Oral
Gadolinium & Beyond I
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
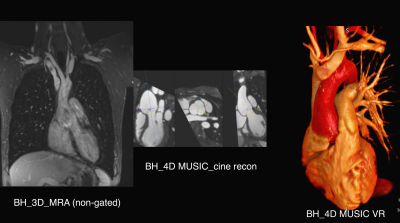 |
0402. Four-Dimensional,
Ferumoxytol-Enhanced MUSIC in a Single Breath-Hold: Technical
Feasibility in Structural Heart Disease
J. P. Finn, S-F Shi, K-L Nguyen, A. Bedayat, T. Yoshida, N.
Jin, F. Han, X. Zhong
UCLA, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: Ferumoxytol-enhanced single breath-held 4D MUSIC
is feasible, extending its potential applications beyond
children under anesthesia to adults and older children with
cardiovascular disease.
|
| 08:27 |
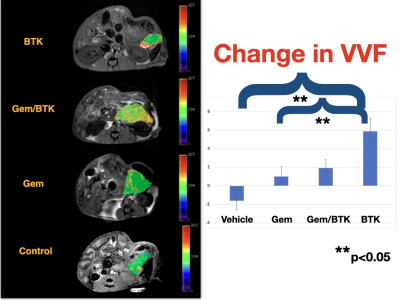 |
0403. MRI
using ferumoxytol quantifies changes of pancreatic tumor
microenvironment that predicts effect of immune therapy
A. Guimaraes, C. Wyatt, B. Smoody, L. Coussens
OHSU, Portland, United States
Impact: We have developed a method of monitoring the
PDAC TME with possibilities of human translation.
|
| 08:39 |
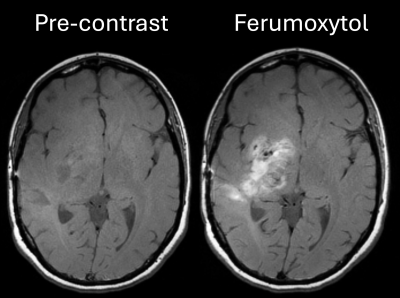 |
0404. Superiority
of Ferumoxytol MRI Over Pre-Contrast Imaging in Patients With
Intra-Axial Malignant Brain Lesions
W. Strauss, C. Varallyay, R. Fu, L. Szidonya, L. Muir, A.
Huddleston, D. Branton, E. Neuwelt
RAYUS Radiology, Portland, United States
Impact: The results from this study provide strong
evidence that ferumoxytol could serve as a safe and
effective alternative to gadolinium-based contrast agents,
particularly for patients with contraindications,
potentially leading to its FDA approval for brain tumor
imaging.
|
| 08:51 |
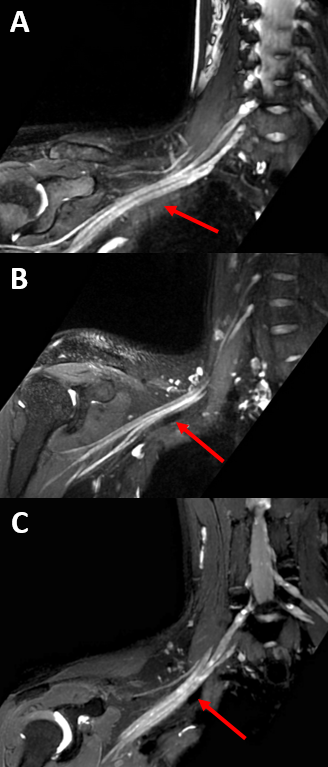 |
0405. Subject-specific
Dose of Ferumoxytol for Vascular Suppression in Brachial Plexus
Magnetic Resonance Neurography
A. Lowe, S. Turbin, D. Sneag, M. Duong, E. T. Tan
Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, United States
Impact: Subject weight- or blood-volume-specific
Ferumoxytol doses may provide effective vascular suppression
for MR neurography evaluation of peripheral neuropathies
like Parsonage Turner Syndrome (PTS), to reduce the dose and
infusion time required.
|
| 09:03 |
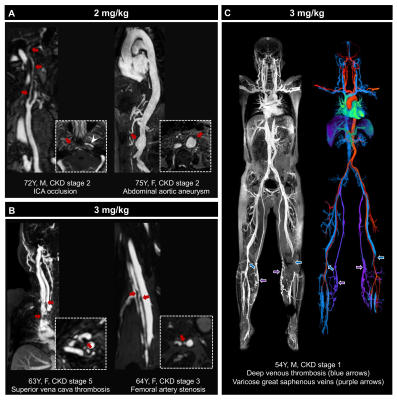 |
0406. Efficacy
and Safety of Generic Ferumoxytol for Whole-Body MRA in Patients
with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Dose-Optimization Clinical Trial
Y. Liu, M. Jin, H. Li, X. Wang, C. Zhang, J. An, Q. Sun, N.
Gu, Q. Yang
Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Impact: This study provides a cost-effective dosing
regimen for future Phase III trials and for the clinical
screening of polyvascular diseases in CKD patients.
