Traditional Poster
Insights from Neuroimaging of CNS, Head & Neck Pathology
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

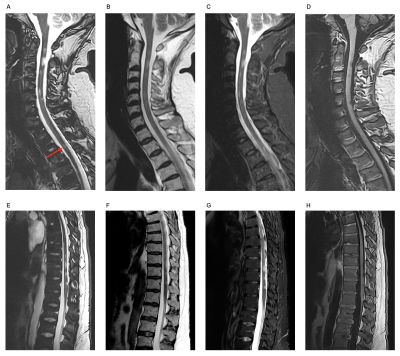 |
5028. Enhanced
Spinal Cord Lesion Detection in Multiple Sclerosis Using
White-Matter-Nulled 3D MPRAGE with Deep Learning Reconstruction
F. Munsch, A. Ravache, T. Yamamoto, B. Zhang, M. Lacoste, H.
Fukutomi, T. Tourdias, V. Dousset
University of Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France
Impact: This study demonstrates that 3D WMn MPRAGE
combined with deep learning reconstruction significantly
improves spinal cord lesion detection in multiple sclerosis,
offering superior contrast and fewer artifacts than
conventional MRI, potentially enhancing early diagnosis and
treatment outcomes.
|
|
 |
5029. Cross-modal
deep learning to predict multiple sclerosis cervical spinal cord
damage with digital monitoring of motor function
P-J Lu, T. Woelfle, A. Cagol, M. Ocampo-Pineda, F. Spagnolo,
Ó. Reyes, L. Melie-Garcia, M. Weigel, J. Kuhle, L. Kappos,
J. Lorscheider, C. Granziera
University Hospital and University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland
Impact: The performance of the proposed cross-modal
neural network indicates that smartphone walking tests
correlate with structural changes in cervical spinal cord
and might assist clinical assessments in multiple sclerosis.
|
|
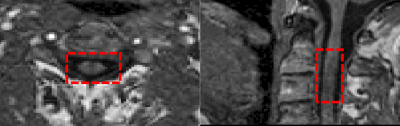
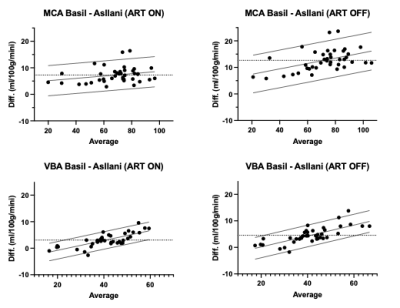 |
5030. Macrovascular
contamination may confound partial volume correction in
ASL-derived CBF maps in patients with cerebrovascular disease
J. M. Sousa, T. Wettervik, J. Berglund, P. Enblad, A. Lewén,
J. Wikström, M. Fahlström
Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Impact:
The choice of macrovascular correction method can negatively impact CBF estimates, depending on the PVC approach used. Linear regression PVC demonstrated greater precision, both with and without macrovascular correction, compared to the Bayesian method |
|
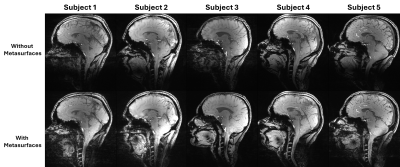 |
5031. Metasurface
Enabled In Vivo Cervical Spine Imaging at 7T
P. Jacobs, N. Wilson, M. Elliott, R. Reddy
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: By utilizing a pair of inexpensive metasurfaces
higher quality c-spine imaging can be accomplished at 7T
without the need for dedicated RF coils.
|
|
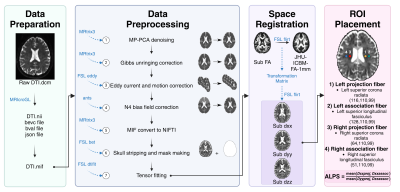 |
5032. Glymphatic
System Alterations in Thyroid Eye Disease: Evidence from
DTI-ALPS Analysis
H. Zhang, M. Jiang, Y. Liu, X. N. Lee, Z. Fang, J. Li, Y.
Li, J. Sun, X. Tao, X. Song, H. Zhou, X. Fan
Department of Ophthalmology, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study highlights the glymphatic system's
potential role in TED-related brain changes, emphasizing the
need for further exploration of its pathophysiological
mechanisms. Future validation of these findings may open new
avenues for understanding and managing neurological impacts
in TED.
