Oral
Body Diffusion MRI: Modeling, Microstructure & Analysis
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
Introduction
Gregory Simchick
|
|
| 08:27 |
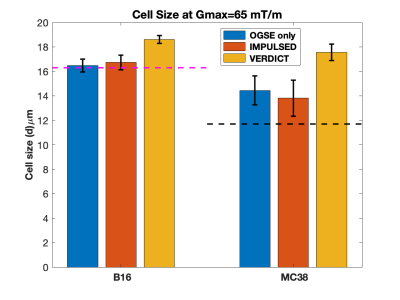 |
0762. Influence
of Diffusion Time and Gradient Strength on the Estimation of
Cell Size in MRI Cytometry
S. Adhikari, C. Jin, J. Xie, J. Wang, Y. Huo, J. Gore, X.
Jiang, J. Xu
Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Nashville, United States
Impact: OGSE only and IMPULSED derived mean cell size
were comparable at all gradient strengths while VERDICT
overestimated the mean cell size at 65mT/m suggesting to
include OGSE in estimating tumor cell size.
|
| 08:39 |
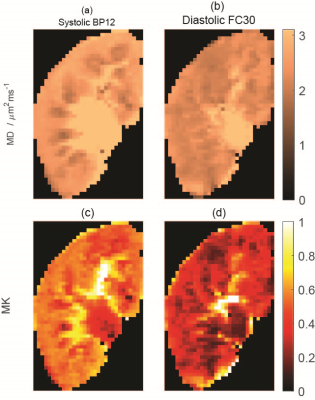 |
0763. The
effects of cardiac gating, flow compensation, and robust fitting
on diffusion kurtosis imaging of the kidneys
N. Gilani, M. Kumbella, M. Bruno, J. Veraart, D. Basukala,
H. Chandarana, E. Sigmund
NYU Langone Health, New York, United States
Impact: Cardiac gating, flow compensation, and advanced
processing pipelines mitigate artifacts and flow effects on
diffusion kurtosis imaging of the kidney and allow more
specific renal microstructural investigations.
|
| 08:51 |
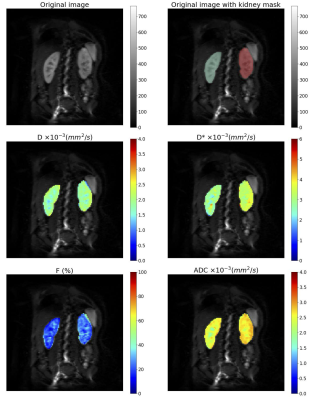 |
0764. Multi-center
test-retest repeatability and reproducibility of in-vivo renal
diffusion MRI measurements: preliminary findings
S. Pasini, L. Garcia-Ruiz, G. Villa, S. Ringgaard, A.
Strittmatter, A. Raj, R. Echeverria-Chasco, V.
Aramendía-Vidaurreta, J. María Mora Gutierrez, N. García
Fernández, M. Bozzetto, P. Brambilla, M. Trillini, L. Itu,
I. Urdea, L. Micu, N. Buus, M. Aastrup, E. Hansen, S.
Francis, F. Zoellner, C. Laustsen, M. Fernandez-Seara, A.
Caroli
Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS, Bergamo, Italy
Impact: This study supports the reliability of
diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in multi-center studies and
demonstrates excellent repeatability and reproducibility of
diffusion parameters.
|
| 09:03 |
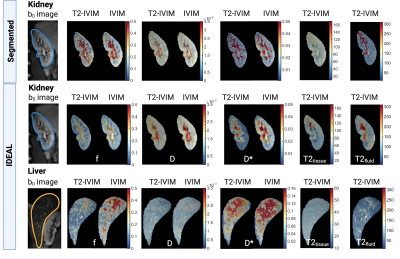 |
0765. 2D
fitting improves simultaneous intravoxel incoherent motion
(IVIM) and compartmental T2 mapping in the human kidney and
liver

J. Stabinska, T. Thiel, A. Ljimani, H-J Wittsack, H.
Zöllner
Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore, United States
Impact: The extended 2D T2-IVIM model efficiently
minimizes the bias in f values and allows simultaneous
estimation of the IVIM parameter and compartmental T2 values
in the liver and kidney.
