Oral
Gadolinium & Beyond II
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
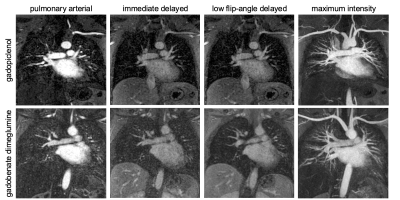 |
0770. Pulmonary
MR angiography with gadopiclenol can reduce gadolinium exposure
while maintaining signal enhancement.
J. Heidenreich, S. Chu, J-P Grunz, J. Starekova, P. Nagpal,
S. Reeder, T. Grist
University Madison Wisconsin, Madison, United States
Impact:
The use of high relaxivity gadopiclenol can reduce gadolinium exposure by 50% while maintaining adequate contrast enhancement. This may improve the safety and sustainability of gadolinium-enhanced MRA. |
| 08:27 |
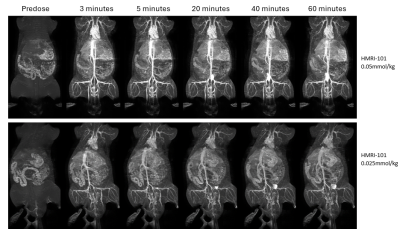 |
0771. Gadolinium
Nanoparticle with Blood Pool Properties for Whole Body MRA to
Support 60-Minute Image Acquisition Time
J. Reddington, A. Lang, J. Thorball, R. Ho, U. Schmiedl
Hawkeye MRI AG, Pfäffikon SZ, Switzerland
Impact: A blood pool lipid-based GBCA allows superior
vascular images at 1.5 or 3T. Lower doses of gadolinium and
route of excretion are of potential safety benefit, and
longer imaging times provide greater flexibility and
expanded radiological applications.
|
| 08:39 |
 |
0772. Novel
biological Gadolinium contrast agents for MRI developed using
artificial intelligence
N. Dayan, N. Scalzitti, I. Miralavy, W. Banzhaf, A. Gilad
Michigan State University, East Lansing, United States
Impact: The Gadolinium binding motifs found in this
research will be used to develop biological MRI contrast
agents that will allow safer and more effective imaging
procedures.
|
| 08:51 |
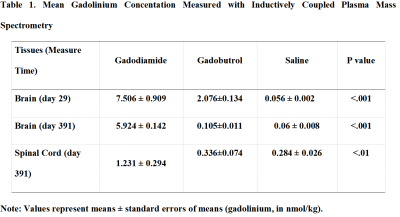 |
0773. Long-Term
Effects of Linear versus Macrocyclic Gadolinium-Based Contrast
Agents on Gene Expression in the Central Nervous System of Mice
c. wang, s. wang
The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, nanjing, China
Impact: Our study pioneers in detecting genetic and
protein-level changes in the central nervous system from
prolonged gadolinium accumulation, highlighting the need for
further research to understand mechanisms and assess the
long-term safety of linear GBCAs.
|
| 09:03 |
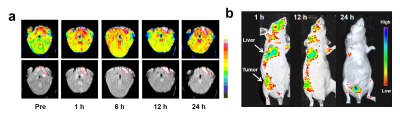 |
0774. Metal-Organic
Supramolecular Cage based Microenvironment Responsive
Nanomedicine for Photodynamic Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast
Cancer
D. Li, X. Yan, Y. Su, X. Chen, J. Peng, F. Zeng, J. Shen
Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, guangzhou, China
Impact: Nano carriers (MM) exhibit significant MRI -
monitoring ability in vivo during the treatment process,
with a longer imaging window and good PDT effects. These MRI
- related features show great potential as a therapeutic -
diagnostic platform for TNBC treatment using nanomedicine.
|
| 09:15 |
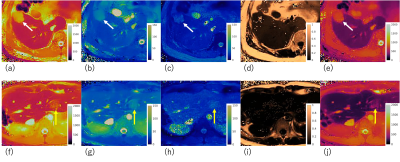 |
0775. Liver
Tumor Differentiation Enhanced by Adding Hepatobiliary Phase MR
Fingerprinting: A Multi-parametric Diagnostic Approach
K. Sano, S. Fujita, G. Cruz, C. Velasco, D. Pedraza, H.
Kawasaki, Y. Fukumura, A. Suzuki, Y. Ikenouchi, T. Arai, Y.
