Traditional Poster
AI-Based MR Image Analysis
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

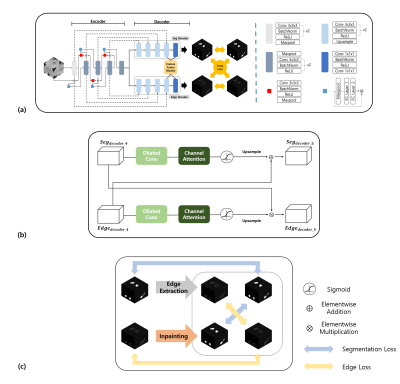 |
5109. Automated
Hippocampus Segmentation from CT Scans Using Hippocampus Dual
Decoder Network (HDD-Net)
W. Son, J. Y. Lee, S. J. Ahn, H. Lee
Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of
Impact: CT-based hippocampal segmentation via HDD-Net
would be a promising alternative to conventional MRI-based
procedures, and is expected to find a number of
applications, for example, studies on Alzheimer’s disease.
|
|
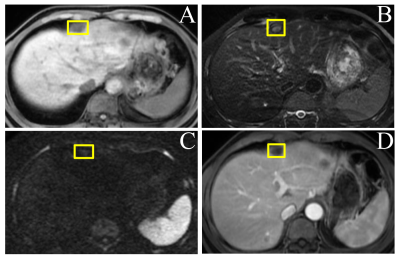 |
5110. Evaluating
the performance of commercial liver MRI AI software in detecting
malignancy in post-treatment lesions.
S. Luo, Y. Shen
Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Impact: Accurate identification of liver lesion
malignancy is essential for determining effective treatment
regimens. AI software can support junior radiologists in
assessing malignancy in post-treatment lesions, regardless
of the familiarity with specific treatment techniques.
|
|
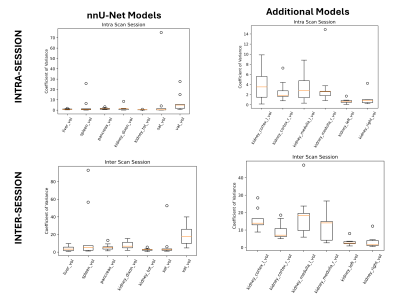 |
5111. Evaluating
Intra- and Inter- scan session consistency of Machine Learning
Multi Organ Segmentation
S. Lloyd-Brown, E. Cox, M. Craig, C. Bradley, A. Daniel, A.
Cooper, X. Chen, S. Francis
University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom
Impact:
Assessment of intra- and inter- scan session reproducibility provides an understanding of the detectable change in organ volume in longitudinal studies and the accuracy of masks used to derive associated quantitative metrics. |
|
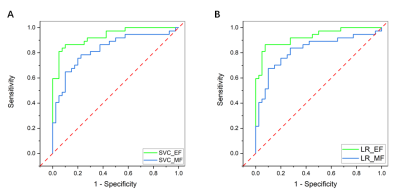 |
5112. Machine
Learning Detects Symptomatic Plaques on 3D high-resolution MR
vessel wall images
J. Chen, W. He, L. Yang, Q. Li, X. Yang, L. Wan, Y. Li, D.
Liang, X. Liu, H. Zheng, S. Lu, N. Zhang
Paul C. Lauterbur Research Center for Biomedical Imaging, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China
Impact: This study validated the importance of signal
features, such as enhancement degree, in identifying
high-risk plaques, providing data support for future
radiomic research. This approach aids in early screening and
targeted preventive measures, potentially reducing the
incidence of stroke.
|
|
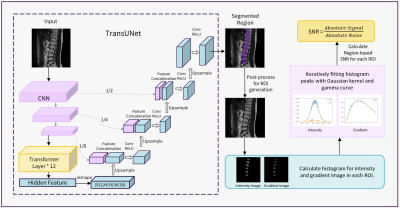 |
5113. An
automatic region-based no-reference image quality evaluation
method
S. Shen, X. Liu, Q. Dai, Y. Ge, K. Wang
GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Impact: Conventional automatic image quality assessment
approaches rely on the full image. The method proposed in
this paper pays more attention on anatomical regions of
interest to clinicians, yielding results that better meet
clinical needs.
|
|
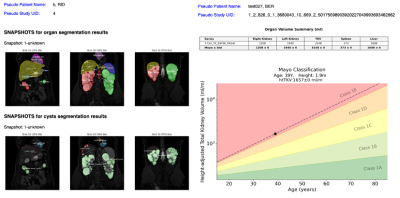 |
5114. TraceOrg:
An AI Platform for Reproducible ADPKD Organ/Cyst Contouring on
MRI
X. He, Q. Xiong, C. Zhu, Z. Hu, Y. Kim, H. Dev, K. Teichman,
A. Caroli, E. Scalco, G. Villa, F. Lussana, S. Pasini, M.
Sabuncu, M. Prince
Cornell University, New York, United States
Impact: TraceOrg provides accurate and efficient
segmentations for measuring kidney liver and renal cyst
volumes to enhance radiologist subjective assessments of
ADPKD abdominal MRI and is readily accessible via internet.