|
|
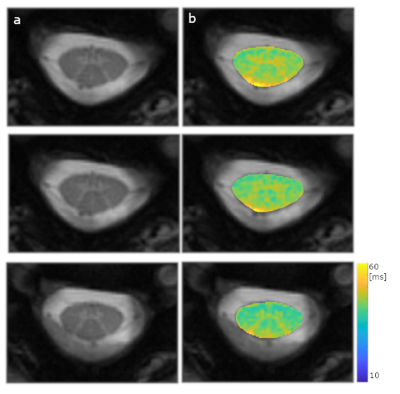 |
5033. Spinal
Cord T2* mapping with Multi-echo Radial Stack of Star
Acquisition at 7T
S. N. Adnani, T. Denney, R. Beyers, A. Bashir
Auburn University Neuroimaging Center, Auburn, United States
Impact: Imaging small-diameter structures such as
the spinal cord at high spatial resolutions demands new data
acquisition and processing techniques to mitigate
limitations due to motion artifacts. Radial MRI acquisition
can help reduce motion artifacts and increase speed.
|
|
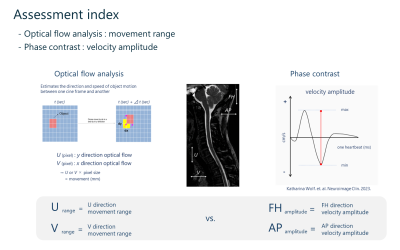 |
5034. Quantitative
evaluation of spinal cord cine-MRI with optical flow analysis:
comparison with phase contrast
R. Iwasaki, T. Horie, M. Kawakubo, N. Konta, S. Takano, H.
Atsumi, T. Niwa
Tokai University Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan
Impact: This approach holds potential for diagnosing and
evaluating spinal conditions by providing quantitative
insights into spinal cord motion. It could improve clinical
decision-making for Chiari I malformation , aiding in
assessing treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
|
|
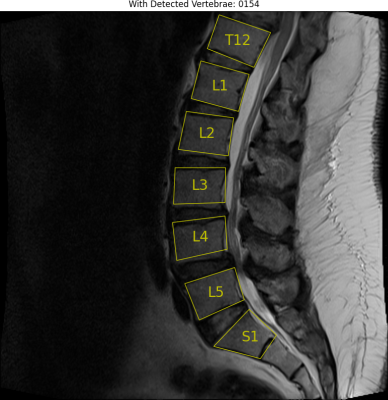 |
5035. Evaluation
of Publicly Available Deep Learning Lumbar Spine MRI Analysis
Tool for Prioritizing MRI Evaluation
N. Kurt, S. Akbas, R. Russo, S. Soman
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, United States
Impact: The SpineNetV2 publicly available deep learning
software has potential to serve as a prioritization tool for
moderate to severe vertebral canal narrowing, which can aid
in screening for patients with potentially critical spinal
stenosis.
|
|
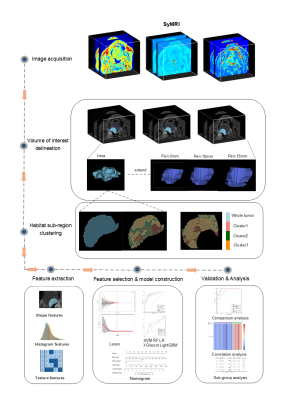 |
5036. Habitat-based
radiomics analysis utilizing Synthetic MRI for the prediction of
lymph node metastasis in oral cancer
R. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Shi, Y. Yuan, X. Tao
Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
Impact: This habitat-based radiomics model improves
accuracy in predicting lymph node metastasis in oral cancer,
aiding clinical decision-making and patient management.
|
|
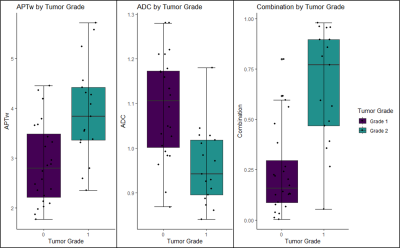 |
5037. Amide
Proton Transfer-weighted MRI and DWI as Biomarkers for
Predicting Tumor Grades in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
H. Wei, F. Yang, X. Yu, L. Xie, M. Lin
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China, Beijing, China
Impact: APTw and ADC provide unique insights into tumor
microenvironment. Incorporating these imaging modalities
into clinical practice offers a non-invasive approach for
tumor grading, which could enhance preoperative assessment
and potentially improve patient management.
