Oral
High-Field MRI
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 16:00 |
Introduction
Tom Scheenen
|
|
| 16:12 |
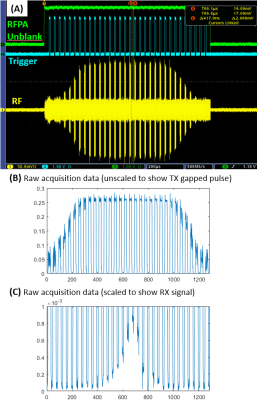 |
0263. An
ultra-fast RF switch for 23Na SWIFT imaging at 10.5T
R. Lagore, S. Schmidt, E. Auerbach, N. Kobayashi, C.
Schildknecht, S. Moeller, G. Adriany, G. Metzger
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: Enabling imaging of nuclei with fast relaxation
times with custom-built fast-switching PIN drivers and RF
frontend which features sub-microsecond switching speeds and
isolations of up to 100 dB between transmit and receive.
|
| 16:24 |
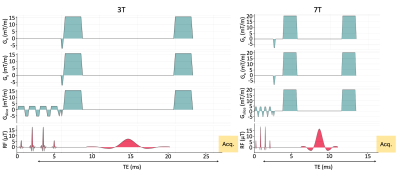 |
0264. Mapping
amide protons in the human brain at 3 and 7 Tesla using
downfield MRSI
İ. Özdemir, S. Etyemez, P. Barker
Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, United States
Impact: Amide
mapping using DF-MRSI at 7T showed significantly superior
precision compared to 3T, and therefore is the preferred
field strength for future research studies of DF
metabolites.
|
| 16:36 |
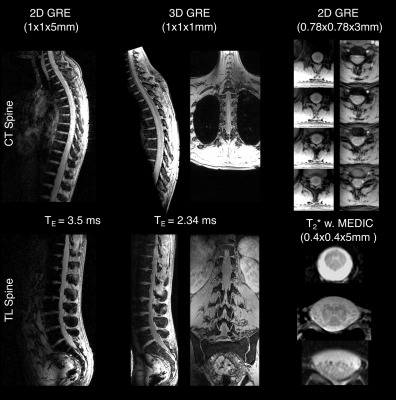 |
0265. Imaging
of the Entire Spinal Cord with a 32-Channel pTx Body Array at 7
T
C. Aigner, J. Grimm, C. Neelsen, J. Jende, S. Orzada, T.
Fiedler, S. Kühn, M. Ladd, S. Schmitter
Max Planck Institute for Human Development, Berlin, Germany
Impact: This study demonstrates the potential of a 7
Tesla pTx body array with optimized pTx techniques for
imaging the entire spinal cord in a large field of view,
paving the way for improved diagnosis of spinal cord
pathologies.
|
| 16:48 |
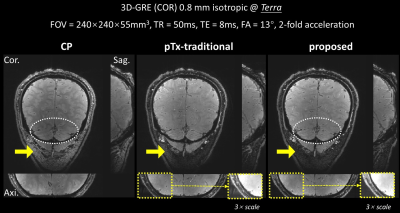 |
0267. Real-4D
parallel transmit pulse design for slab-selective uniform water
excitation: demonstration in humans at 7T

X. Shao, Z. Zhang, H. Guo, K. Ugurbil, X. Wu
Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Impact: Our new design method provides an effective
solution for slab-selective uniform water excitation with no
out-of-slab fat excitation, holding a promise to many
applications including mesoscale fMRI and fat-free body
imaging at ultrahigh field.
|
| 17:00 |
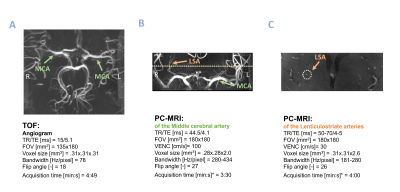 |
0268. Increased
intracerebral blood pulsatility as measured with 7T MRI is
related to cognitive impairment in a memory clinic sample
M. van der Thiel, M. van den Kerkhof, A. Postma, I.
Ramakers, W. Backes, J. Jansen
Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, Netherlands
Impact: This study highlights the clinical value of 7T
MRI in measuring small vessel pulsatility and damping,
revealing insights into local fluid dynamics and the
distinct mechanisms related to cognitive performance in
memory clinic patients and healthy controls.
|
| 17:12 |
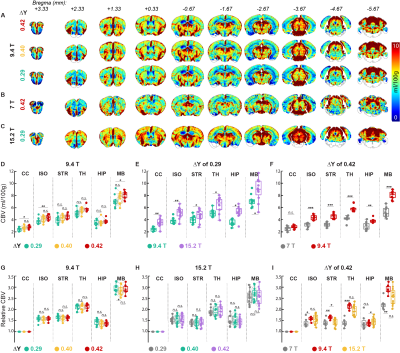 |
0269. Whole-brain
BOLD Responses to Graded Hypoxic Challenges at 7T, 9.4T, and
15.2T: Implications for Ultrahigh-Field BOLD-DSC MRI

