Power Pitch
Software Tools
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:30 |
 |
Screen Number: 1
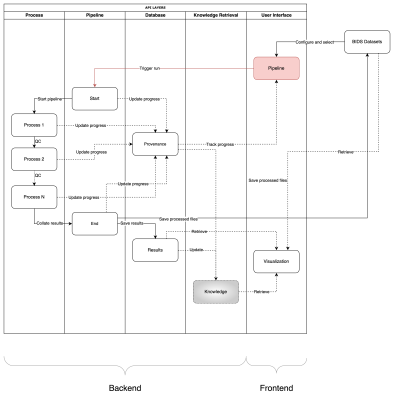
0937. NeuroAnalyst:
Developing a Standardized, Containerized Framework for
Reproducible Neuroimaging Analysis
C. Mokashi, S. Bajaj, C. Quarles
University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, United States
Impact: NeuroAnalyst aims to significantly reduce
technical barriers in neuroimaging research and enhance
reproducibility. This standardized platform will enable more
efficient collaboration, potentially leading to faster
advancements in understanding brain function and
neurological disorders.
|
| 13:32 |
 |
Screen Number: 2
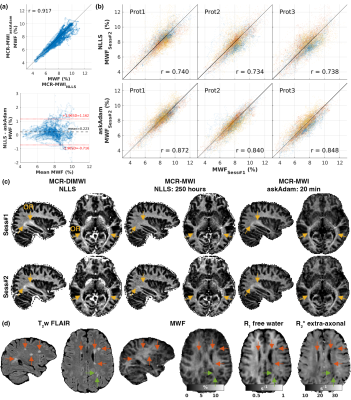
0938. GACELLE:
GPU-AcCELerated toolbox for high-throughput multidimensionaL
quantitative parameter Estimation

K-S Chan, Y. Ma, H. Lee, S. Huang, J. Marques, H-H Lee
Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, United States
Impact: GACELLE removes
the obstacle of time-consuming data processing associated
with quantitative MRI multi-parametric non-linear problems,
promoting wider adoption of quantitative MRI for the
scientific community.
|
| 13:34 |
 |
Screen Number: 3
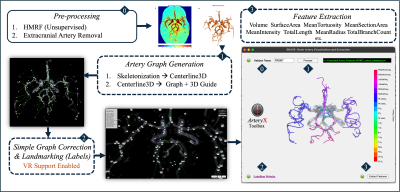
0939. ArteryX:
Enhancing Sensitivity in Brain Artery Feature Extraction Using
Arterial Graph Network
A. Faiyaz, N. Hoang, G. Schifitto, M. N. Uddin
University of Rochester, Rochester, United States
Impact: Demonstrated increase in sensitivity and
usability of artery features, hold promise of our approach's
reliable application in other cerebrovascular studies.
Features generated from this approach will be used for
training and validation of automated artery extraction
technique.
|
| 13:36 |
 |
Screen Number: 4
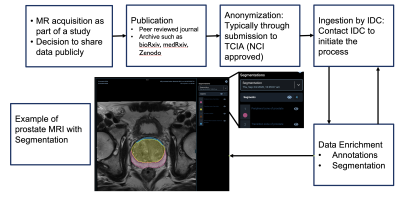
0940. The
Cancer Imaging Data Commons: Paving the Way for Open Science
R. Kikinis, D. Krishnaswamy, S. Pieper, A. Fedorov
Harvard Medical School, Boston, United States
Impact: IDC accelerates cancer research by promoting
data sharing and reproducibility, empowering researchers to
collaborate, develop innovative algorithms, and improve
patient care.
|
| 13:38 |
 |
Screen Number: 5
0941. Process
& Analysis of MRI data: 3D Slicer: A Versatile Toolkit for
Personalized MRI Analysis
Z. Kikinis, R. Kikinis
Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, United States
Impact: 3D Slicer’s versatility supports research
innovation in MRI analysis, facilitating advances in
imaging-based biomarkers and new approaches to surgical
planning and diagnostics.