|
|
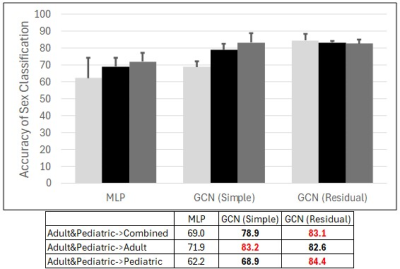 |
5115. Graph
Neural Network Learning on the Pediatric Structural Connectome
A. Srinivasan, R. Raja, J. Glass, M. Hudson, N. Sabin, K.
Krull, W. Reddick
St Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, United States
Impact: Our demonstrated 84.4% accuracy using GNNs to
predict sex from pediatric structural connectomes
underscored the capacity of GNNs to advance our
understanding of sex-specific neurological development and
highlighted the potential benefit of using adult connectomic
data to enrich pediatric datasets.
|
|
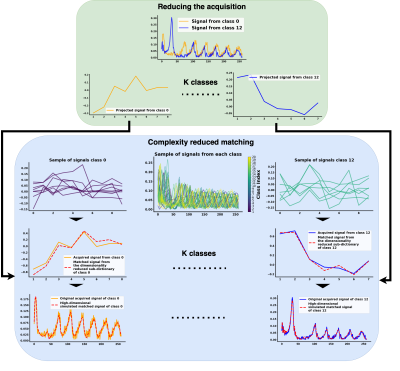 |
5116. Robust
Subspace Clustering Approach for High-Dimensional MRF: Novel
Simultaneous Clustering and Dimensionality Reduction at Scale
G. Oudoumanessah, T. Coudert, A. Barrier, A. Delphin, C.
Lartizien, M. Dojat, E. L. Barbier, T. Christen, F. Forbes
Univ. Grenoble Alpes, Inserm, U1216, Grenoble Institut Neurosciences, GIN, Grenoble, France
Impact: This work tackles the computational challenges
inherent to MRF for various tissue parameters, including
relaxometry, magnetic field characteristics, and
microvascular properties. While the method is demonstrated
on MRF reconstruction, it can be applied to other
large-scale dimensionality reduction tasks.
|
|
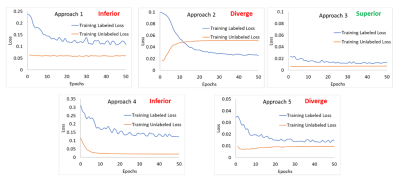 |
5117. Efficient
Utilization of Unlabeled Data during Training of Semi-Supervised
Learning Model
A. Saxena, V. Singhal, C. Bhushan, D. Shanbhag
GE Healthcare, Bangalore, India
Impact: We propose a simultaneous semi-supervised model
training methodology that ensures efficient utilization of
all the available unlabeled data in each training epoch.
|
|
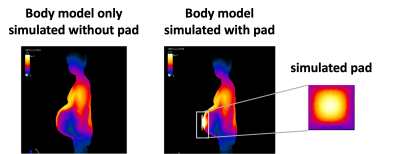 |
5118. Proved
feasibility of rapid dielectric shimming prediction in MRI using
Convolutional Neural Network on enriched dataset
M. Zhang, N. Murad, F. Robb, S. Winkler
Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, United States
Impact: This study demonstrates the feasibility for
AI-assisted real-time calculation of dielectric shimming
effect and electromagnetic fields, which could be applied to
ultra-high field strengths, where significant inhomogeneity
hinders proper evaluation, providing an insightful approach
to improve image shading and diagnostics.
|
|
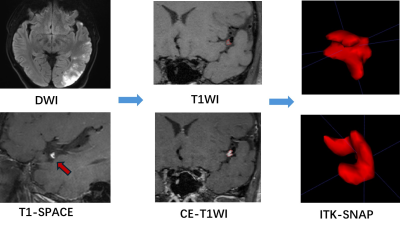 |
5119. Identification
of vulnerable intracranial atherosclerotic plaques via the
3D-HRMR-VWI radiomics model
T. Cao, T. Wang, L. Zhu, J. Zhang
The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Jiangsu, China
Impact: Integrating radiomics into intracranial plaque
risk assessment enables quantitative scoring of plaque
vulnerability, enhancing diagnostic performance and
supporting clinical risk stratification of intracranial
atherosclerotic plaques.
|
|
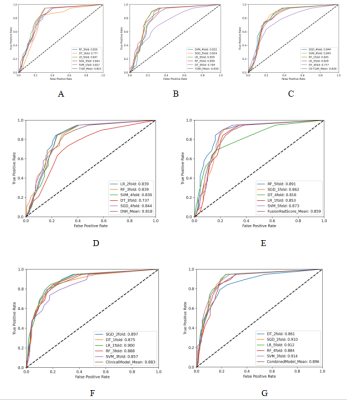 |
5120. MRI-based
radiomics model for predicting the nature of nodules in
cirrhotic liver
X. Wen, J. Luo, W. Pan, W. Wang, C. Yu
The Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian city, Liaoning province, China
Impact: It provides a promising tool for non-invasive
characterization of cirrhotic nodules.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.