Oral
Dementia & Other Neurodegeneration
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 15:45 |
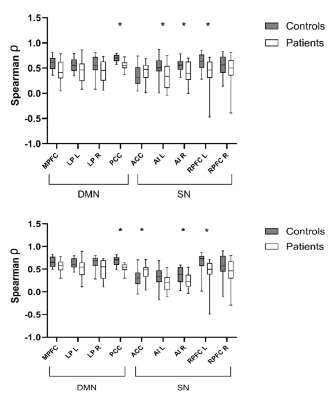 |
1055. Impact
of Frontotemporal Dementia on the Coupling of Cerebral Energy
Metabolism to Neuronal Activity: A hybrid PET/MR study
M. Joshy, P. Dassanayake, L. Liu, M. Aiello, U. Anazodo, E.
Finger, K. St. Lawrence
University of Western Ontario, London, Canada
Impact: Decoupling of cerebral glucose metabolism and
functional connectivity is not limited to Alzheimer's, but
evident in other neurodegenerative conditions. This
dissociation is most associated with resting state networks
impacted by the specific condition.
|
| 15:57 |
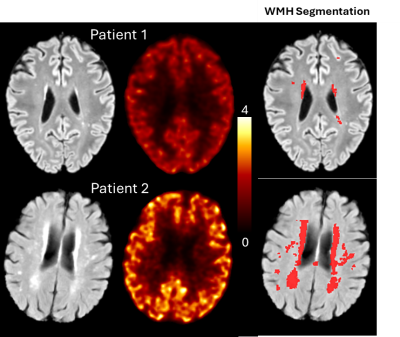 |
1056. Exploring
the Link between Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Alzheimer’s
Disease with [11C]CS1P1, a Novel PET Tracer of Neuroinflammation
I. Orukari, Y. Wang, Y. Chen, B. Wang, K. Friedrichsen, M.
Brier, Y. H. Nai, L. Jones, F. Rahmani, J-P Okafor, J.
Rajamanickam, S. Flores, J-M Lee, A. Ford, Z. Tu, T.
Benzinger, H. An
Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, United States
Impact: [11C]CS1P1
PET could be a biomarker of early AD and cSVD. This imaging
approach could guide the timely application of
disease-modifying therapies and possibly enhancing treatment
outcomes.
|
| 16:09 |
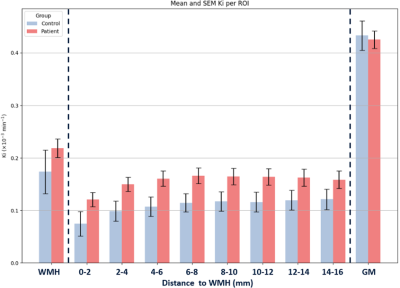 |
1057. DCE-MRI
reveals elevated blood-brain barrier leakage of heterogeneous
white matter in cerebral small vessel disease

D. Verstappen, J. de Jong, P. Voorter, M. van Dinther,
M. Gidding, R. van Oostenbrugge, J. Staals, J. Jansen,
W. Backes
Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, Netherlands
Impact: A more regionally targeted analysis is required
to determine the subtle BBB leakage in the NAWM of patients
with cSVD and to assess differences with controls.
|
| 16:21 |
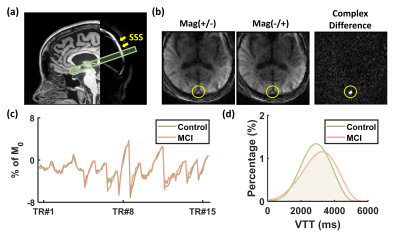 |
1058. The
role of venous hemodynamics in cerebral small vessel disease

W. Shi, D. Jiang, J. Song, Y. Gou, Z. Hu, K. Hazel, G.
Pottanat, E. Jones, J. Suconic, C. Xu, V. Yedavalli, P.
Rosenberg, R. Kalyani, A. Moghekar, S. Yasar, D. Lin, M.
Albert, H. Lu
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, United States
Impact: Venous hemodynamics such as transit time and
blood volume are associated with white matter hyperintensity
and vascular risks. These measures may be useful as imaging
markers to characterize venous abnormalities in cerebral
small vessel disease.
|
| 16:33 |
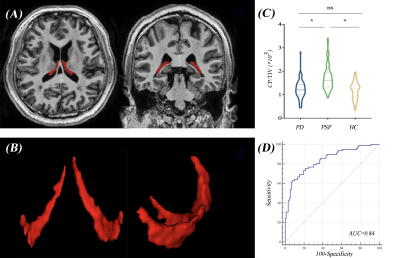 |
1059. Choroid
Plexus Enlargement related to tau deposition in progressive
supranuclear palsy
N. Wang, L. Liu, Y. Wu
Fudan university, HuaShan hospital, Shanghai, China
Impact: CP volume expansion may serve as a promising
imaging biomarker of tau accumulation in PSP patients and
could potentially be used to differentiate PSP from PD.
|
| 16:45 |
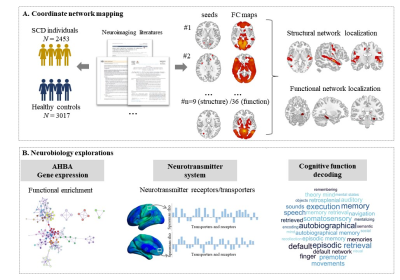 |
1060. Mapping
Subjective Cognitive Decline to a Common Brain Network and
Linking to Gene Expression Profiles

