Oral
AI in AD & Aging
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:30 |
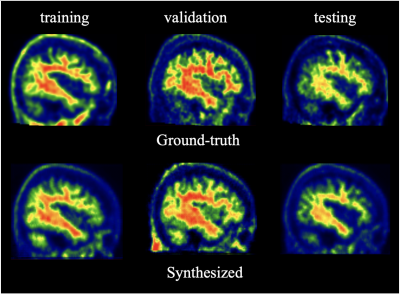 |
0870. Synthesis
of amyloid PET images based on structural MRI data using
specialized VQGAN

Z. Zhang, J. Wu, P. Wang, K. Chai, S. Jiang, C. Onyike,
J. Zhou
Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, United States
Impact: This MRI-based deep learning method provides a
cost-effective, non-invasive alternative to amyloid-PET
imaging, potentially expanding diagnostic tools in clinical
settings, especially where PET imaging is unavailable.
|
| 13:42 |
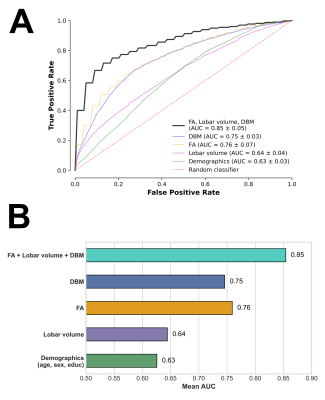 |
0872. MARBLE:
An MRI-based in-vivo marker of limbic-predominant age-related
TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC)
M. Tazwar, A. Evia, A. R. Ridwan, D. Bennett, J. Schneider,
K. Arfanakis
Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, United States
Impact:
LATE-NC is common in older adults and can only be diagnosed at autopsy. MARBLE is a novel in-vivo marker of LATE-NC and may significantly contribute towards diagnosis, monitoring, prevention, and treatment of this devastating disease. |
| 13:54 |
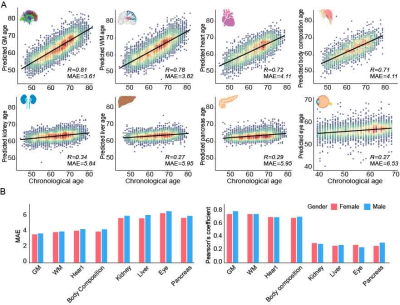 |
0873. Imaging-based
organ-specific aging clock predicts human diseases and
mortalities
P. Ren, W. Su, Y. Liang, J. You, W. Gong, W. Cheng
Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact: Our research has, for the first time,
illustrated organ specificity of imaging-based aging clock
from the macroscale and microscale perspective. Furthermore,
imaging-based organ aging could predict the incident of
organ-specific diseases, highlighting potential targets
aimed at slowing organ-specific aging processes.
|
| 14:06 |
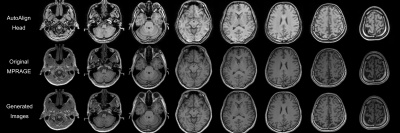 |
0874. Generation
of high-resolution MPRAGE-like images from head MRI localizer
images
Y. Fushimi, H. Tagawa, K. Fujimoto, S. Nakajima, S. Okuchi,
A. Sakata, S. Otani, K. Wicaksono, Y. Wang, S. Ikeda, S.
Ito, M. Umehana, Y. Nakamoto
Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan
Impact: MPRAGE-like images generated from MRI localizer
images and the reference MPRAGE image showed good agreement
with respect to visual assessment of medial temporal lobe
atrophy by radiologists. Voxel-based morphological analysis
was also acceptable for evaluation of temporal lobe atrophy.
|
| 14:18 |
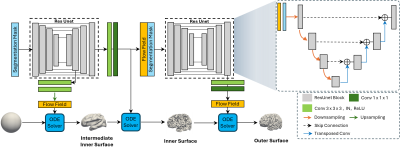 |
0875. A
deep learning pipeline for lifespan cortical surface
reconstruction, spherical mapping, and anatomical correspondence
J. Zhao, G. Lin, X. Chen, S. Ahmad, P. T. Yap
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, United States
Impact: Our end-to-end pipeline offers a fast and
accurate method for generating cortical surfaces, making it
an efficient tool for surface-based analysis of cortical
morphology.
|
| 14:30 |
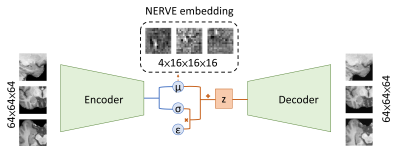 |
0876. NERVE:
Neuroimaging Embedding Representation via Variational Encoding
P-S Chen, T-Y Huang, Y-R Lin, T-C Chuang, H-W Chung
National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei, Taiwan
Impact: NERVE encodes brain MRI into a compressed embed.
A generalized and open-source NERVE model offers broad
applications in neuroscience.
|
| 14:42 |
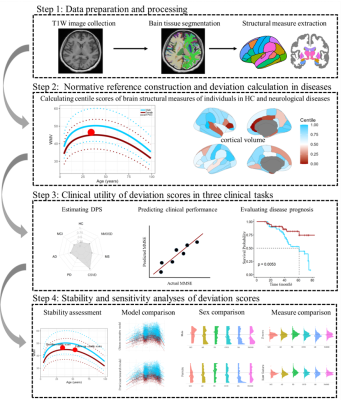 |
0877. Quantifying
individualized brain structural deviations of multiple
neurological diseases from normative references
Z. Zhuo, L. Chai, J. Weng, Y. Liu
Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Impact: The study proposed that utilizing
population-specific normative references can lead to a more
precise quantification of deviations in brain structure.
|
| 14:54 |
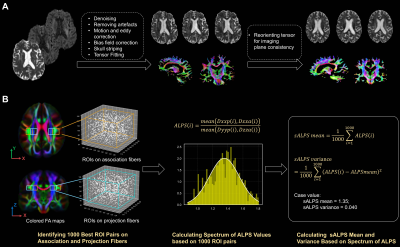 |
0878. Automated
sALPS: Advancing Non-Invasive Glymphatic Imaging for Early
Cognitive Impairment Diagnosis and Staging
X. Xu, N. Wu, M. Xu, P. Wang
Tongji Hospital Affiliated Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study provides a novel, automated sALPS
biomarker that enhances early detection of glymphatic
dysfunction, potentially improving diagnostic precision and
staging of cognitive impairment through its application in
machine learning models for robust classification across
cognitive stages.
|
| 15:06 |
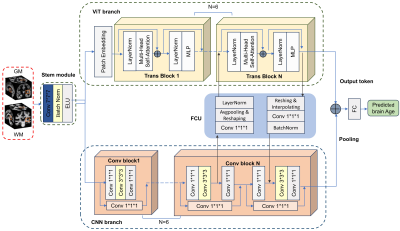 |
0879. A
brain-age prediction model in 3D-CNN-ViT deep learning network
S. Gan, C. Fang, X. Xu, R. Xu, J. Huang, D. Sun, Q. He
Institute of Artificial Intelligence, Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center, Hefei, China
Impact: The fused local and global features of MRI data
improve the performance in brain-age prediction paradigm,
suggesting that the CNN-ViT architecture has potential to
promote prognosis prediction or biotype classification in
clinical applications using MRI data.
|
| 15:18 | 0871. WITHDRAWN |
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.