Oral
Biomarkers in Musculoskeletal Disease
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:30 |
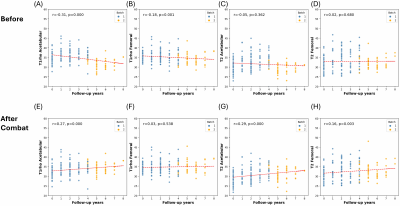 |
0557. Multi-Scanner
harmonized 8-year longitudinal hip cartilage T1ρ and T2
Y. Qian, R. Thahakoya, R. Bhattacharjee, M. Han, Z. Zhu, Y.
Yang, V. Pedoia, R. Souza, S. Majumdar
University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, United States
Impact: The harmonized longitudinal T1ρ and T2 data
provides insights into hip cartilage degeneration, aiding in
understanding osteoarthritis progression.
|
| 13:42 |
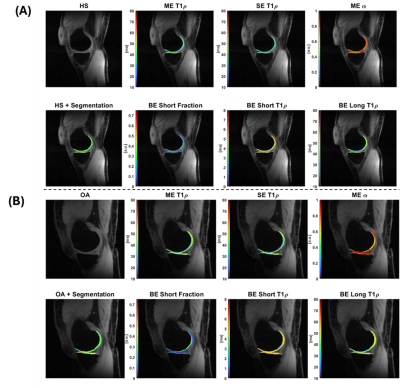 |
0558. Multi-component
3D-T1ρ Mapping of Early Knee Osteoarthritis
H. Lise de Moura, A. Monga, D. Singh, M. Zibetti, J.
Samuels, R. Regatte
NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: The study shows that combining multi-component
MRI parameters into a single composite biomarker can enhance
diagnostic performance and outperform mono-exponential T1ρ
analysis. Our proposed approach has broader potential for
improving early OA detection and assessment of other
diseases.
|
| 13:54 |
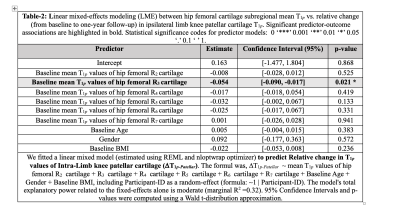 |
0559. Patellar
Cartilage Evolution is Linked to Intra-Limb Baseline Hip Femoral
Cartilage: Longitudinal Compositional Multi-Joint Study
R. Bhattacharjee, R. Thahakoya, Y. Qian, M. Han, F. Jiang,
R. Souza, V. Pedoia, S. Majumdar
University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), San Francisco, United States
Impact: Relationship between longitudinal changes in
patellar T1p and baseline T1p of intra-limb hip-femoral
load-bearing cartilage, might be useful for the prevention
of polyarticular OA development and lead to a better
understanding of the propagation of OA from hip to knee.
|
| 14:06 |
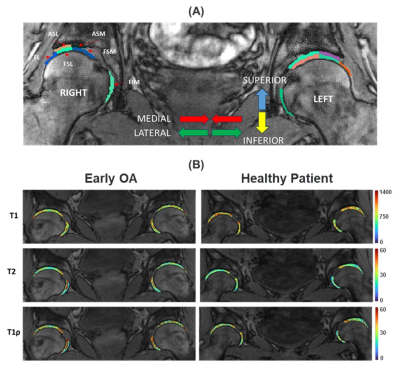 |
0560. Simultaneous
Bilateral T1, T2, and T1ρ Relaxation Mapping of Hip
Osteoarthritis with 3D-MRI Fingerprinting
A. Monga, H. Moura, M. Zibetti, T. Youm, J. Samuels, R.
Regatte
NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: Our preliminary study demonstrates that T1, T2,
and T1ρ values from 3D-MRF can potentially be used to detect
early OA in the hip joint.
|
| 14:18 |
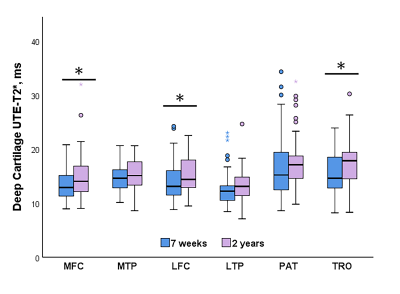 |
0561. Longitudinal
Changes to Patellar Cartilage UTE-T2* After Anterior Cruciate
Ligament Reconstruction Associate with Improved Knee Pain
A. Williams, C. Chu
Stanford University, Redwood City, United States
Impact: UTE-T2* qMRI evaluation shows that longitudinal
changes to deep knee cartilage composition associate with
concurrent clinically meaningful improvements in patient
reported knee pain following ACL reconstruction.
