Oral
Mesoscale fMRI
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:15 |
Introduction
Benedikt Poser
|
|
| 13:27 |
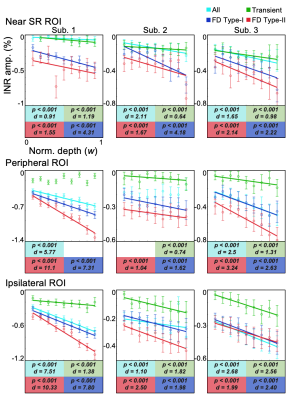 |
1254. Depth-dependent
dynamics of negative BOLD response in the human primary visual
cortex
N. J. Fesharaki, A. Vinogradov, J. Kim
UTHealth Houston, Houston, United States
Impact: This study demonstrated a linear increase in NBR
from deep to superficial gray matter, paralleling the depth
trend of PBR, and revealed distinct nHRF types with
consistent depth trends across both contralateral and
ipsilateral side.
|
| 13:39 |
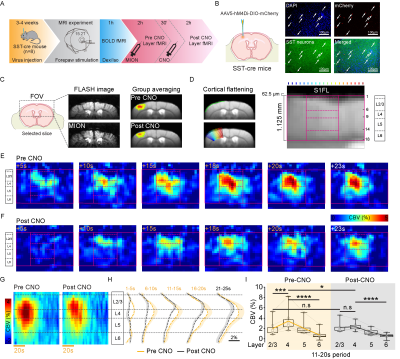 |
1255. Delayed
layer-specific CBV fMRI response is driven by somatostatin
neuron-astrocyte-vasodilation pathway

T. Vo, W. Jung, T. Jin, G. H. Im, S. Lee, S-G Kim
Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (CNIR), Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Suwon 16419, Rep, Suwon, Korea, Republic of
Impact: Our findings have significant implications for
the neurovascular coupling field by revealing a novel
contribution of interneurons and astrocytes. They also offer
important insights for human fMRI, the interpretation of
laminar-specific fMRI data and the design of
laminar-specific fMRI paradigms.
|
| 13:51 |
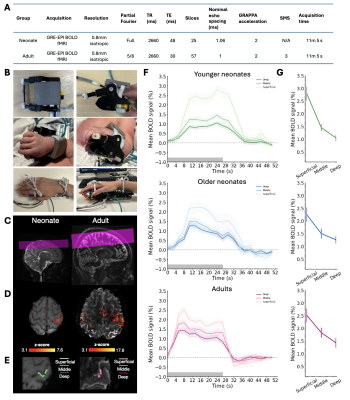 |
1256. Developmental
differences in haemodynamics drives temporal features of the
cortical-depth-dependent BOLD response in neonates at 7T
J. Willers Moore, E. Pickles, P. Bridgen, P. Di Cio, L.
Billimoria, I. Tomazinho, C. Da Costa, D. Gallo, G. Hartung,
A. D. Edwards, J. Hajnal, S. Malik, K. Uludag, J. Polimeni,
T. Arichi
King's College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: Developmental differences in haemodynamics and
cerebral physiology significantly alter temporal and
amplitude features of the cortical-depth-dependent BOLD
response in neonates. This has clear implications for using
fMRI to study the emergence of brain activity across this
critical period.
|
| 14:03 |
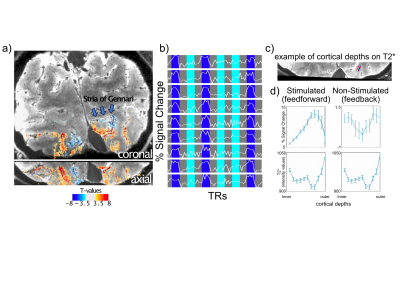 |
1257. Ultra-high
resolution Functional and Anatomical imaging in humans at 10.5T
.
