Oral
Imaging the Brain Across the Lifespan in Rodents & NHP
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:30 |
Introduction
Sahar Ahmad
|
|
| 13:42 |
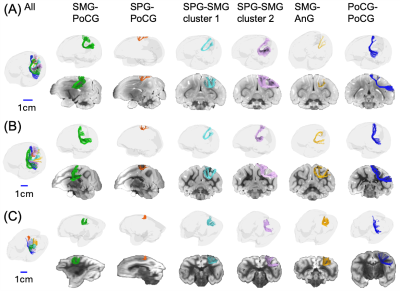 |
0528. Maturation
of long- and short-range tracts in macaque brain with
ultra-high-resolution diffusion MRI

R. Lin, T. Zhu, Z. Zhang, M. Ouyang, H. Huang
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: The revealed maturational processes of the
developmental macaque brain WM tracts, specifically the
short-range WM tracts, offer unprecedented insights into
common and unique features of brain development across
primate species.
|
| 13:54 |
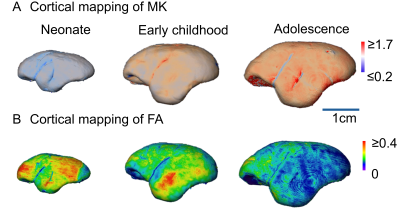 |
0529. Maturation
of marmoset cortical cytoarchitecture from birth to adolescence
with ultra-high-resolution diffusion MRI

T. Zhu, Z. Zhang, J. Guo, M. Ouyang, Y. Zheng, A. Sousa,
J. Levine, A. Kriegstein, H. Huang
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: We reveal heterogenous cortical cytoarchitecture
maturation patterns in developing marmoset brains,
highlighting increased mean kurtosis and decreased
fractional anisotropy over time. Our study provides a
foundation for understanding neurodevelopmental milestones
and evolutionary aspects of cortical maturation in primate
models.
|
| 14:06 |
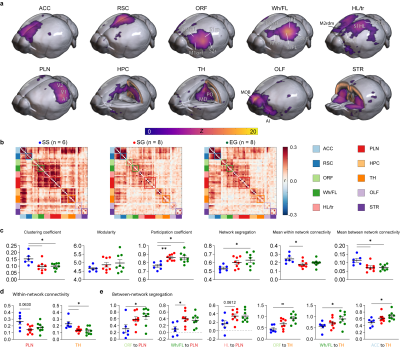 |
0530. Differential
impacts of social isolation and enriched environment on
multi-sensory brain-wide functionality and network segregation
T. You, T. Lee, G. H. Im, S-g Kim, S. Chung, J. H. Lee
Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea, Republic of
Impact: Our results emphasizes the global brain network
changes due to environmental conditions. In particular, we
show that both the visual and olfactory network are the most
vulnerable to changes due to social isolation highlighting
the importance of visual/olfactory social cues.
|
| 14:18 |
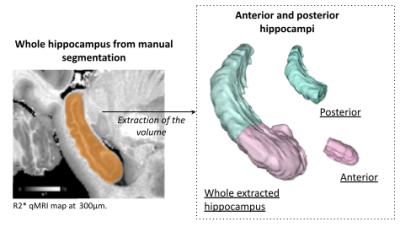 |
0531. Impact
of environmental range size on hippocampal structure in
chimpanzees
M. Chauvel, E. Kirilina, I. Lipp, P-L Bazin, C. Jäger, K.
Pine, L. Edwards, T. Gräßle, C. Crockford, R. Wittig, N.
Weiskopf
Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany
Impact: This research reveals that the ranging area size
affects hippocampal structure linked to spatial memory in
chimpanzees, contributing to our understanding of cognitive
adaptations and the neural mechanisms underlying spatial
navigation in primates.
|
| 14:30 |
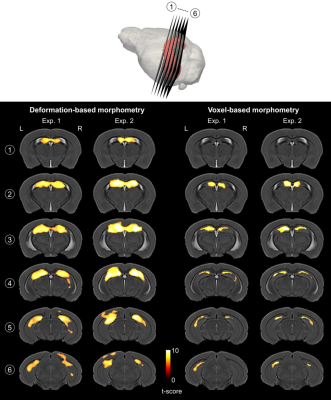 |
0532. MRI-detectable
hippocampal volume changes associated with CA1 dendritic growth
and branching in adult mice following environmental enrichment
A. Sumiyoshi, R. Ryoke, R. Kawashima
Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan
Impact: Combined MRI and histology study in adult mice
revealed the causal relationship between MRI-detectbale
volume changes and changes in neuronal morphology. These
results provide microscopic interpretations of human MRI
studies that have reported structural brain plasticity under
various intervention protocols.
|
| 14:42 |
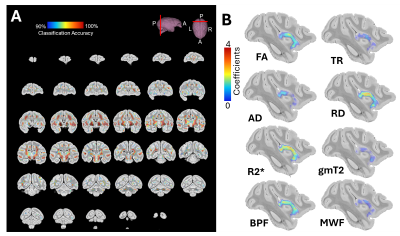 |
0533. Bias-Free
Multi-dimensional MRI Analysis to Resolve Age-related
Microstructural Differences in the Ex-Vivo Female Bonnet Macaque
Brain

