Traditional Poster
Analysis Methods
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

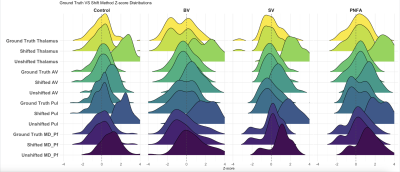 |
4820. Applications
of Normative Modeling: A Shift Method for Site-Independent
Normative Modeling and Brain Age Prediction
S. Balakrishnan, A. Banerjee, T. Young, M. Saranathan
University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School, Worcester, United States
Impact: The ability to incorporate new datasets from
external sites allows new research to better understand the
effects disease have on the brain. Brain age prediction also
allows new research to dive into the association between
disease and brain age.
|
|
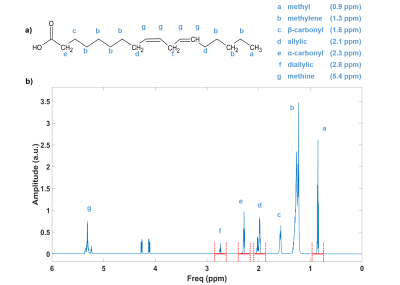 |
4821. Assessing
correction factors for calculation of hepatic fatty acid
composition with 1H-MRS – A multicenter setup
B. Korzekwa, Y. Kupriyanova, J. Mevenkamp, V. Fritz, L. N.
Rodehutskors, K. Bochinsky, H. Heise, M. Roden, J. Machann,
V. Schrauwen-Hinderling
German Diabetes Center, Leibniz Institute for Diabetes Research at Heinrich Heine University, Düsseldorf, Germany
Impact:
Noninvasive determination of hepatic fatty acid composition supports research of metabolic disease pathology and progression. Providing consistent, site-specific processing for this 1H-MRS data is essential for comparing results in large multicenter studies with different MR-scanner setups. |
|
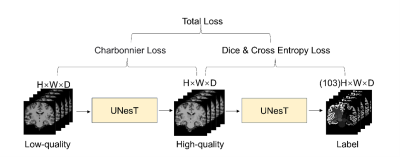 |
4822. Ultra-Fast
High-Resolution 3D Brain MRI at 5.0T: 36-Second 3D T1W Imaging
and Whole-Brain Segmentation
S. Li, W. Cai, Y. Li, H. Wang, H. Li
Institute of Science and Technology for Brain-inspired Intelligence, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study implemented a dual-task
transformer-based network on a 5.0T MRI platform, enabling
high-resolution 3D T1W brain imaging and accurate
segmentation in 36 seconds. With performance comparable to
conventional 3-min 36-second scans, this approach offers a
promising ultra-fast clinical solution.
|
|
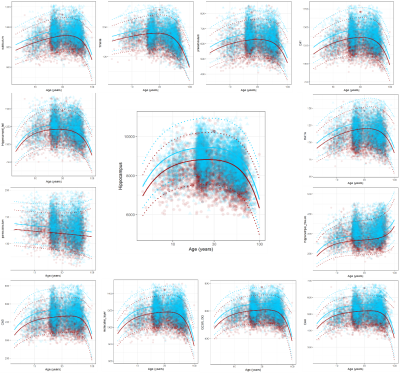 |
4823. Normative
Modeling of Hippocampal Subfield Volumes Reveals
Disease-Specific Atrophy Patterns in Neuroinflammatory diseases
X. DU, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu
BEIJING TIANTAN HOSPITAL, BEIJING, China
Impact: This study underscores the value of hippocampal
subfield metrics as potential biomarkers for diagnosing and
monitoring neuroinflammatory diseases. By revealing
disease-specific atrophy patterns, it advances understanding
of hippocampal vulnerability,guiding precision diagnostics
and individualized treatment strategies for improved patient
outcomes.
|
|
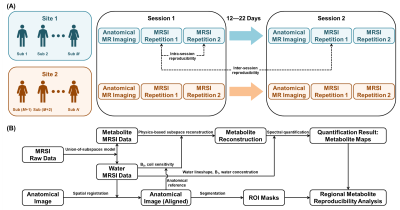 |
4824. Reproducibility
of Ultrafast High-Resolution MRSI at 3T Using SPICE
Y. Zhao, Y. Li, W. Jin, R. Guo, B. Sutton, Z. Meng, B. Bo,
Y. Zhang, W. Zhang, C. Xu, W. Tang, Y. Li, Z-P Liang
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, United States
Impact: This study demonstrated very good intra-session
and inter-session reproducibility of SPICE. The results
indicate that changes larger than the reported intra-session
CVs (for cross-sectional studies) or inter-session CVs (for
longitudinal studies) are likely attributable to biological
metabolic alterations.