L. Vizioli, S. Moeller, L. Dowdle, K. Ugurbil, E. Yacoub
CMRR, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: Imaging with the highest spatial resolution at
10.5T, while moving towards the 0.01µL voxel volume goal
(Brain Initiative 2.0), reduces single voxels to a few
thousand neurons, heralding new avenues in human
neuroscience with fMRI
|
| 14:15 |
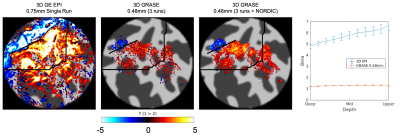 |
1258. Development
of GRASE Pulse Sequence with larger field of view for Mesoscale
functional MRI on the Next Generation (NexGen) 7T scanner
A. Beckett, S. Park, S. Häkkinen, E. Walker, A. Vu, D.
Feinberg
University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, United States
Impact: The advanced hardware of the NexGen 7T combined
with accelerated 3D GRASE incorporating random sampling
allows for increases in coverage and resolution to enable
mesoscale imaging. GRASE images show decreased pial vein and
brain surface layer bias than GE-EPI
|
| 14:27 |
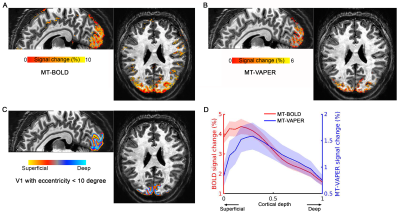 |
1259. Blood-nulling
versus tissue-suppression: Enhancing integrated VASO and
perfusion (VAPER) contrast for laminar fMRI
Y. Chai, L. Li, R. Stirnberg, L. Huber, T. Stöcker, P.
Bandettini, B. Sutton
UIUC, Urbana, United States
Impact: We proposed an innovative MT-enhanced VAPER
imaging sequence for layer fMRI that enhances sensitivity by
30% compared to traditional VAPER without MT, while
maintaining superior laminar specificity without increasing
acquisition time.
|
| 14:39 |
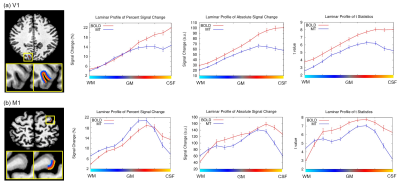 |
1260. Magnetization-Transfer
2D Echo Planar Imaging for 7T Laminar fMRI

B. Qin, X. Ma, Y. Chai, J. Qu, J-H Gao
Center for MRI Research, Peking University, Beijing, China
Impact:
The MT-EPI method enhances the spatial specificity in laminar fMRI. It is time-efficient and allows flexible adjustment of MT parameters to optimize the sequence under SAR constraints. |
| 14:51 |
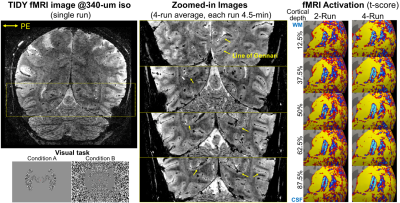 |
1261. Mesoscale
fMRI at ultra-high spatiotemporal resolutions using 3D Echo
Planar TIme- and DYnamic-resolved Imaging (TIDY)
Z. Dong, D. Haenelt, S. Nasr, B. Rosen, L. Wald, J.
Polimeni, F. Wang
Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, United States
Impact: We introduce a novel acquisition/reconstruction
technique, named 3D echo planar TIme- and Dynamic-resolved
imaging (TIDY), to achieve distortion-free mesoscale fMRI at
ultra-high spatiotemporal resolutions (e.g., whole-brain
500-um-iso at 885-ms volume-TR; partial-brain 340-um-iso at
1.2-s volume-TR).
|
| 15:03 |
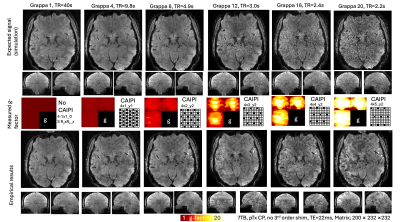 |
1262. Advanced
Echo-planar Parallel Imaging with Gradient Harmonization (AEPIG):
an optimization strategy for fast high resolution fMRI
R. Huber, M. Koehler, R. Stirnberg, J. Evans, L. Knudsen, A.
T. Morgan, D. Feinberg, D. Handwerker, M. Rubin, B. Akin, S.
Swegle, P. Bandettini
NIH, Bethesda, United States
Impact: The proposed optimization approach AEPIG
(Advanced Echo-planar Parallel Imaging with Gradient
Harmonization) allows layer-fMRI protocols with GRAPPA
acceleration factors up to R=20. This enabled researchers to
perform whole brain layer-fMRI while maintaining common TRs
(<3s).
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.