L. Dieckhaus, K. McDermott, J-P Galons, C. Barnes, E.
Hutchinson
University of Arizona, Tucson, United States
Impact: Multi-variate approaches, such as a support
vector machine classifier are advantageous when assessing
aging and show potential in being applied to
neurodegenerative disease studies.
|
| 14:54 |
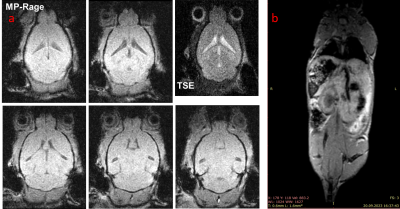 |
0534. Self-contained
Small Animal Imaging Insert for Clinical MRI Systems
T. Lobmeyer, A. Abaei, F. Bschorr, T. Huefken, V. Rasche
University Hospital Ulm, Ulm, Germany
Impact: The easy-to-use system shows adequate SNR for
imaging mice in-vivo. The possibility of using the clinical
scanners console, sequences, the main magnetic field and the
gradient system, allows for a high degree of transferability
between preclinical and clinical trials.
|
| 15:06 |
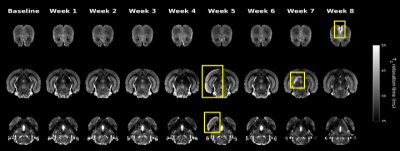 |
0535. Longitudinal
MRI Assessment of ARIA in 22 month old PS2APP Mice Treated with
Anti-Amyloid-ß Antibodies
M. K. Choy, M. Xiong, W. Meilandt, R. Virgincar, J. Imperio,
S. Vito, T. Wu, F. Frank, P. Sharma, C. Bohlen, R. Weimer,
L. Xie
Genentech, Menlo Park, United States
Impact: This study demonstrates that ARIA-E and ARIA-H
can be induced in aged PS2APP mice, replicating key human
dynamics. This model enables preclinical ARIA evaluation,
potentially accelerating development of safer anti-amyloid-ß
therapies for Alzheimer’s disease.
|
| 15:18 |
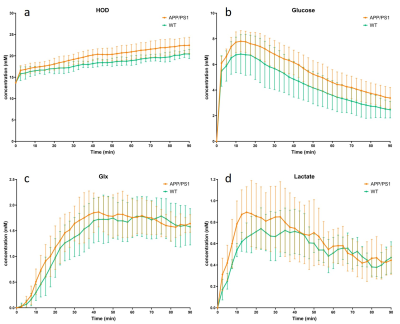 |
0536. Deuterium
MR Spectroscopy (DMS) identifies altered Glucose Metabolism in
the Brain of an Alzheimer Mouse Model at 6 months of age
A. Veltien, J. Van Asten, M. Wiesmann, T. Scheenen, A.
Kiliaan, A. Heerschap
Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands
Impact: Employing the non-invasive potential of
Deuterium MR Spectroscopy for the simultaneous assessment of
glucose uptake, glycolytic and TCA-cycle activity, we
demonstrate a hypermetabolic cerebral state in an early
stage Alzheimer’s mouse model, which may resemble mild
cognitive impairment in humans.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.