|
| 13:40 |
 |
Screen Number: 6
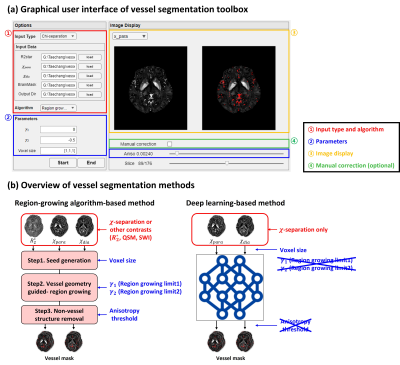
0942. Vessel
segmentation toolbox for susceptibility imaging: Region-growing
algorithm and deep learning
T. Kim, H. Park, S. Ji, J. Lee
Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact:
The vessel segmentation toolbox generates a high-quality vessel mask through a user-friendly GUI, supporting the reliability of analysis of χ-separation results by effectively excluding vessel artifacts for improved quantification of iron and myelin. |
| 13:42 |
 |
Screen Number: 7
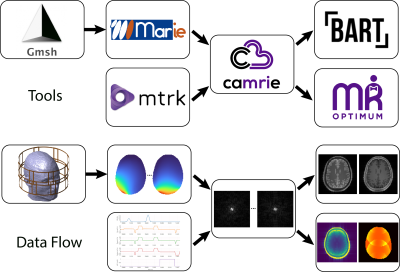
0943. A
Modular End-to-End Open-Source Software Pipeline to Simulate the
Entire MRI Experiment
E. Montin, J. E. Cruz Serrallés, I. Giannakopoulos, A.
Artiges, C. Castillo-Passi, R. Lattanzi
New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: The comprehensive cloud-compatible simulation
pipeline will make MR research freely accessible via
internet. By enabling virtual experiments, this tool will
allow users to generate synthetic data to train neural
networks and will constitute a valuable tool for education
and training.
|
| 13:44 |
Screen Number: 8
0944. WITHDRAWN |
|
| 13:46 |
 |
Screen Number: 9
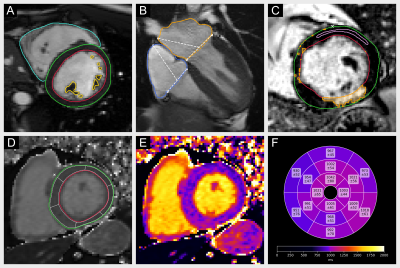
0945. Cardiometry:
Open-Source, Reliable and Efficient Computation of Quantitative
Parameters in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
C. Ammann, T. Hadler, P. Reisdorf, R. Hickstein, H. Noyan,
J. Gröschel, J. Gavrysh, J. Schulz-Menger
Working Group on CMR, Experimental and Clinical Research Center, a joint cooperation between the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association, Berlin, Germany
Impact: Cardiometry produces equivalent clinical results
to proprietary medical software. As an open-source library,
it enables efficient and automated quantification of cardiac
function, T1 and T2 parametric mapping and late gadolinium
enhancement for research applications in cardiovascular
magnetic resonance.
|
| 13:48 |
 |
Screen Number: 10
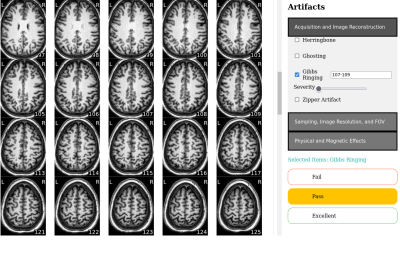
0946. EZ-QC:
A User-Friendly Tool for Multi-site, Multimodal Neuroimaging
Data Triage and Visual Quality Control
J. DeBrosse, T. Goodwin-Allcock, R. Tripathi, K. L. Phan, L.
Wang, T. Huerta, H. Zhang, N. Kraguljac
The Ohio State University, Columbus, United States
Impact: EZ-QC improves QC efficiency by prioritizing
data that are most likely to indicate systemic errors and
standardizing rater training. This approach supports
consistent and efficient QC, helping to maximize usable data
and ensure reliable data quality in large, multisite
studies.
|
| 13:50 |
 |
Screen Number: 11
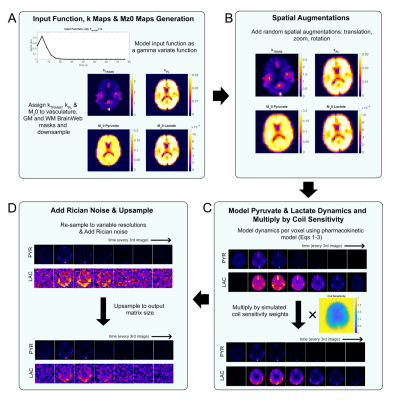
0947. Anatomic-Based
Metabolic Phantom Suite: Open-Source, Digital Hyperpolarized 13C
MR Imaging
A. Bennett Haller, S. Sahin, D. Yeh, J. Gordon, Y. Kim, A.
Sinha, J. Hu, T. Nickles, D. Vigneron, P. Larson
University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, United States
Impact: Metabolic digital phantoms create ground truth
data providing opportunities to accurately characterize the
performance of new sampling and acquisition strategies,
validate advanced data analysis techniques and create
faithful synthetic data to supplement training datasets for
machine learning applications.
