Traditional Poster
Evolving Body MRI - Part 2
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

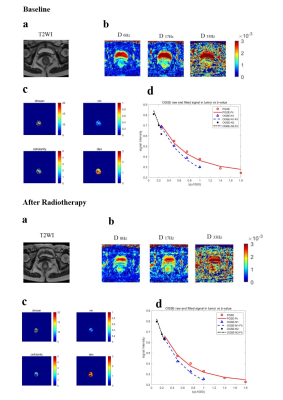 |
5170. Td-dMRI
for early predicting pCR to neoadjuvant short-course
radiotherapy followed by camrelizumab and chemotherapy in LARC
L. Zhang, Z. Jin, P. Sun, S. Xu, X. Li
Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Impact: Time-dependent diffusion MRI has potential in
characterizing changes of cellular tissue microstructures
after short-course radiotherapy and then predicting pCR to
neoadjuvant treatment including immunotherapy, which may
promote the clinical application of immunotherapy in LARC.
|
|
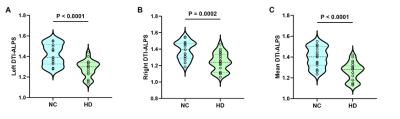 |
5171. Association
between glymphatic dysfunction and cognitive impairment in
patients with hemodialysis
Y. Cui, C. Zheng, B. Xu, J. Lu
Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Impact: Multimodal neuroimaging techniques could provide
non-invasive assessment of glymphatic dysfunction in HD
patients, providing new insights into the pathophysiology of
cognitive impairment in HD patients.
|
|
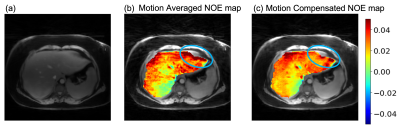 |
5172. Motion-Compensated
Free-Breathing MRI for GlycoNOE Imaging in the Human Liver
L. Feng, J. Chen, D. Xia, M. Breilyn, S. Lewis, X. Xu
New York University, New York, United States
Impact: This technique can improve glycoNOE imaging in
the human liver. The method could be valuable for studying
the glycogen distribution and monitoring treatment in
patients with glycogen storage disease.
|
|
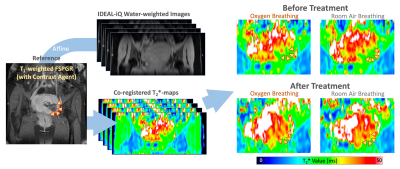 |
5173. Assessing
Uterine Myomas and adenomyosis with BOLD Imaging After
MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound: Preliminary Findings
P-H Chuang, Y-H Yang, L-W Liu, S-Y Wei, C-W Lee, C-Y Lin,
Y-C Lin, S-J Chen
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
Impact: T2*-mapping, which can reveal the variations in
oxygenation, would be an effective tool for assessing
treatment outcomes of high-intensity focused ultrasound
(HIFU) in uterine myomas and adenomyosis, without the need
for contrast injection.
|
|
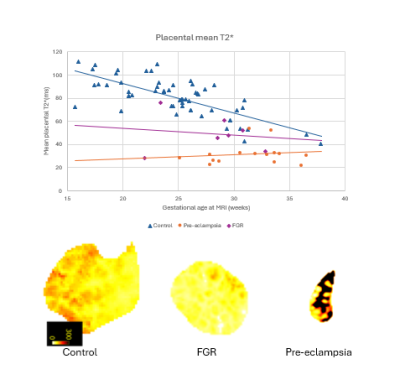 |
5174. Functional
differences in the placenta of pregnancies affected by
pre-eclampsia or fetal growth restriction
M. Hall, J. Aviles Verdera, J. Hutter, L. Story
King's College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: Placental diseases are common in pregnancy. As
well as highlighting deviations from normal, placental MRI
results vary between conditions. This highlights the
potential for MRI to provide better correlation with
histopathology and outcomes than is currently possible
clinically.