|
|
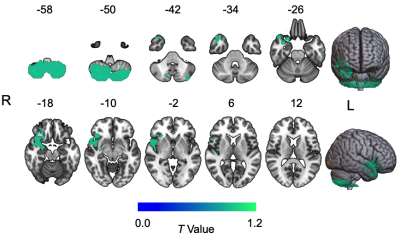 |
5038. MRI
Assessment of Intrinsic Neural Timescale and Gray Matter Volume
in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
X. Niu, H. Xu, Y. Guo, S. Zhang, B. Cheng, X. Cai
Department of Radiology, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Impact: This research provided a comprehensive DMD
neurobiological profile. The identification of
neurobiomarkers through advanced MRI techniques could
facilitate early diagnosis of cognitive issues in DMD, guide
personalized treatments, ultimately enhancing the quality of
life for individuals with DMD.
|
|
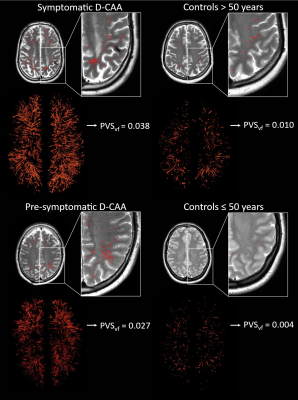 |
5039. Quantification
of Total White Matter Perivascular Space Volume: Follow-up in
Dutch-type Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
M. Schipper, T. van Harten, A-T Razoux-Schultz, K. Kaushik,
L. Hirschler, S. Voigt, I. Rasing, E. Koemans, R. van Dort,
R. van der Zwet, S. Schriemer, E. van Zwet, J. van der
Grond, M. van Buchem, S. Greenberg, M. Wermer, M. van Osch,
M. van Walderveen, S. van Rooden
Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands
Impact: Sensitive measurement of PVS-enlargement will
increase our understanding of disease mechanisms and allow
monitoring of disease progression. This is relevant for
developing treatment strategies and especially for tracking
the effectiveness of treatments.
|
|
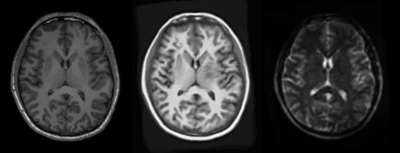 |
5040. High
Resolution Super-Resolved Structural FSE at Ultra-low Fields for
Source Reconstruction in MEG
J. Gholam, L. Tait, J. Benacek, S. Manolova, H. Statham, G.
Perry, F. Padormo, M. Cercignani, K. Singh, D. Jones
CUBRIC, School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom
Impact: MEG source localisation is significantly aided
by knowledge of participant neuroanatomy. ULF-MRI offers
accessible imaging to implanted populations, as well as
providing nervous or younger participants clear
lines-of-sight and freedom to be comforted by caregivers.
|
|
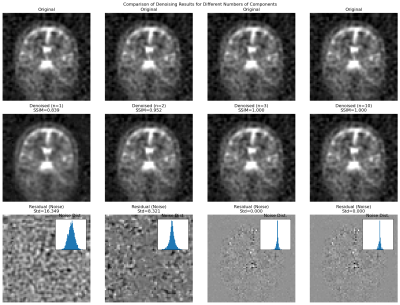 |
5041. Optimizing
MPPCA for Complex Sodium MRI: Component Analysis and Noise
Characterization at 3T
A. Das, Y-C Lin, Y. Qian
New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: This comprehensive validation establishes MPPCA
as a robust denoising method for complex sodium MRI,
providing specific guidelines for component selection and
quality metrics. The improved image quality enhances sodium
MRI's potential for clinical applications in metabolic and
neurological assessments.