|
|
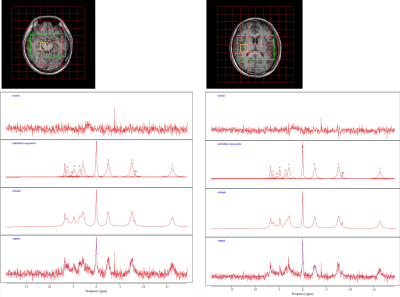 |
4825. Towards
a high-resolution Neuro 31P-MRS at 3T
Q. Yu, N. He, X. Zhang, J. Weng, P. Wu, Y. Zhou, Y. Teng, R.
Li, F. Yan
Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study optimized a high-resolution neuro 31P
protocol via CRLB simulation. Suggested NSA numbers were
provided for different metabolites and different brain
regions.
|
|
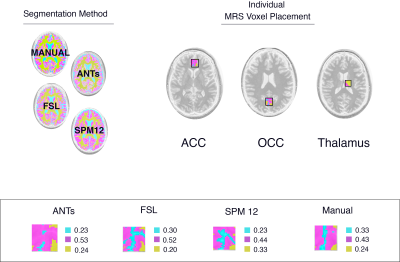 |
4826. BIASS:
Benchmarking the Impact of Anatomical Segmentation in
Spectroscopy
J. Archibald, K. Igwe, A. Kaiser, J. Lee, J. Kramer, A.
Zimmerman, A. Gudmundson, H. Zöllner, C. Fleischer, G.
Oeltzschner, J. Near, M. Mikkelsen
Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: This study demonstrates that segmentation tools
obtain different tissue volume fraction estimates in a
typical MRS voxel. These findings help researchers and
clinicians understand the variability that the choice of
segmentation algorithm contributes to the uncertainty of
water-scaled concentration estimates.
|
|
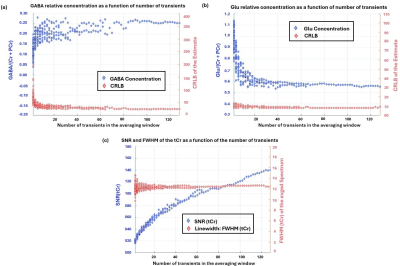 |
4827. Stability
of single-subject estimation of glutamate and GABA dynamics in
concurrent fMRI-fMRS at 7 T
S. Abbasi-Rad, R. Frost, J. Augustinack, Z. Kourtzi, U.
Emir, A. van der Kouwe
Harvard Medical School, Boston , United States
Impact: In single-subject fMRS, choosing averaging
window sizes with sufficient SNR is important for reliable
measurements of glutamate and GABA dynamics. Further
technical development both on the analysis side (temporal
fitting) and acquisition side (real-time frequency drift
correction) should be explored.
|
|
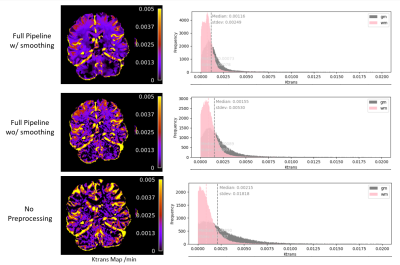 |
4828. Fully
Automated Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI Image Processing
Pipeline Reduces Variance in Ktrans
L. Saca, A. Chakhoyan, R. Gaggar, I. Pappas, A. Toga, B.
Zlokovic, D. Nation, S. Barnes
Loma Linda University Medical Center, Loma Linda, United States
Impact: This software will facilitate more reproducible
and consistent DCE processing across a variety of imaging
sites and research labs.
|
|
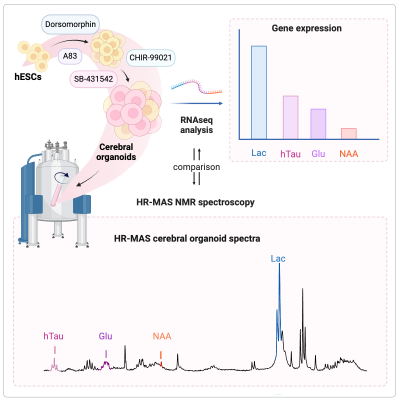 |
4829. Modelling
HR-MAS NMR spectra of human cerebral organoids using COLMAR1D
Deep Neural Networks – comparison against peak integration
A. Castilla Bolanos, V. Chinchalongporn, R. Ghosh Biswas, C.
Bailey, R. Soong, D. Li, R. Bruschweiler, A. Simpson, C.
