Oral
Sustainability - Late Breaking Abstracts
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:30 |
Introduction |
|
| 13:42 |
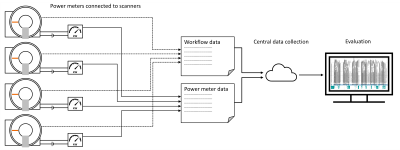 |
5412. Optimizing
Energy Efficiency in MRI Scanners: A Workflow Analysis for
Enhanced Sustainability
F. Wagner, F. Raab, J. Wohlers, S. Varadarajan, J. Gühring,
R. Schneider, J. Herrmann, K. Nikolaou, S. Afat, T. Küstner
Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany
Impact: This study provides new insights into MRI power
use and on a per-sequence and protocol level. Initial
findings of optimized magnet cooling and workflow
optimization shows substantial potential to reduce idle
power consumption in MRI operations, enhancing
sustainability.
|
| 13:54 |
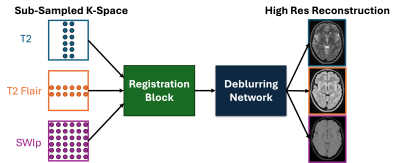 |
5413. Fast
and Sustainable Brain MRI by Triple-Modality Deblurring
A. Nazarov, D. Roizen, N. Kiryati, G. Grinberg, A. Mayer
Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel
Impact: The proposed method enhances MRI sustainability
by significantly reducing acquisition time, energy usage
(approximately 60-75% reduction in gradient and RF power),
and susceptibility artifacts. Improved efficiency enables
sustainable imaging practices, benefiting clinical
throughput in high-volume or resource-constrained settings.
|
| 14:06 |
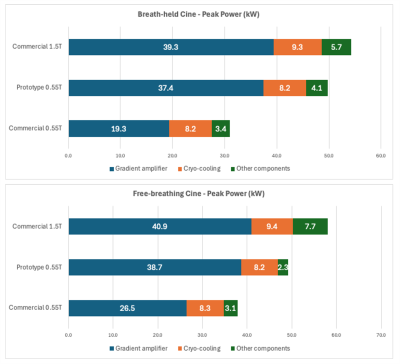 |
5414. Measuring
power efficiency of cardiovascular MR across gradient
performance and field strength
R. Ramasawmy, A. Campbell-Washburn
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, Bethesda, United States
Impact: This is a preliminary study comparing the power
efficiency of cardiac imaging across 0.55T and 1.5T field
strengths.
|
| 14:18 |
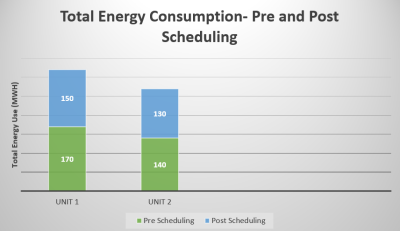 |
5415. COMPARISON
OF OLDER AND NEWER GENERATION MRI AND ASSESSING ROLE OF WORKFLOW
OPTIMIZATION IN ENERGY SAVING IN IMAGING. AN EXPERIENCE IN NORTH
INDIA
G. Raj, K. Gupta
Dr Ram Manohar Lohia Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India
Impact: New generation MR Units are efficient than older
generation models with manufacturer enabled low power mode.
Optimizing workflow and judiciously managing the low power
mode results in significant decrease in long term energy
costs without need for expensive software such as AI
hardware modifications and goes a long way, especially in
developing countries
|
| 14:30 |
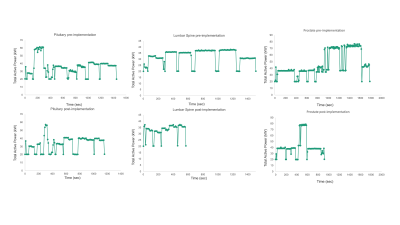 |
5416. Creating
a Greener Outpatient MRI Facility: Enhancing Sustainability and
Energy Efficiency through Fast Imaging Techniques
A. Tabari, M. Lang, W-C Lo, A. Becker, V. Deshpande, P. Su,
S. Woolen, S. Huang
Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, United States
Impact: The implementation of fast MRI sequences
significantly reduced the acquisition times for common
outpatient MRI protocols, leading to higher energy
efficiency during active net scan time and system-on modes
and ultimately substantial sustainability and cost-saving
potential.
|
| 14:42 |
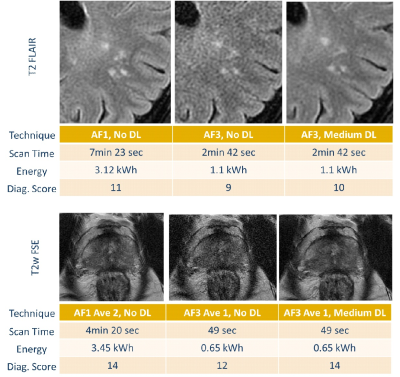 |
5417. Sustainable
MRI: Energy and Environmental Benefits of Accelerated Imaging
with Deep-Learning Reconstruction
Y. Jung, R. Alizadeh, S. Yoon, M. Corwin, L. Hacein-Bey, A.
Hernandez
University of California, Davis, Sacramento, United States
Impact: Accelerated MRI with DLR enables significant
clinical efficiency and sustainability improvements,
facilitating rapid, high-quality imaging. Future studies can
explore enhanced DLR algorithms, optimizing diagnostic
performance while maximizing energy savings and emissions
reductions across healthcare settings.
|
| 14:54 |
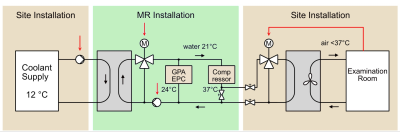 |
5418. Towards
MRI Greening: Sequence-Specific Energy Profiles and Sustainable
Cooling Solutions Using Waste Heat Recovery
H. Dillinger, R. Bruehl, D. Trepte, H. Duzinski, B.
Ittermann
PTB Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Impact: Given the pressing need for reducing energy
consumption and CO2 emissions world-wide, our work presents
insights on how to tackle it in MRI without compromising on
the image quality or patient experience.
|
| 15:06 |
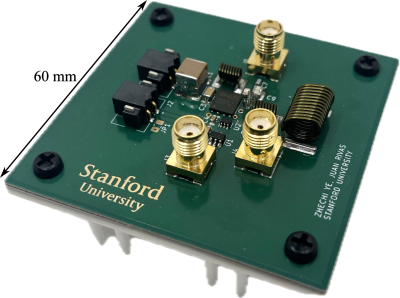 |
5419. Highly-Efficient
Switched-Mode Radio Frequency Power Amplifier for Magnetic
Resonance
Z. Ye, J. Rivas
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: The proposed technology significantly improves
the efficiency of RF power amplifiers, contributing to more
sustainable MR systems. It also provides advantages by
reducing both the cost and size of hardware, potentially
increasing the accessibility and portability of MR systems.
|
| 15:18 | Discussion |
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.