|
| 13:52 |
 |
Screen Number: 12
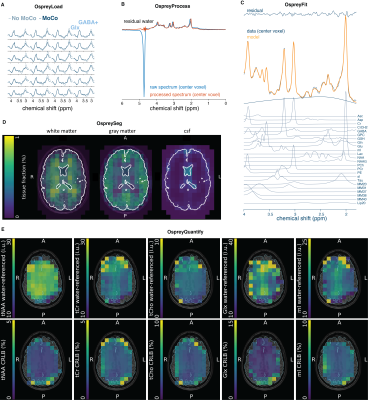
0948. Open-source
analysis of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) data
in Osprey
H. Zöllner, D. Senapati, İ. Özdemir, D. Lin, G. Oeltzschner,
P. Barker
The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, United States
Impact: The implemented MRSI analysis workflow offers
state-of-the-art methods with minimal user interaction
available for non-expert users and easily visualized in
FSLeyes. The modular workflow allows rapid adoption of new
model approaches to be developed in Osprey.
|
| 13:54 |
 |
Screen Number: 13
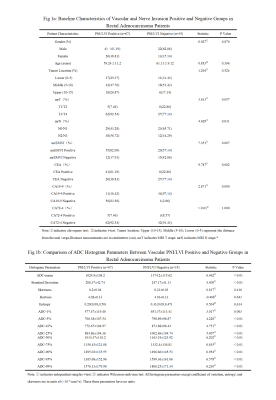
0949. The
value of whole - tumor ADC histogram parameters combined with
imaging biomarkers in predicting PNI/LVI in rectal
adenocarcinoma
H. Wang, H. Liu, Z. Wang, R. Gao, K. Zhu, J. Liu, P. Luo, Y.
Sun, Y. Li
The Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, LAN ZHOU, China
Impact: Combining
whole-tumor ADC histogram parameters with mrEMVI can
significantly improve the accuracy of preoperative PNI/LVI
prediction in rectal adenocarcinoma. This approach has the
potential to become an important tool in clinical diagnosis,
advancing the application of imaging in tumor detection.
|
| 13:56 |
 |
Screen Number: 14
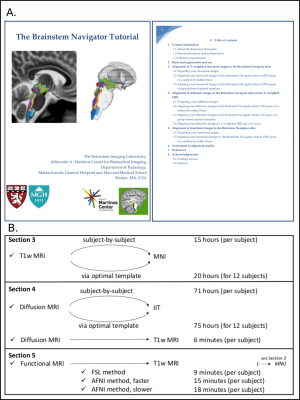
0950. The
Brainstem Navigator Toolkit v1.0: An Atlas of Brainstem Nuclei
and Coregistration Tutorial in Younger Adults
F. F. Hannanu, S. Cauzzo, G. Garcia-Gomar, K. Singh, N.
Toschi, M. Bianciardi
Brainstem Imaging Laboratory, Department of Radiology, Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Charlestown, United States
Impact: The Brainstem Navigator toolkit v1.0 includes a
probabilistic atlas of 31 brainstem nuclei and comprehensive
coregistration routines for 3Tesla/7Tesla MRI. This toolkit
facilitates precise structural, diffusion, and functional
MRI coregistration, significantly advancing research into
brainstem-related disorders and neuroscientific inquiries.
|
| 13:58 |
 |
Screen Number: 15
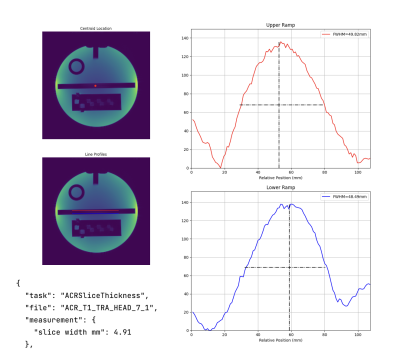
0951. Hazen:
an open-source MRI QA analysis software library
M. Buckley, Z. Ratkai, T. Roberts, R. Satnarine, J. Ansell,
L. Gabriel, Y. Azma, R. Thornley, L. Jenkins, B. Laureano,
M. Lowe, S. Shah, R. Franklin, R. Johnstone, S. Ahmad, M.
Liljeroth, L. Jackson, L. Cester, D. Vilic, S. Culley, J.