|
| 09:15 |
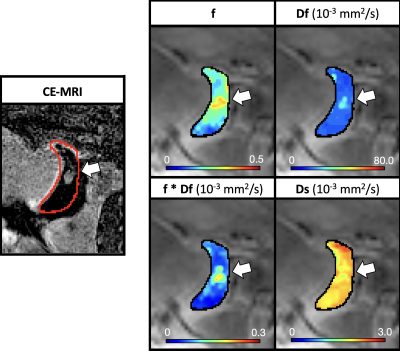 |
0766. Evaluation
of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) to detect bone marrow
ischemia and perfusion in a piglet model of Legg-Calvé-Perthes
disease

A. Amann, E. Buko, S. Parvaze, A. Armstrong, F. Tóth, C.
Johnson
University of Minnesota, St. Paul, United States
Impact: Our results provide additional evidence that
IVIM can serve as a non-contrast-enhanced alternative to
gadolinium CE-MRI in detecting regions of bone marrow
ischemia and perfusion, with potential benefit for pediatric
patients with ischemic bone disorders including LCPD.
|
| 09:27 |
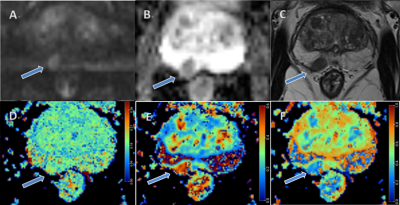 |
0767. The
Value of Hybrid Multidimensional MRI in Identifying Prostate
Cancer and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Feasibility Study
H. Ji, H. Cheng, M. Chen, X. Li, J. Zhu, C. Li
Department of Radiology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology; Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, P. R. China, Beijing, China
Impact: HM-MRI enables efficient and accurate
identification of PCa and BPH, thereby providing reliable
guidance for clinicians. HM-MRI also shows potential for
other clinical applications.
|
| 09:39 |
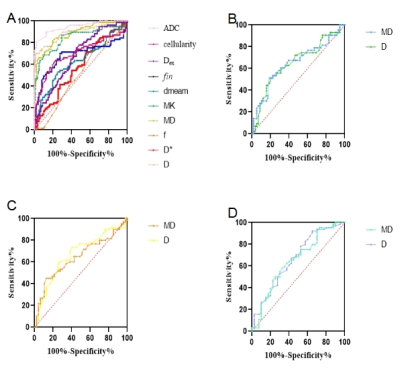 |
0768. Prediction
of prognostic factors of breast cancer with multimodal diffusion
MRI
X. Wang, y. zhang, J. Cheng, Y. Hu, L. Lin, P. Sun, Y. Hu,
A. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, K. Zhang, W. Zhang
The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Impact: Microstructural mapping with multimodal
diffusion MRI demonstrates promise for characterizing breast
cancer and helpful for prognostic evaluation.
|
| 09:51 |
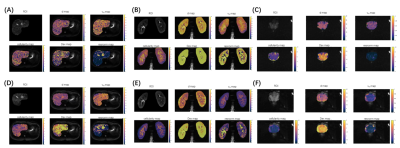 |
0769. Tailored
Parameter Optimization Framework for Time-dependent Diffusion
MRI: Feasibility in Multi-Region Body Imaging at 5.0T
Z. Zhang, L. Wang, W. Cai, H. Li, J. Zhu, X. Zhang, J. Yuan,
H. Wang, H. Li
The Institute of Science and Technology for Brain-inspired Intelligence, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact:
This framework supports broader clinical adoption of td-dMRI by enhancing diagnostic reliability, enabling multi-center standardization, and extending the approach’s applicability to other diffusion imaging models.
|
| 10:03 |
Discussion
Gregory Simchick
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.