|
| 09:15 |
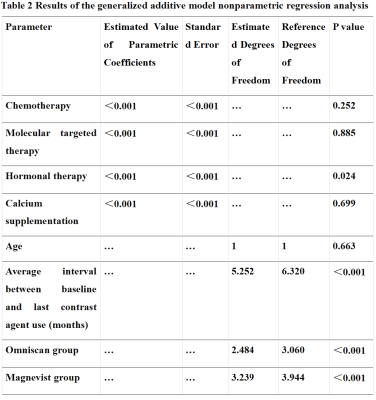 |
0407. Using
a Generalized Additive Model to Correlate Dentate Nucleus High
Signal on T1-Weighted MRI with Linear Gadolinium Agent Type
C. b. Wang, s. wang
the First Affiliated Hospital Of Nanjing Medical University, Nan jing, China
Impact: Our results suggest that hormone therapy in
breast cancer patients may lead to re-metabolism of
gadolinium ions in the body, potentially increasing the
toxicity of gadolinium when combined with other particles.
This finding warrants further investigation.
|
| 09:27 |
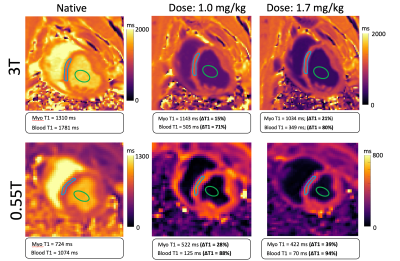 |
0408. Comparison
of T1 sensitivity to ferumoxytol at 0.55T versus 3T: a
preclinical cardiac MRI study
S. Zeynali, H. Benan Unal, E. Anttila, D. Gross, R.
Dharmakumar, B. Sharif
Purdue University, Indianapolis, United States
Impact: The increased ferumoxytol sensitivity at 0.55T
enables potential dose reduction while maintaining
diagnostic quality, offering a more robust platform for MBV
assessment. This could particularly benefit stress/rest T1
reactivity measurements where detecting subtle MBV changes
is crucial.
|
| 09:39 |
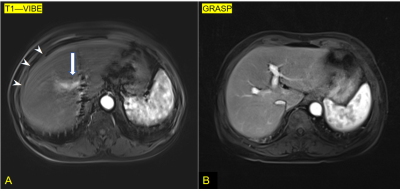 |
0409. Reduction
of Transient Respiratory Motion Artifacts in Gadoxetate-Enhanced
MRI using GRASP Technique
C. Li, R. Chai, Y. Jiang, Y. Li
The First Hospital of China Medical University, China, China
Impact: The GRASP technique can improve the quality of
gadolinium disodium enhanced MRI images.
|
| 09:51 |
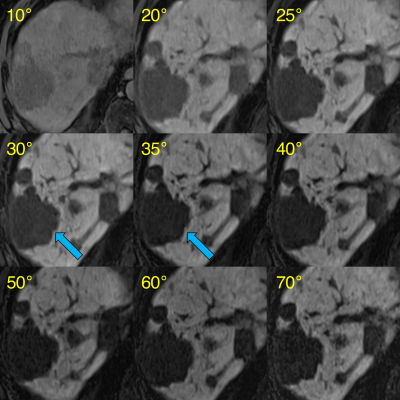 |
0410. Flip
Angle Optimization for Hepatobiliary Phase MRI at 0.55 T in
Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors
C. Hong, Y. Yang, I. Remick, P. Su, P. Itriago-Leon, W.
Majeed, E. Bergsland, T. Hope, M. Ohliger
University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, United States
Impact: In patients with metastatic neuroendocrine
tumors imaged at 0.55T, a flip angle of 30 degrees maximizes
lesion contrast on the hepatobiliary phase. Improving
hepatobiliary phase quality at 0.55T may improve MRI
accessibility for patients with known or suspected liver
lesions.
|
| 10:03 |
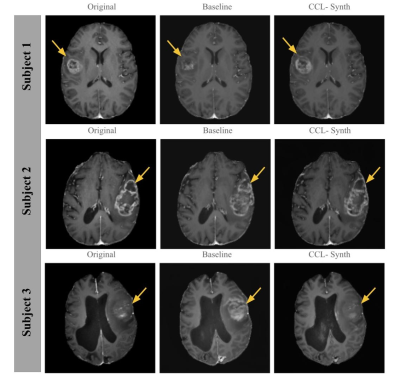 |
0411. Deep
Learning Framework for Gadolinium-free MR Imaging
P. Abdali, Y. Wang, L. Feng, L. Umapathy
New York University, New York, United States
Impact: Our approach leverages multi-contrast MR images
to capture tissue-specific information through a
self-supervised contrastive learning framework. By
synthesizing gadolinium-free T1-weighted images from
unenhanced scans, we aim to retain diagnostic quality while
potentially reducing the related risks, costs, and
acquisition times.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.