Schuurmans, J. Near
University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Impact: This study presents a convenient method for
modelling and quantification of HR-MAS spectra in cerebral
organoids using deep deconvolution. By reliably quantifying
metabolite concentrations in human brain models, our
approach will enable studies to better understand human
brain metabolism.
|
|
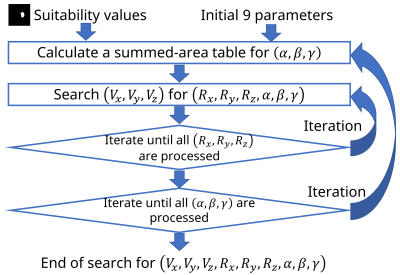 |
4830. A
Fast 3-dimensional Full Search Algorithm for Setting Volume of
Interests of MR Spectroscopy in Brain Tumor Images
H. Takeshima, S. Maruyama
Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
Impact: This abstract presents a fast search method
using a new fast 3-dimensional full search algorithm for
setting volume of interests of MRS using a segmentation
network. The proposed algorithm accelerated search
approximate 200 times using 3-dimensional summed-area
tables.
|
|
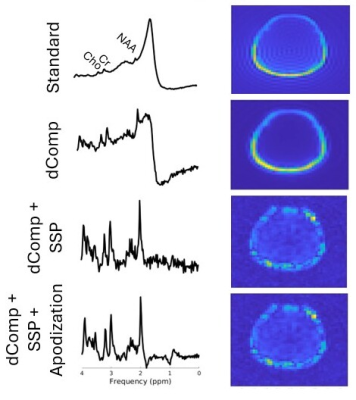 |
4831. End-to-end
acquisition and analysis of whole-slice rosette MRSI for brain
metabolic imaging at 3 Tesla
L. Burki, K. Hara-Lee, S. Senthil, J. Near
University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Impact: Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI)
is a powerful tool for quantifying biomarkers in vivo.
However, clinical adoption of MRSI has been slow. We propose
a complete and coherent pipeline for rapid MRSI acquisitions
pre-processing to address this clinical need.
|
|
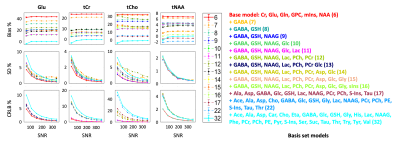 |
4832. Influence
of basis set composition on metabolite quantification using
1H-MRS at 3T: combining in-silico, in-vivo, and in-vitro
evidence.
P. Emeliyanova, L. M. Parkes, S. Williams, C. Lea-Carnall
University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
Impact: We demonstrate reliable metabolite
quantification with reduced-basis sets (<16 metabolites) for
data with typical SNR at 3T, with an 11-metabolite basis set
appear to offer optimal accuracy and low SD. These findings
have a potential to enhance reproducibility across studies.
|
|
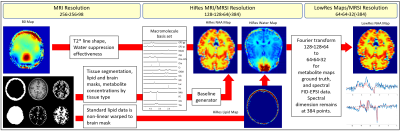 |
4833. Preliminary
Results from the 2024 MRSI Data Processing and Quantification
Challenge
B. Soher, J. LaMaster, J. Merkofer, B. Strasser, D. van de
Sande, C. Ma
Duke University Medical Center, Durham, United States
Impact: This is a resource, both code and data, that the
MRS community can use to create repeatable simulated data
based on real world data inputs. It is a platform that
encourages collaboration to simplify creation of reusable
infrastructure.
|
|
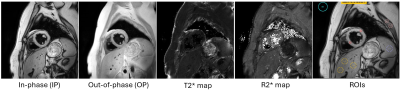 |
4834. MRI-PDFF
liver fat changes in patients with diabetes treated with SGLT2
inhibitor versus controls.
A. Naumova, G. Cunha, A. Mahdavi, N. Firoozeh, F. Kim, K.
Ordovas
University of Washington, Seattle, United States
Impact: Hepatic steatosis is both a complication and a
risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Noninvasive measurement of
proton density fat fraction (PDFF) can be used to detect
hepatic steatosis decrease after one year treatment with
sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.