Traditional Poster
AI-Based Image Recon, Enhancement & Analysis
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

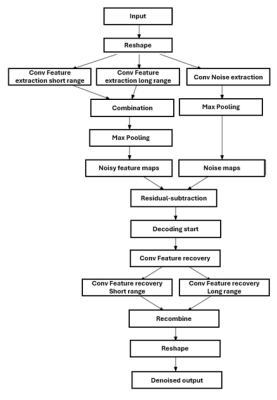 |
5139. Deep
learning-based residual-subtractive denoising with latent
mapping of noise: Application to Z-spectra
S. Mohammed Ali, N. Yadav, R. Wirestam, P. van Zijl, J.
Prasuhn, L. Knutsson
Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Impact: Denoising is crucial for usability of Z-spectra
from CEST-images. Our developed DL-based solution is
designed to map noise in latent space and subsequently
remove it in a residual fashion allowing for an increased
potential to recover overshadowed signal in Z-spectra.
|
|
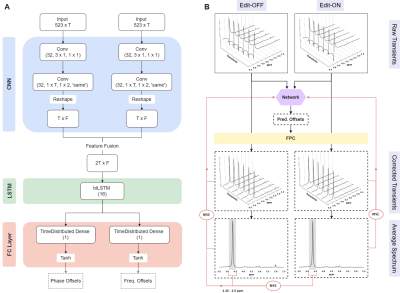 |
5140. Frequency
and Phase Correction of MRS Data by Leveraging Sequential
Patterns along the Transient Dimension
C. Wu, K. Igwe, J. Guo
Columbia University, New York, United States
Impact: The 2D-FPC method proposed follows an
unsupervised learning approach that allows it to be directly
applied in vivo dataset without the need for pre-training.
The simultaneous processing of all transients allows the
algorithm to capture long-range patterns in the data.
|
|
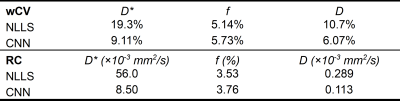 |
5141. A
Physics-Informed Convolutional Neural Network to Estimate
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in the Liver
M. Brown, J. Vasquez, A. Moody, M. Abdul-Ghani, R. DeFronzo,
J. Blangero, G. Clarke
University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio, San Antonio, United States
Impact: This study showed that CNNs improve the
repeatability of D* and D estimates
in the liver, though it remains unclear if the
within-subject variability of IVIM parameters is sufficient
to accurately differentiate fibrosis stages.
|
|
 |
5142. Accelerating
7T Quantitative MRI with Self-Supervised Few-Shot Deep Learning
R. Qiu, M. Safari, Z. Eidex, S. Wang, M. Hu, H. Mao, E.
Middlebrooks, X. Yang
Emory University, Atlanta, United States
Impact: The proposed DL approach for accelerating 7T
qMRI reduces scan times without compromising image quality,
facilitating broader adoption of high-field MRI. Its
generalizability with limited training data enhances
advanced neuroimaging accessibility and efficiency,
contributing to better clinical utility.
|
|
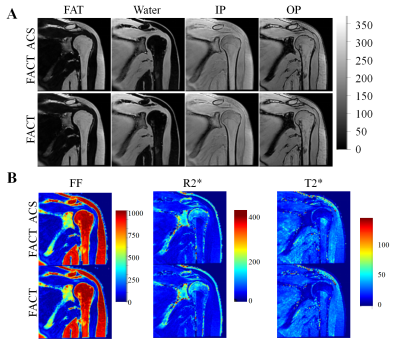 |
5143. Evaluation
of AI-Assisted Compressed Sensing for Accelerated Shoulder FACT
MRI Sequences
M. Yang, C. Tian, M. Shao, Z. Wang, Y. Guo, Z. Lin, X. Yang,
X. Zhang
Department of Radiology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, No. 321, Zhongshan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210008, China , Nanjing, China
Impact: The study demonstrates that ACS improves the
clinical efficiency of FACT sequences in shoulder imaging by
reducing scan times without affecting quantitative metrics
or image quality.
|
|
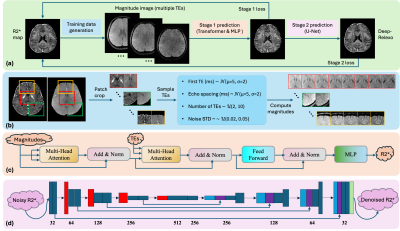 |
5144. DeepRelaxo:
A Generalizable Self-supervised Method for Brain R2* Mapping
S. Prima, Z. Xiong, A. H. Wilman, H. Sun
The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Impact: Self-supervised training removes the need for
real-world scans and allows DeepRelaxo adaptable across
diverse clinical sites. Improved shorter echo
reconstructions facilitates significantly scan time
reduction.