Tracey, H. Richardson, B. Johnston, A. Drysdale, P. Wilson,
N. Heraghty, D. Price, H. Shuaib, G. Charles-Edwards
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
Impact: Hazen enables clinicians and scientists to
perform rapid, standardised MRI QA across multiple vendors,
reducing analysis time by ~75%. This facilitates faster
troubleshooting, improves imaging consistency, overcomes
licensing barriers, and fosters collaboration - ultimately
enhancing diagnostic quality and patient care.
|
| 14:00 |
 |
Screen Number: 16
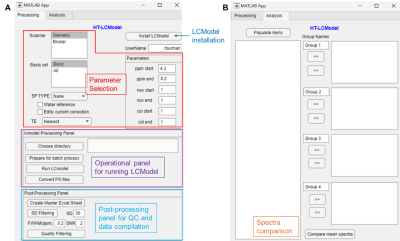
0952. Building
a standalone automated High-Throughput LCModel prototype
application for 1H-MRS data processing: HT-LCModel
R. Burman, S. Guthrie, Y. Pang, A. Bag, K. Krull, W.
Reddick, P. Bagga
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, United States
Impact: HT-LCModel provides an intuitive, user-friendly,
high-throughput pipeline for MRS processing for processing
1H-MRS data with LCModel, the most widely used
MRS-processing application. By offering a built-in viewer
accessible on any computer, HT-LCModel enhances research
consistency and accessibility in MRS studies.
|
| 14:02 |
 |
Screen Number: 17
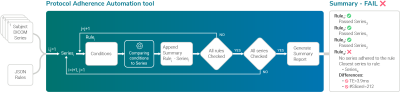
0953. A
data-agnostic and automatic tool for quality protocol adherence
Ó. Peña-Nogales, E. Neylon, T. Boshkovski, M. Ramos, V.
Ferrer-Gallardo, P. Rodrigues, V. Prchkovska, K. Trivodaliev
QMENTA, Barcelona, Spain
Impact: The protocol adherence automation tool
agnostically and automatically assesses the fidelity of the
acquired data to a predefined set of rules. Consequently, it
allows real-time identification of protocol deviations
across manufacturers and sites minimizing potential human
error and reducing costs.
|
| 14:04 |
 |
Screen Number: 18
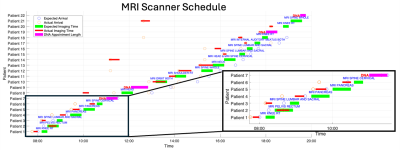
0954. Smart
MRI Departments: Intelligent Patient Scheduling Using Real-Time
Appointment Duration Metrics and an FNN to Predict Lateness
O. Lally, A. Schneider, M. Buckley, S. Shah
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
Impact: By increasing patient throughput, our work will
be a crucial step towards a smart, sustainable MRI
department. More patients will be scanned with less scan
idle-time, improving patient outcomes in the long-term,
whilst contributing to a greener and cost-effective service.
|
| 14:06 |
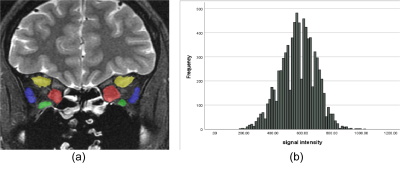 |
Screen Number: 19
0955. Prediction
of Graves’ ophthalmopathy activity via histogram analysis of
T2WI
Z. Yingcong, B. Qiu, G. Xiarong, W. Yunzhu
College of Medicine,Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming,China;, Kunming, China
Impact: T2WI histogram analysis is reliable for
predicting GO activity, enhancing clinical decision-making,
and providing treatment personalization.
|
| 14:08 |
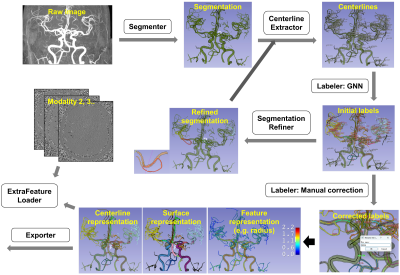 |
Screen Number: 20
0956. VesselDigitizer:
A deep learning-powered 3D Slicer extension for digitizing
cerebral vasculature from 3D medical images
Z. Chen, L. Liu, X. Chao, J. Wang, Y. Liao, X. Li, H. Wang
Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact: VesselDigitizer makes large-scale analysis of
cerebral vasculatures easier and more accurate.