|
|
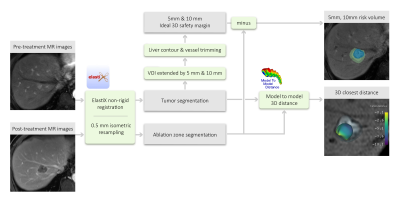 |
5175. Evaluating
3D MR Ablation Margins in Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Thermal
Ablation Using Open-Source Software
L. J. Qian, L. Wang, T. S. Yang, H. N. Ren, X. H. Gong, Y.
Song, Y. Zhou
Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
Impact: Open-source software can quantify 3D ablation
margins at MR images, offering a practical tool in assessing
HCC thermal ablation efficacy.
|
|
 |
5176. P53
status combined with MRI findings for prognosis prediction of
single hepatocellular carcinoma
H. Huang, G. Zhou, Q. Wu, H. Qiao, S. Chen, S. Hu, Q. Wen
Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University, WuXi, China
Impact: The integrated nomogram combining P53 status and
preoperative MRI findings can be a valuable prognostic tool
for predicting postoperative recurrence of single HCC,
suggesting the potential to assist clinicians in developing
more aggressive and personalized treatment strategies.
|
|
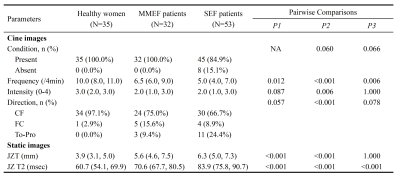 |
5177. Noninvasive
evaluation of the peristalsis and structure of uterine
junctional zone in endometrial fibrosis patients using cine MRI
and T2 mapping
Z. Zhou, H. Liang, N. Zhou, W. Chen, P. Jiang
Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China
Impact: This study demonstrated the feasibility of cine
MRI and T2 mapping in evaluating the peristalsis and
microstructure of UJZ which can help clinicians to better
understand infertility in patients with different degrees of
EF and select the optimal treatment scheme.
|
|
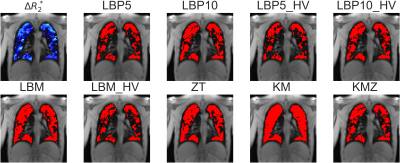 |
5178. Choice
of Segmentation Algorithm to Determine Ventilated Volume
Fraction from Oxygen-Enhanced MRI in Cystic Fibrosis and Healthy
Volunteers
M. Tibiletti, C. Short, J. Naish, J. Waterton, M. Abkir, T.
Semple, S. Padley, J. Davies, G. Parker
Bioxydyn Ltd, Manchester, United Kingdom
Impact: This study provides a direct comparison of
segmentation methods for quantifying ventilated lung volume
in cystic fibrosis from dynamic oxygen-enhanced MRI. Our
results could improve the assessment of lung function in
patients, by improving repeatability and sensitivity to
disease.
|
|
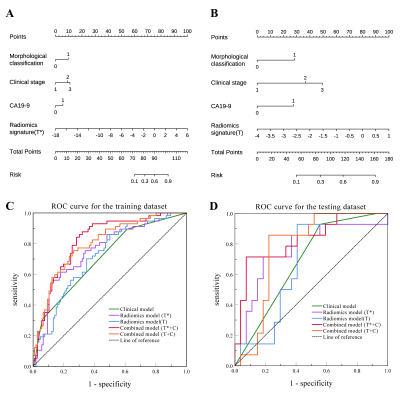 |
5179. Nomogram
Based on MRI Radiomics Combined with Clinical Features for
Assessing Lymphovascular Invasion in Node-Negative Rectal Cancer
L. Peng, X. Zhang, F. Zhang, F. Ma, K. Ai, L. Wang
Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou, China
Impact: The treatment approach for RC without lymph node
and distant metastasis but with LVI-positive is equivalent
to that for with LNM-positive. The nomogram model offers a
non-invasive tool for prediction of LVI, avoiding the risks
associated with invasive pathological detection.
|
|
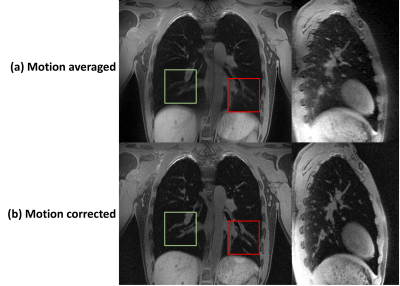 |
5180. Free-breathing
High Quality Pulmometry MRI: 3D Cones Acquisition with Motion
Compensation
B. Li, Q. Liu, J. Xu, H. Gu, H. Li, Y. Dong, Z. Zhong
University of Southern California, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: Free-breathing 3D conical acquisition with
motion compensation enables isotropic, high-resolution
volumetric lung imaging with reduced motion blurring. This
technique is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring lung
diseases like COPD and pulmonary fibrosis, significantly
enhancing noninvasive diagnostic capabilities and treatment
planning.
