel
Segmentation in χ-separation using Deep Learning
H. Park, T. Kim, R. Hong, J. Kim, J. Lee
Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: The proposed deep neural network can produce
high-quality vessel masks, eliminating the need for
hyperparameter tuning in the original region-growing method.
The result may improve the accuracy and efficiency of χ-separation
map analysis, supporting precise susceptibility studies.
|
| 14:15 |
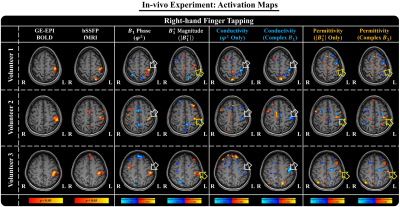 |
1268. Preliminary
Study on Functional MRI-Related Conductivity and Permittivity
Changes using Electrical Properties Tomography
K-J Jung, C. Cui, C. Park, S. Lee, S. Jung, D. Han, D-H Kim
Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: Functional MRI-related changes in both
electrical conductivity and permittivity are observed during
brain activation, potentially enhancing our understanding of
the relationships between fMRI effect, vascular factors, and
tissue electrical properties.
|
| 14:27 |
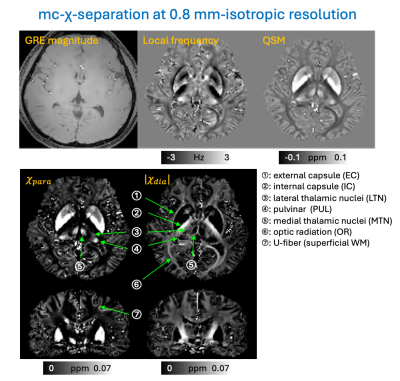 |
1269. Multi-compartment
susceptibility source separation (mc-chi-separation) using GRE
data only: Integrated model of QSM and myelin water imaging
H-G Shin, S. Saidha, J. Lee, P. Calabresi, P. van Zijl, X.
Li
Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore, United States
Impact: Mc-chi-separation enhances susceptibility source
separation by enabling chi-separation using GRE data only,
expanding its applications to clinical settings and
pre-acquired data lacking R2 measurements. This may also
facilitate better monitoring of iron and myelin-related
neurodegenerative disease with reduced inter-site
variability.
|
| 14:39 |
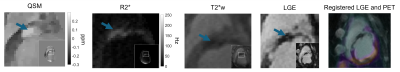 |
1270. Quantitative
Susceptibility Mapping and R2* of Ischemia-reperfusion Injury
and its Relationship with Reactive Oxygen Species Activity

M. Awad, S. Swago, C. Camillo, E. Thompson, A. Bhattaru,
B. Moon, G. Ferrari, E. Castillero, E. Gallagher, M.
McManus, V. Ferrari, R. Gorman, C. Tschabrunn, R. Mach,
J. Karp, P. Bravo, W. Witschey
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: The observed associations between magnetic
susceptibility and R2* with ROS activity allows for better
understanding of IRI and potential to develop new targeted
interventions. This suggests that iron could be a catalyst
for ROS production in ischemia-reperfusion injury.
|
| 14:51 |
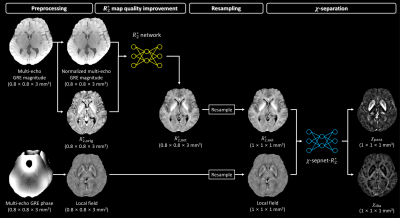 |
1271. Development
of χ-separation pipeline for UK Biobank dataset
J. Koo, H. Jeong, J. Kim, R. Hong, H-G Shin, X. Li, Y. S.
Hong, Y. Qiao, D. Arking, J. Lee
Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: This study proposes a processing pipeline for
high-quality χ-separation
in the UKB dataset. For high-quality χ-separation,
B0-field
inhomogeneity artifact in $$$R_2 ^*$$$ was removed using a
neural network. Our pipeline enables us to investigate the
large cohort UKB data.
|
| 15:03 |
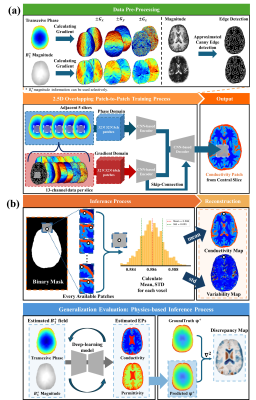 |
1272. Uncertainty-Aware
Conductivity Reconstruction via a 2.5D Patch-to-Patch
Data-driven Model
C-H Park, T. Meerbothe, K-J Jung, C. Cui, C. van den Berg,
S. Mandija, D-H Kim
Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: A 2.5D uncertainty-aware data-driven framework
is developed for conductivity reconstructions. This approach
enhances estimation accuracy and quantifies variability,
providing insights into model reliability and improving
performance compared to conventional physics-based and
end-to-end deep-learning methods.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.