Oral
Young Investigator Awards: Oral Presentations
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
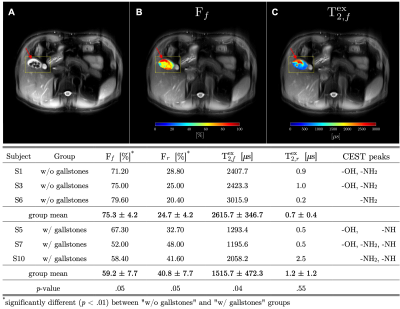 |
0001. Multiparametric
exchange protons using Z-Spectrum Analysis Proton (ZAP) and CEST
on phantoms and human abdomen.
V. Malis, M. Miyazaki
University of California San Diego, La Jolla, United States
Impact: Combining ZAP and CEST detects not only CEST
protons but a wide spectrum of exchange protons. ZAP metrics
demonstrate two proton exchange environments with good
sensitivity. The combined CEST and ZAP outcomes indicates a
possibility of biomarkers.
|
| 08:30 |
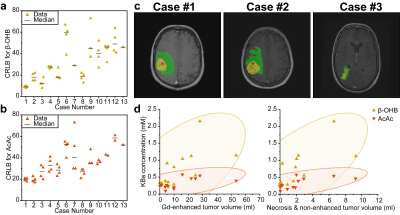 |
0002. 2D
1H sLASER long-TE and 3D 31P chemical shift imaging at 3T for
monitoring fasting-induced changes in brain tumor tissue
S. Alcicek, I. Divé, D. Thomas, V. Prinz, M-T Forster, M.
Czabanka, K. Weber, J. Steinbach, M. Ronellenfitsch, E.
Hattingen, U. Pilatus, K. Wenger
Goethe University, Frankfurt/Main, Germany
Impact: We report on the validation of a dedicated,
multinuclear MRSI protocol with fully automated
multiparametric segmentation of glioma sub-regions for
monitoring cerebral, fasting-induced changes in patients
with glioma.
|
| 08:45 |
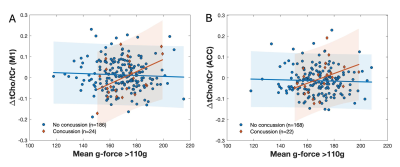 |
0003. Associations
Between Brain Metabolites Measured With MR Spectroscopy & Head
Impacts in High School American Football Athletes
Z. Liu, J. Dudley, J. Diekfuss, N. Ahmed, A. Edmondson, K.
Cecil, W. Yuan, T. Zuleger, A. Slutsky-Ganesh, K. Barber
Foss, G. Myer, C. Fleischer
Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, Atlanta, United States
Impact: In a clinical trial of high school American
football athletes evaluating MRS-quantified brain
metabolites and head impacts, choline emerged as a key
metric of injury, supporting the continued use of
neuroimaging metrics in charactering changes after repeated
head impacts.
|
| 09:00 |
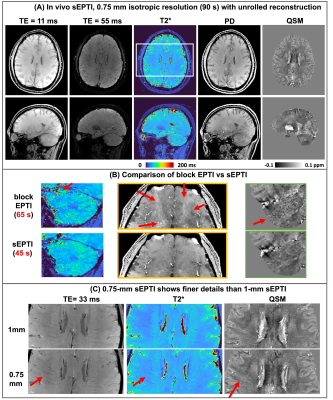 |
0004. Spherical
Echo-Planar Time-resolved Imaging (sEPTI) for rapid 3D
quantitative T2* and susceptibility imaging
N. Wang, C. Liao, X. Cao, M. Nishimura, Y. Brackenier, M.
Yurt, M. Gao, D. Abraham, C. Alkan, S. Srinivasan Iyer, Z.