|
|
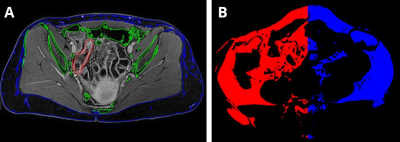 |
5181. Preliminary
results on the relation between creeping fat and MRI markers of
small bowel lesions in Crohn’s disease
A. Kneib, P. Soullié, A. Basile, L. Peyrin-Biroulet, V.
Laurent, F. Odille
INSERM, Université de Lorraine, Nancy, France
Impact: Visceral fat is known to have a specific
distribution in Crohn’s disease, however its relation to
lesion severity has not been assessed thoroughly. Here we
provide preliminary results on this relation using several
quantitative MRI markers.
|
|
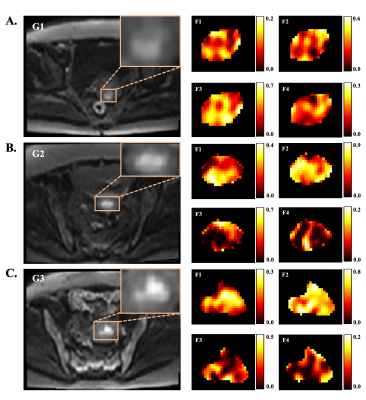 |
5182. Four-compartment
Restriction Spectrum Imaging model for Preoperative Grading in
Endometrial Cancer
T. Yang, Y. Dai, D. Wu, H. Liu, G. Shi
Renji hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: Four-compartments RSI model demonstrated a
potential for preoperative discrimination across all grades
of EC lesions, especially between grade-2 and grade-3. Our
findings underscore the potential of the RSI model for
non-invasive preoperative imaging grading of lesions in EC
patients.
|
|
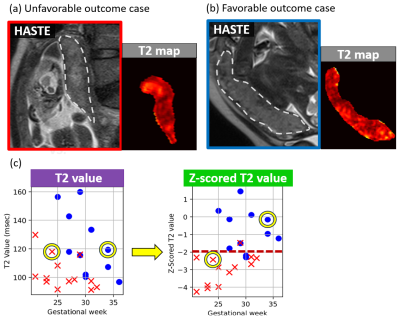 |
5183. Z-scored
Placental T2 Values Facilitate Accurate Risk Stratification for
Fetal Growth Restriction
A. Yoshida, Y. Himoto, K. Fujimoto, M. Kikuchi, K. Harada,
M. Kirita, Y. Matsumoto, Y. Chigusa, M. Mandai, Y. Nakamoto
Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University , Kyoto, Japan
Impact: Compared to T2 values, Z-scored placental T2
values facilitate a more accurate risk stratification of
pregnancies with fetal growth restriction. This methodology
provides essential guidance for intensive monitoring and
optimal timing decisions regarding pregnancy termination.
|
|
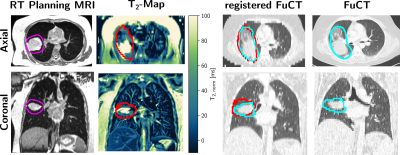 |
5184. Towards
Automated Detection and Localization of Radiation-Induced
Pneumonitis based on T2-Maps of Lung Cancer Patients
R. Klaar, M. Rabe, K. Begaj, S. Corradini, C. Eze, C. Belka,
G. Landry, C. Kurz, J. Dinkel
Department of Radiology, LMU University Hospital, LMU Munich, Munich, Germany
Impact: The acquisition of T2-maps for lung tumor
patients 2-3 months after the end of radiotherapy could
replace the repeated follow-up CT-scans for these patients
and could also allow to automatically identify
radiation-induced pneumonitis patients and the affected lung
area.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.