|
| 14:30 |
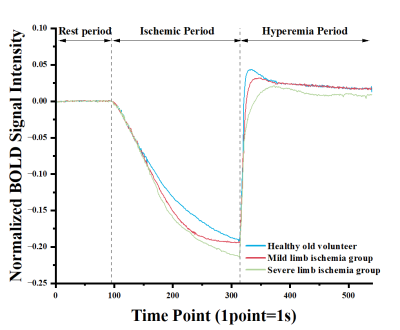 |
0562. Assessment
of lower limb lesions in diabetic patients utilizing BOLD-MRI at
7T: a feasibility study
H. Pang, X. Zhang, J. Chen, Z. Zhen, S. Zhou, W. Chen, W.
Chen
7T Magnetic Resonance Translational Medicine Research Center, Department of Radiology, Southwest Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
Impact: BOLD-MRI could enhance the precision in
assessing lower limb perfusion in diabetes, thereby aiding
accurate classification and diagnosis at early stages while
overcoming current diagnostic limitations through
non-invasive quantitative analysis of peripheral lesions
associated with diabetes.
|
| 14:42 |
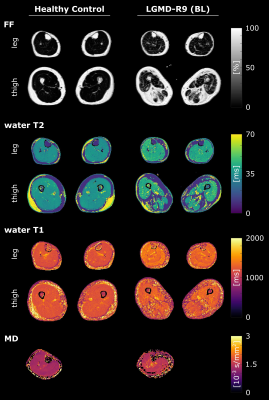 |
0563. Multi-parametric
quantitative MRI of the lower limb muscles in a longitudinal
study of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy R9

S. Rauh, P-Y Baudin, T. Stojkovic, S. Birnbaum, V.
Decostre, R-L Zanfongnon, Y. Fromes, M. Hooijmans, G.
Strijkers, J-Y Hogrel, S. Olivier, B. Marty, H.
Reyngoudt
Institute of Myology, Paris, France
Impact: QMRI parameters in LGMD-R9 patients were
significantly different from controls, with water-T2 and
water-T1 correlating with the increase in FF. These findings
may be valuable for identifying biomarkers in clinical
trials or selecting eligible LGMD-R9 patients for
therapeutic treatment studies.
|
| 14:54 |
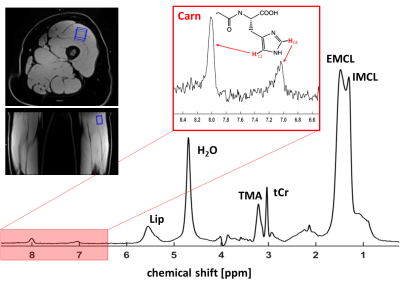 |
0564. Reduced
muscular carnosine levels in patients with Proximal Myotonic
Myopathy (PROMM) - an 1H-MR spectroscopy study
A. Gussew, A. Deistung, M. Rothe, D. Stoevesandt, W.
Wohlgemuth, A. Kölsch, M. Heuschen, A. Mensch
University Hospital Halle, Halle (Saale), Germany
Impact: This study demonstrates 1H-MR
spectroscopy’s potential for non-invasive monitoring of
PROMM-related metabolic changes by tracking carnosine
concentration declines in skeletal muscle. This approach
allows early detection of atrophy, supporting personalized
disease management and guiding therapeutic interventions.
|
| 15:06 |
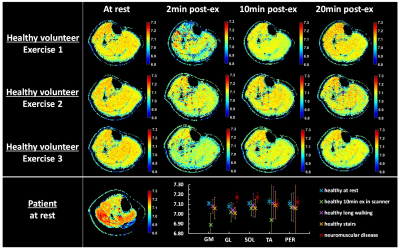 |
0565. CEST
Z-spectra fitting via Bloch-McConnell equations for pH mapping:
in vitro validation and application in healthy and pathological
leg muscles
V. Henriet, P-Y Baudin, C. Slioussarenko, B. Marty, M.
Lapert, H. Reyngoudt
Institute of Myology, Paris, France
Impact:
This work advances high-resolution pH mapping for neuromuscular disease assessment, offering non-invasive insights into muscle homeostasis. By enhancing sensitivity and spatial resolution in pH measurement, it could improve the monitoring of muscle disorders, benefiting clinical research. |
| 15:18 |
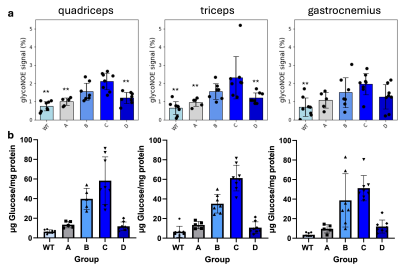 |
0566. Monitoring
glycogen levels and treatment effect in a mouse model of Pompe
disease
Q. Zeng, Y. Li, D. Timm, T. Johnson, N. Mehta, B. Fox, P.
van Zijl, N. Yadav
Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, United States
Impact: Monitoring of glycogen levels is essential for
assessing Pompe disease load and treatment efficacy.
GlycoNOE MRI offers the possibility to non-invasively map
glycogen levels in tissue using standard MRI scanners.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.