T. T. Le, S. H. Choi, G. H. Im, C. H. Lee, D. Lee, J.
Schulman, H. Cho, K. Uludağ, S-G Kim
Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (CNIR), Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Suwon, Korea, Republic of
Impact: We investigated hypoxia-induced blood and tissue
ΔR2* responses
across varying ΔY levels and field strengths, alongside CBV
assessments. This study provides biophysical insights into
field-dependent BOLD signals at ultrahigh fields and
addresses challenges in quantification of
susceptibility-based CBV measurements.
|
| 17:24 |
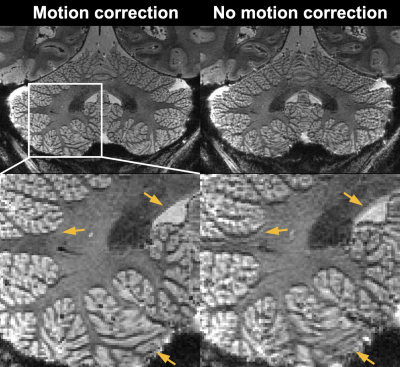 |
0270. Mesoscale
T2*-weighted MRI of the human cerebellum at 10.5 Tesla: initial
experience
S. Qu, J. de Zwart, P. Van Gelderen, J. Duyn, A. Grant, A.
Bratch, E. Auerbach, M. Waks, R. Lagore, L. Delabarre, A.
Tarakameh, Y. Eryaman, G. Adriany, K. Ugurbil, G. Oz, X. Wu,
J. Liu
CMRR, Radiology, Medical School, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: The demonstrated feasibility and utility of
motion-robust mesoscale multi- echo EPI in humans at 10.5T
may shed light on future optimal implementation of
anatomical T2*-weighted
cerebellum MRI at ultrahigh field, paving the way for future
neuroscience applications.
|
| 17:36 |
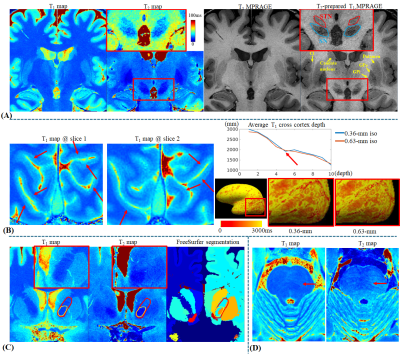 |
0271. In-vivo
quantitative histology using 0.36-mm MR Fingerprinting:
technical development

X. Cao, A. Beckett, C. Liao, M. Gao, E. Walker, Z. Zhu,
A. Kerr, Y. Yang, D. Feinberg, K. Setsompop
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: This work provides a high-quality,
motion-robust, and field-inhomogeneity-robust quantitative
tool, enabling whole-brain T1 and T2 maps at 0.36-mm
resolution, unprecedented for in-vivo quantitative imaging.
It makes in-vivo quantitative histology research feasible,
providing possibility to quantitative analysis on fine brain
structures.
|
| 17:48 |
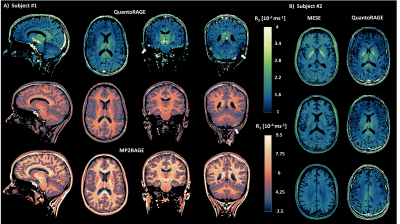 |
0272. Simultaneous
T1 and T2 mapping of the brain at 7 Tesla with optimized and
accelerated QuantoRAGE
G. Bonanno, T. Nguyên, J. Marques, T. Yu, D. Nickel, B.
Açikgöz, J. A. Bastiaansen, R. Kreis, P. Radojewski, B.
Maréchal, T. Kober, T. Hilbert
Siemens Healthineers International AG, Bern, Switzerland
Impact:
QuantoRAGE allows for simultaneous T1 and T2 mapping of the whole brain at ultra-high field with high isotropic resolution and in less than 7 minutes, bringing quantitative MRI closer to clinical UHF applications. |
| 18:00 | 0266. WITHDRAWN |
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.