|
|
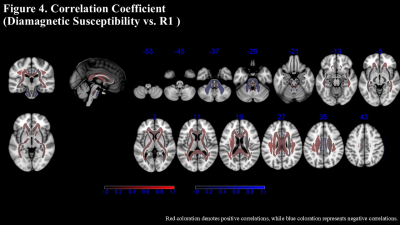 |
5042. Myelin
Assessment in Neurodegeneration: Correlation of R1 Relaxation
and Diamagnetic Susceptibility in White Matter Using
χ-Separation
M. Hori, K. Kamiya, J. Ebina, M. Kobayashi, S. Mizumura, H.
Terada, K. Murata, J. Lee, O. Kano
Toho University, Tokyo, Japan
Impact: A novel methodχ-separation enables myelin
assessment in neurodegenerative white matter, reducing
iron's confounding effects. This method allows researchers
to study myelin independently, potentially enhancing
diagnostic precision in neurodegenerative disease Synopsis
|
|
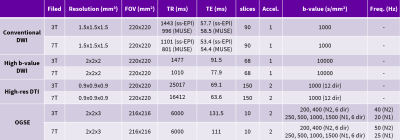 |
5043. Benefits
and limitations of diffusion imaging at 7T with a
high-performance gradient system: a comparative study with 3T
H. Liang, S. Li, L. Nie, Y. Xiong, B. Xu, B. Wu
GE HealthCare MR Research, Beijing, China
Impact:
This study enhances neuroimaging by demonstrating significant advantages and limitations of 7T diffusion imaging, informing future research and clinical applications in brain health assessment. |
|
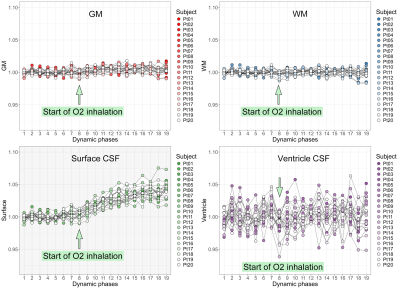 |
5044. Oxygen-enhanced
MRI of the brain using 3D VIBE and 3D MR fingerprinting
Y. Fushimi, S. Okuchi, A. Sakata, T. Yamamoto, S. Otani, S.
Nakajima, S. Ikeda, S. Ito, M. Umehana, Y. Ma, S. Morooka,
J. Fujimoto, H. Imai, Y. Urushibata, Y. Nakamoto
Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan
Impact: Oxygen-enhanced MRI (OE-MRI) utilizing 3D
volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination (3D VIBE)
can indicate rapid drainage from interstitial fluid (ISF)
into cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) via intramural periarterial
drainage (IPAD) pathway.
|
|
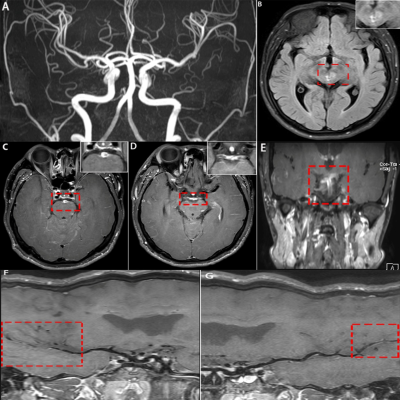 |
5045. Application
of high-resolution 3D vessel wall MRI (HR-3D-VW-MRI) in Primary
Angiitis of the Central Nervous System
H. Zhou, T. Li, X. Zhang, Y. Jiang, Y. Meng, S. Yin, Y. Wang
Department of Radiology, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
Impact: This study significantly improved the diagnostic
accuracy of Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System
(PACNS) and provided a new effective tool for monitoring
disease progression by using high-resolution 3D-VW-MRI
technology.
|
|
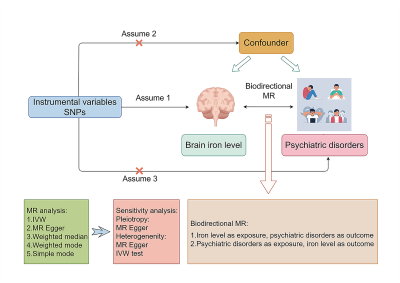 |
5046. Causal
associations between iron levels in subcortical brain regions
and psychiatric disorders: a Mendelian randomization study
W. Du, B. Tang, W. Zhang, S. Lui
West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Impact: The observed bidirectional trends between
subcortical iron levels and psychiatric disorders,
indicating the importance of the underlying biomechanical
interactions between brain iron regulation and these
disorders.
|
|
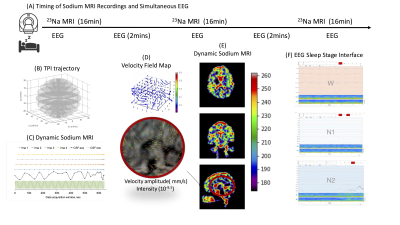 |
5047. Simultaneous
Dynamic Sodium (23Na) MRI and EEG Analysis of Cerebrospinal
Fluid Flow Velocity in the Human Brain During Sleep
Y-C Lin, K. Watson, X. Chen, S. Henin, N-M Kumbella, J.
Quimbo, Y. Ge, A. Masurkar, A. Liu, Y. W. Lui, Y. Qian
Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, New York Universi, New York, United States
Impact: This work may clarify sleep’s role in Aβ
clearance in humans.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.