Oral
Relaxometry Across Different Tissues
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
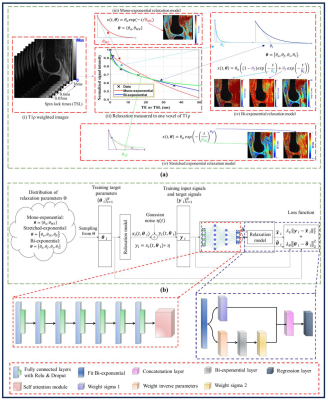 |
0056. SGDNet:
Synthetic Data Guided Supervised Deep Learning Network for
Multi-Component T1$$$\rho$$$ Mapping in the Knee Joint
D. Singh, R. R. Regatte, M. V. W. Zibetti
Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: Our results indicate that SGDNet is faster for
whole knee joint T1$$$\rho$$$ mapping than the NLS-based
methods, with comparable errors. Thus, SGDNets is an
alternative to replace NLS and RNLS for T1$$$\rho$$$ mapping
when computational time is an issue.
|
| 08:27 |
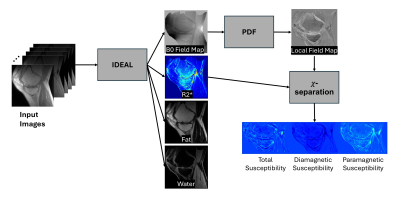 |
0057. Ultrashort
Echo Time Quantitative Susceptibility Source Separation in the
Musculoskeletal System: A Feasibility Study
S. Sedaghat, J. Park, E. Fu, A. von Drygalski, D. Moazamian,
Y. Ma, E. Chang, J. Du, L. Nardo, H. Jang
University Hospital Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany
Impact: UTE-based QSM enables precise separation of
paramagnetic and diamagnetic sources in musculoskeletal
tissues, improving detection of iron deposits in joints.
This technique promises enhanced accuracy in diagnosing
conditions like hemophilic arthropathy and assessing
biochemical tissue composition in clinical applications.
|
| 08:39 |
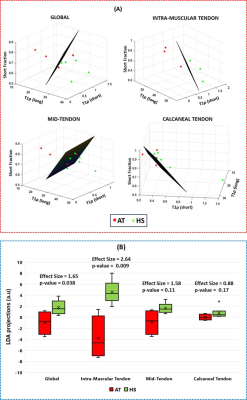 |
0058. Ultra-short-echo
time Sequence for Bi-exponential T1ρ Mapping of Achilles
Tendinopathy
A. Monga, H. Moura, M. Zibetti, S. Rao, R. Regatte
NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: The study demonstrates that the T1ρ mapping
obtained from magnetization-prepared 3D-UTE Sequence can
potentially detect AT, particularly with BE relaxation
models when combined with LDA.
|
| 08:51 |
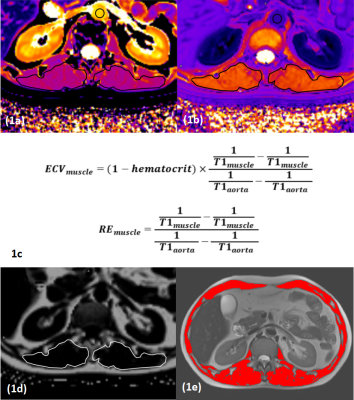 |
0059. The
Exploration of Skeletal Muscle Abnormalities in Advanced Chronic
Liver Disease using Muscle ECV Measured by T1-mapping MRI
Y. Young
Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
Impact: The muscle ECV fraction, quantified by
T1-mapping MRI, may help elucidate the pathophysiological
mechanisms of skeletal muscle abnormalities in patients with
ACLD.
|
| 09:03 |
 |
0060. Water
specific T1 in Skeletal Muscle: Validation, Normative Values and
the Confounding Influence of Fat
S. Foulkes, M. Haykowsky, R. Sherrington, A. Kirkham, J.
Grenier, P. Seres, C. Beaulieu, D. Paterson, R. Thompson
University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
Impact: The SR-CSE approach jointly quantifies skeletal
muscle fat and water-specific T1 (T1Water, removing T1 bias
from fat), offering detection of muscle fibrosis and/or
edema with co-existing fatty infiltration (e.g. sarcopenia).