Morita, W. Uchida, A. Saiura, K. Ikejima, K. Kamagata, R.
Kuwatsuru, R. Botnar, C. Prieto, S. Aoki
Juntendo University, Tokyo, Japan
Impact: Incorporating a multi-parametric approach with
MRF during the hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic
acid-enhanced MRI improves diagnostic accuracy in liver
tumor differentiation, potentially reducing reliance on
dynamic phases and enhancing non-invasive diagnostic
capabilities in clinical liver assessments.
|
| 09:27 |
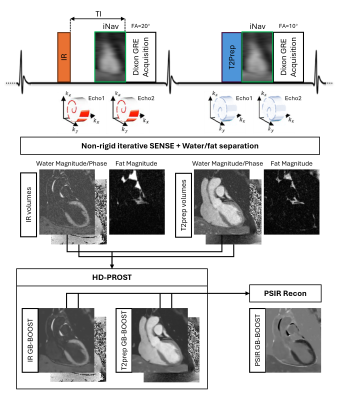 |
0776. Free-breathing
3D High-resolution Simultaneous Grey-blood Late Gadolinium
Enhancement and MR Angiography at 3T
D. Si, S. Littlewood, M. Crabb, K. Kunze, C. Prieto, R.
Botnar
School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: The proposed sequence can achieve co-registered
3D whole-heart grey-blood late gadolinium enhancement and
cardiac MR angiography at a resolution of 1.2mm3 in
a single fast scan of approximately 10 mins with comparable
image quality as separately acquired images.
|
| 09:39 |
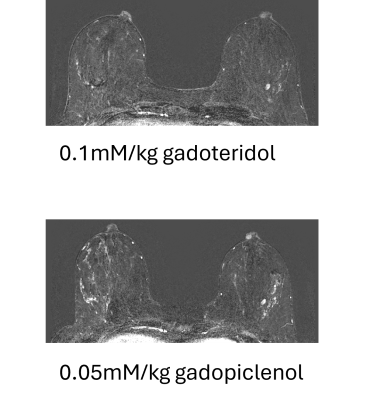 |
0777. Quantitative
characterization of background parenchymal enhancement in
abbreviated breast MRI acquired with a high relaxivity contrast
agent
F. Pineda, Y. Cao, A. Lu, M. Zuley
University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, United States
Impact: Abbreviated breast MRIs acquired with
0.05mmol/kg gadopiclenol showed slightly higher levels of
signal enhancement in background parenchyma than those
acquired with 0.1mmol/kg gadoteridol. Further investigation
is underway to determine whether these differences lead to a
higher false positive rate.
|
| 09:51 |
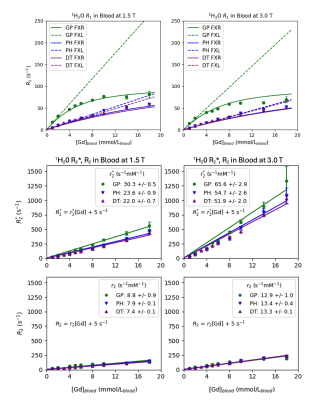 |
0778. R1,
R2 and R2* Relaxivity Measurements of the Contrast Agent
Gadopiclenol in Human Blood; Application to Administration
Strategies
J. Maki, T. Clark, A. Barker, G. Wilson
University of Colorado, Aurora, United States
Impact: Different GBCAs have different relaxivity
properties in blood. Knowledge of these properties allows
for accurate modeling and optimization of exams such as
CE-MRA, 1st pass arterial phase imaging and perfusion.
|
| 10:03 |
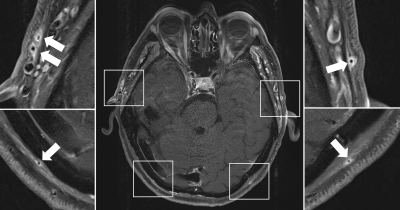 |
0779. Implementation
of gadolinium saving potential utilizing Gadopiclenol in
vasculitis imaging
T. Bley, R. Dazeh, M. Schmalzing, M. Gernert, K.
Guggenberger, V. Hartung
University Medical Center Wuerzburg, Wuerzburg, Germany
Impact: Gadolinium usage could now be reliably reduced
by half utilizing half dose Gadopiclenol while maintaining
clinically needed high contrast in vasculitis imaging and
aortic imaging, a previously unmet need by other contrast
agents.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.