|
|
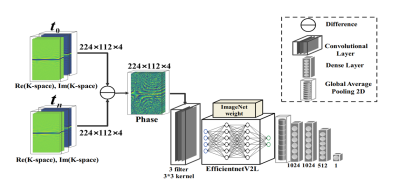 |
5145. Deep
learning-based sub-pixel level motion estimation and correction
in the context of the bSSFP-based radial fMRI
F. Makhsousi, S. Ghaffarzadeh, B. Feizifar, A. Nasiraei
Moghaddam
Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Islamic Republic of)
Impact: In this study, the translational and rotational
motion at the sub-pixel level was estimated and corrected
using the kspace. It may result in more accurate detection
of neural activity and potentially improve fMRI research.
|
|
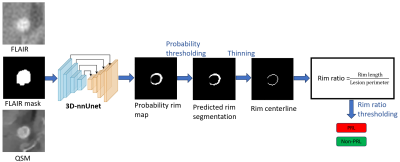 |
5146. QSM-RimDS:
A highly sensitive paramagnetic rim lesion detection and
segmentation tool for multiple sclerosis lesions
H. M. Luu, I. Kovanlikaya, T. Vu, M. Sisman, P.
Spincemaille, Y. Wang, S. Gauthier, T. Nguyen
Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: QSM-RimDS has the potential to replace human
readers for the time-consuming PRL detection and
segmentation task while improving reproducibility.
|
|
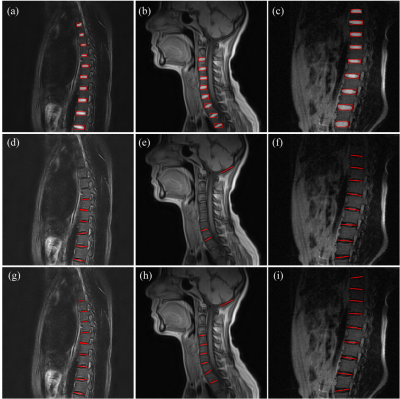 |
5147. Line-based
Instance Segmentation for Robust and Automatic MRI Spine Scan
Planning
M. He, X. Hao, L. Guo, M. Song, L. Chen, B. Qiu
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China
Impact:
Our method improved the accuracy and speed of spine positioning, providing more precise spinal transection scanning results. This can help doctors in diagnosing lumbar spine diseases more effectively and improve the diagnosis experience of patients. |
|
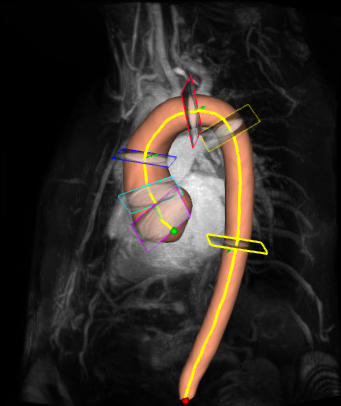 |
5148. Evaluation
of the Automatic Segmentation of Aorta considering Aortic
Diameter Measurements from Native MRI Angiographic Images
Y. Zhou, A. Barrera-Naranjo, T. Decourselle, D.
Marin-Castrillon, B. Presles, M. Delcey, O. Bouchot, J-J
Christophe, A. Lalande
ICMUB laboratory, CNRS 6302, University of Burgundy, Dijon, France
Impact: We validated an automatic method for the aortic
segmentation from native angiography using the diameter
measurements, considering the data from medical reports as
the ground truth, instead of traditional metrics like the
Dice coefficient or Hausdorff Distance.
|
|
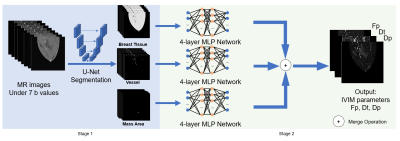 |
5149. Deep
Learning based Tissue Specific MRI-IVIM Parameter Estimation
J. Liu, Z. Yang, R. Moreno
KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden
Impact: IVIM model has gained momentum recently,
especially in the field oncology. Our study improve the
parameter estimation performance for IVIM model, which is
important for tumor and tumor type prediction.
|
|
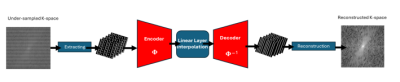 |
5150. K-space
Interpolation using Deep Koopman Autoencoders.
W. Ben Salah, S. McElroy, J. Shapey, S. Ourselin, C.
Bergeles, R. Neji
King's College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: This work introduces an interpretable neural
network for k-space interpolation, enabling good
reconstruction quality and offering avenues for extensions
to enable autoencoder-based scan-specific denoising.