|
| 09:15 |
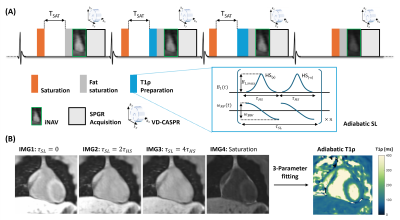 |
0061. Free-breathing
High-resolution 3D Whole-heart Adiabatic T1ρ Mapping at 0.55T
D. Si, M. Crabb, S. Littlewood, K. Kunze, C. Prieto, R.
Botnar
School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: The proposed 3D T1ρ mapping sequence
demonstrates the feasibility of non-invasive myocardial
tissue characterization at 0.55T with 2mm
isotropic-resolution in an efficient free-breathing scan of
7 mins. Both phantom and in-vivo 3D T1ρ measurements showed
excellent agreements with reference sequences.
|
| 09:27 |
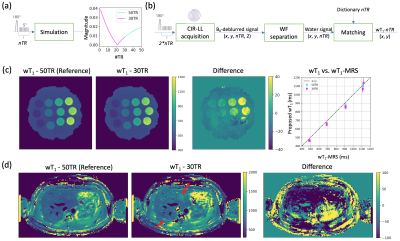 |
0062. Neural-network-based
accelerated liver water T1 mapping

E. Huaroc Moquillaza, V. Spieker, C. Rao, J. Meineke, K.
Weiss, J. Schnabel, M. Doneva, D. Karampinos
Institute of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, TUM School of Medicine and Health, Department Clinical Medicine, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany
Impact: A neural network-based liver wT1 mapping
technique that shortens acquisition times using CIR-LL
without sacrificing the quality of quantitative
reconstruction results, and holds promise for further
mapping applications.
|
| 09:39 |
 |
0063. Non-Contrast
T1ρ Mapping can Differentiate Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy from
Hypertensive Heart Disease: A Prospective Clinical CMR Study
D. Yang, K. Li, H. Qin, J. Zheng
Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning ,China, Nanning, Chile
Impact:
This research employs non-contrast T1ρ mapping to evaluate fibrosis differences between HCM and HHD, providing valuable insights for distinguishing left ventricular hypertrophy, consequently supporting customized, patient-specific treatment approaches. |
| 09:51 |
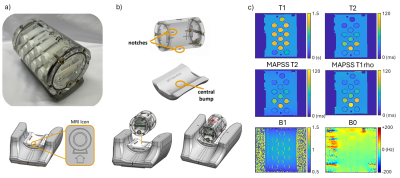 |
0064. Multi-site
Multi-vendor Randomized Controlled Trial of Quantitative Knee
MRI using a Novel MSK Relaxometry Phantom
J. Kim, Z. Zhang, R. Lartey, M. Li, S. Zbyn, S. Tosun, S.
Russek, K. Stupic, C. Stoffer, K. Keenan, D. Rutkowski, J.
Kammerman, J. Brittain, C. Winalski, X. Li
Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, United States
Impact: We established a QA process for knee MRI
relaxometry using a novel MSK relaxometry phantom for
large-scale multi-site studies. By identifying discrepancies
in measurements during the study, the QA process will ensure
data quality in multi-site studies.
|
| 10:03 |
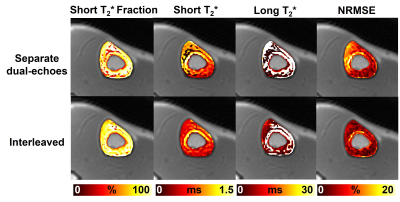 |
0065. Interleaved
ultrashort echo acquisition for motion-robust bicomponent
imaging of cortical bone
S. H. Shin, J. Lo, A. Suprana, J. Wang, D. Moazamian, D.
Berry, S. Jerban, E. Chang, J. Du, Y. Ma
UC San Diego, La Jolla, United States
Impact: The proposed sequence enables motion-insensitive
quantitative imaging of short T2 tissues requiring
multi-echo acquisitions, such as bi-component T2* imaging
and quantitative susceptibility mapping, without
post-acquisition motion correction.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.