|
| 14:10 |
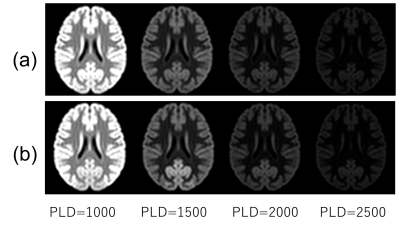 |
Screen Number: 21
0957. Digital
MR brain phantom with vascular territory information:
Application to MR imaging simulation for cerebrovascular
dependent contrast
H. Kabasawa, Y. Kato
International University of Health and Welfare, Narita, Japan
Impact: This study demonstrated the proposed method
could generate blood flow depended MR contrast as synthetic
images. The proposed system can be used to predict MR
contrast change associated with vascular territories. It is
useful for teaching advanced MR imaging methods.
|
| 14:12 |
 |
Screen Number: 22
0958. A
Means of Enforcing Image Alignment at Compile Time for Improved
Safety when Processing Surgical or Radiotherapy Images
L. Reid, P. Starr, D. Wang, A. Lee, M. Morrison
University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, United States
Impact:
Preventing image-orientation errors at compilation time reduces risks in clinical environments, and accelerates software development. The proposed pattern is readily implementable across many programming languages, and our framework making this available to all .Net languages, including Python via Iron Python. |
| 14:14 |
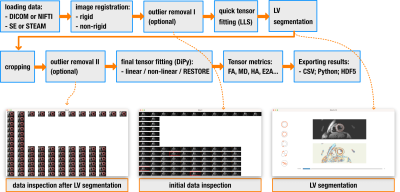 |
Screen Number: 23
0959. INDI:
open-source software for processing cardiac diffusion tensor
imaging data
P. Ferreira, A. Di Biase, C. Munoz-Escobar, A. Scott, D.
Pennell, S. Nielles-Vallespin
Royal Brompton Hospital, London, United Kingdom
Impact: INDI provides an open-source tool, promoting
standardization and dissemination of cardiac diffusion
processing tools to new research groups. It will support a
large multi-center study including non-specialist centers
and enable translation to widespread clinical adoption.
|
| 14:16 |
 |
Screen Number: 24
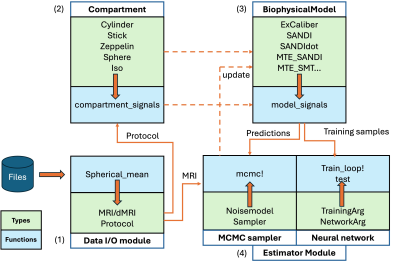
0960. Microstructure.jl:
a Julia Package for Probabilistic Microstructure Model Fitting
with Diffusion MRI

T. Gong, A. Yendiki
Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, United States
Impact: An easy-to-use tool is provided to the community
for microstructural mapping from diffusion MRI across
biophysical models with high computation speed, fitting
evaluation and uncertainty quantification, applicable to
data feasible on typical research and higher-performance
scanners.
|
| 14:18 |
 |
Screen Number: 25
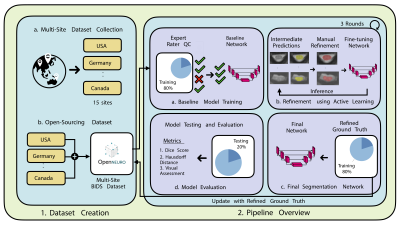
0961. EPISeg:
Automatic Segmentation of Spinal Cord fMRI Data

R. Banerjee, M. Kaptan, A. Tinnermann, A. Khatibi, A.
Dabbagh, C. Buechel, C. Kündig, C. Law, D. Pfyffer, D.
Lythgoe, D. Tsivaka, D. Van De Ville, F. Eippert, F.
Muhammad, G. Glover, G. David, G. Haynes, J. Haaker, J.
Brooks, J. Doyon, J. Finsterbusch, K. Martucci, K.
Hemmerling, M. Mobarak-Abadi, M. Hoggarth, M. Howard, M.
Bright, N. Kinany, O. Kowalczyk, O. Lungu, P. Freund, R.
Deshpande, R. Barry, S. Mackey, S. Vahdat, S. Schading,
S. Medina, S. McMahon, S. Williams, T. Parrish, V.
Marchand-Pauvert, Y. Dhaher, Y. Chen, Z. Smith, K. Weber
II, B. De Leener, J. Cohen-Adad
Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, United States
Impact: EPISeg significantly enhances spinal fMRI
research by enabling automated, accurate segmentations of
EPI data, overcoming limitations of manual segmentation. Its
integration into SCT broadens accessibility and
reproducibility, facilitating robust group-level analyses
essential for advancing studies of spinal processes and
disorders.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.