Zhou, H. Jeong, A. Kerr, J. Halda, K. Setsompop
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: sEPTI technique was developed with synergetic
improvements in sampling, B0 estimation, eddy-current
correction, and unrolled-network reconstruction, which
achieves whole-brain 0.75-mm distortion-free and
blurring-free T2* and QSM quantification at 3T in 90 seconds
with the potentials for wide clinical applications.
|
| 09:15 |
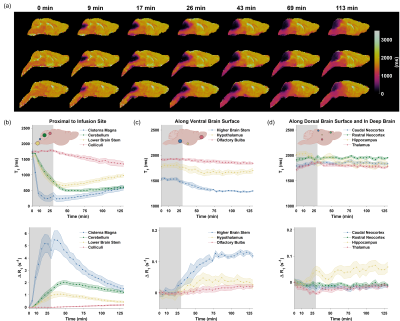 |
0005. 3D
MR fingerprinting for dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging of whole
mouse brain
Y. Zhu, G. Wang, Y. Gu, W. Zhao, J. Lu, J. Zhu, C. MacAskill,
A. Dupuis, M. Griswold, D. Ma, C. Flask, X. Yu
Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, United States
Impact: This 3D MRF method enables unprecedented
quantitative tracking of contrast agents throughout the
mouse brain, significantly advancing our ability to study
cerebrospinal fluid dynamics and potentially transforming
preclinical investigation of neurodegenerative diseases and
therapeutic interventions.
|
| 09:30 |
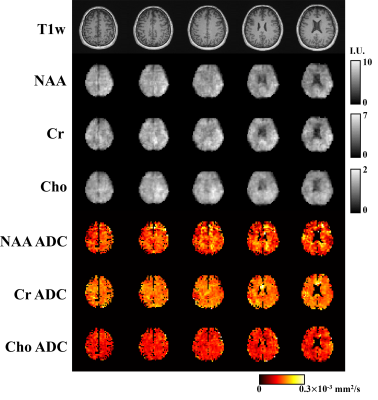 |
0006. High-Resolution,
Volumetric Diffusion-Weighted MR Spectroscopic Imaging of the
Brain
Z. Wang, B. Sutton, F. Lam
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, United States
Impact: Our technology enabled an unprecedented
capability of high-resolution, 3D metabolite-specific
diffusion parameter mapping. This capability has significant
potential to offer tissue-compartment- and
cell-type-specific microstructural information in vivo for
many clinical and neuroscience applications.
|
| 09:45 |
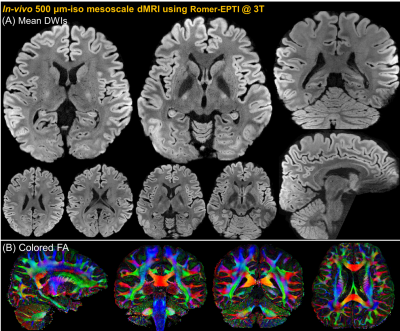 |
0007. Romer-EPTI:
Rotating-View Motion-Robust Super-Res EPTI for SNR-Efficient
Distortion-Free In-Vivo Mesoscale dMRI & Microstructure Imaging
Z. Dong, T. Reese, H-H Lee, S. Huang, J. Polimeni, L. Wald,
F. Wang
Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, United States
Impact: This study introduces a novel Romer-EPTI
technique that addresses key challenges in in-vivo diffusion
MRI acquisition to enable high-resolution dMRI at mesoscale
spatial resolutions and efficient high-b-value
microstructure imaging.
|
| 10:00 |
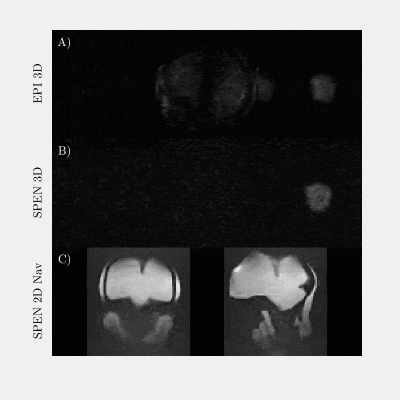 |
0008. Spatiotemporal
Encoding MRI in a Portable Low-Field System
Y. Qiu, P. Lee, K. Dai, S. Zhong, S. Chen, C. Wang, H. Chen,
L. Frydman, Z. Zhang
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: SPEN-based MRI provides a robust and fast
acquisition approach to obtain distortion-free images at
low-cost portable low field systems, thereby expanding the
prospects for rapid imaging, navigation, functional and
implant imaging in low-field portable MRI.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.