H. Lan, W. Liu, X. Suo, Q. Gong
West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Impact: Heterogeneous neuroimaging findings of SCD
converge on common brain networks, which is linked to
specific biological processes and neurotransmitters. This
comprehensive understanding of the neural substrates
underlying SCD may inform more targeted strategies to
prevent dementia.
|
| 16:57 |
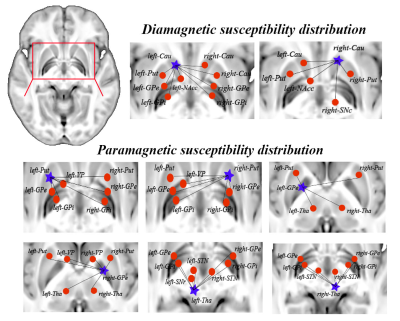 |
1061. Assessing
regional brain magnetic susceptibility in Wilson’s disease using
sub-voxel quantitative susceptibility mapping
Z. Huang, H. Wei, J. Chu
First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
Impact: The APART-QSM could precisely quantify the
paramagnetic and diamagnetic properties in the brain in
Wison’s disease. The present study offers significant
insights into magnetic susceptibility perturbation of the
deep brain nucleus in Wilson’s disease.
|
| 17:09 |
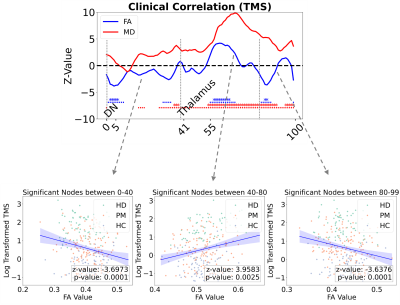 |
1062. Along-Tract
Diffusion Alterations in the Dentato-Rubro-Thalamic Tract
Correlate with Motor and Cognitive Decline in Huntington's
Disease
Z. Wang, A. Solomon, G. Shao, J. Lupo, J. Yao
University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles , United States
Impact: This study reveals the DRTT's involvement in HD
progression and underscores the importance of examining
regional changes along the tract, providing valuable
insights into white matter alterations and potential new
biomarkers of motor and cognitive impairments in HD.
|
| 17:21 |
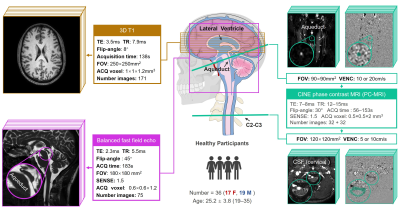 |
1063. Which
Came First: Ventricular Enlargement or Abnormal CSF Circulation?
P. LIU, J. Xie, Y. Attekeble, K. Owashi, O. Balédent
CHU Amiens-Picardie, University Hospital, Amiens, France
Impact: The findings provide insights into the
pathogenesis of hydrocephalus, offering potential markers
for early diagnosis. Understanding the relationship between
aqueduct resistance, Ratio-SV, and Ratio-Area may guide
clinical practice and help identify early indicators of CSF
dynamic disorders.
|
| 17:33 |
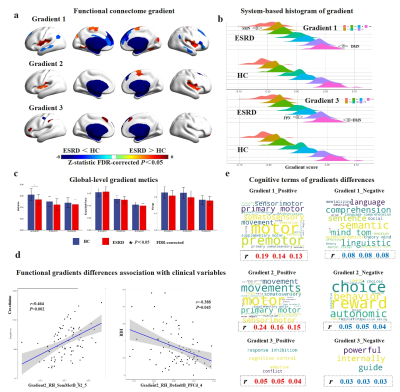 |
1064. Brain
connectome gradient dysfunction in patients with ESRD and its
association with clinical phenotype and cognitive deficits
P. Li, L. Ren, Y. Yang, X. Zhu, H. Yuan, Z. Luo, J. Mu, W.
Wang, M. Zhang
The Second Affiliated Hospital of Air Force Medical University, Xi'an, China
Impact: This is the first study to reveal the brain
connectome hierarchical dysfunction in ESRD patients and its
association with clinical phenotype and cognitive deficits,
which might be used as an potential neuroimaging marker for
clinical symptoms in ESRD patients.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.