|
|
 |
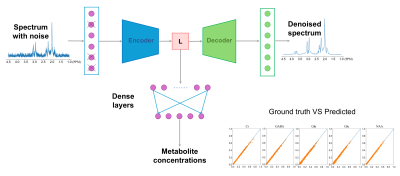
5151. DMnet:
A Reliable Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Quantification
Network and the Verification on 5T scanners
Z. Tu, J. Zhang, Y. Yang, D. Guo, X. Qu
Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Impact:
The DMnet can quantitate MRS more quickly and robustly, even in scenarios with lower SNRs. This method has been integrated into the CloudBrain-MRS platform for convenient one-click access by healthcare professionals, further aiding clinical treatments. |
|
 |
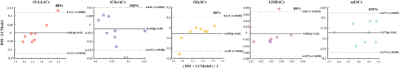
5152. The
Impact of Training Data on MRS Metabolite Quantification with
Deep Learning
Z. Ma, O. Karakus, S. Shermer, F. Langbein
Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom
Impact: This study underscores the importance of
training data quality in deep learning for MRS. By
demonstrating the impact of noise model realism, it provides
insights for developing more accurate metabolite
quantification models, potentially improving clinical
diagnosis and monitoring neurological disorders.
|
|
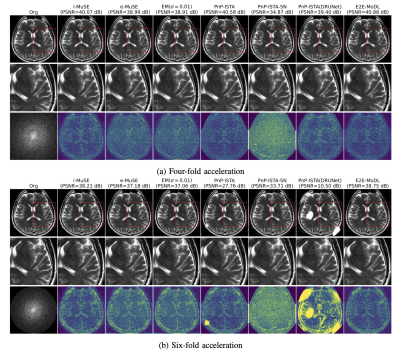 |
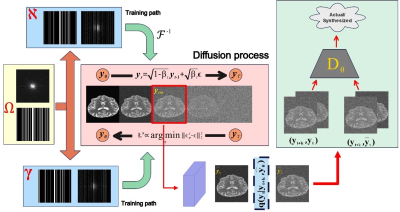
5153. Convex
implicit multi-scale (i-MuSE) energy framework: bridging
compressed sensing and diffusion models
J. Rikhab Chand, M. Jacob
University of Virginia, Charlottesville, United States
Impact: i-MuSE offers a memory-efficient alternative to
unrolled models while guaranteeing convergence, offering
better generalization performance, and facilitating fast
optimization algorithms. It can also perform posterior
sampling, like diffusion models, to estimate uncertainty.
|
|
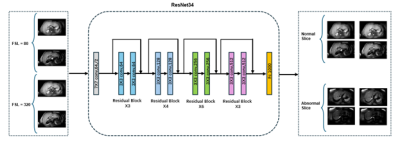 |
5154. Deep
learning enabled motion detection in quantitative macromolecule
proton faction mapping in the liver
Q. Shen, V. Wong, J. Zhong, H. Kang, Z. Yu, Q. Chan, W. Chu,
W. Chen
CU Lab of AI in Radiology (CLAIR), Department of Imaging and Interventional Radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Impact: Our approach enables automated motion detection
of the liver during MPF-SL scan. It can improve reliability
of parameter quantification by either discarding unreliable
measurements retrospectively or prompt data recollection
prospectively during scanning.
|
|
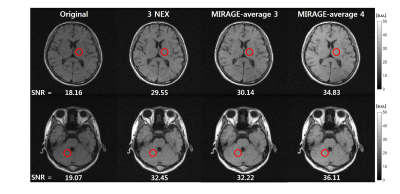 |
5155. MIRAGE:
MR Image Replication without Repeated Data Acquisition Using
Generative Model
Y-J Jeong, C-H Oh
Korea University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: MIRAGE offers a promising solution for efficient
SNR enhancement, with potential applications across various
configurations, including different anatomical regions,
imaging protocols, field strengths, and x-nuclei imaging.
|
|
|
5156. Deep
Learning-based Fast Calculation of Diffusion Tensor Distribution
Parameters
J. Zhou, Z. Zhu, F. Zong, X. Deng, P. Or, D. Topgaard
School of Artificial Intelligence, Beijing University of Post and Telecommunication, Beijing, China
Impact:
This study introduces deep learning for DTD parameter computation, overcoming computational complexity and spatial continuity issues of Monte Carlo methods, with potential for clinical translation across various diseases. |
||
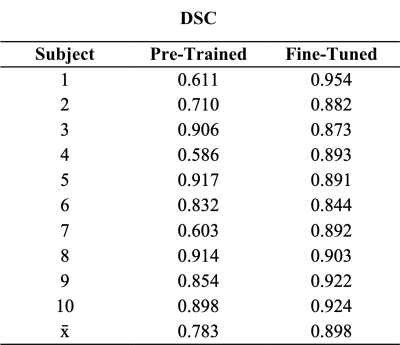 |
5157. Transfer
Learning for Segmentation of the Whole Prostate and
Intraprostatic Lesions in Multi-Parametric MRI
A. Ali, L. Muralidharan, S. Punwani, A. Retter, K. Shmueli
University College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: A
nnU-Net network trained on large public
datasets, then fine-tuned with a small
clinical dataset improved whole-prostate segmentation. This network will facilitate processing requiring
whole-prostate masks, such as Quantitative Susceptibility
Mapping, and could potentially reduce radiological
workload or automate quantification.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.