Traditional Poster
Psychiatric Disorders & Sytemic Pathology Affecting Normal Appearing Brain
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 5069. WITHDRAWN | ||
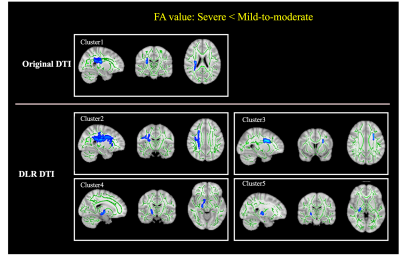 |
5070. The
impact of deep learning based image reconstruction on the
quantification of DTI for assessing the severity of depression
Y. Cui, S. Dong, Y. Zhang, J. Dai, S. Liu, Y. Xiao
Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China
Impact: DLR can significantly increase the SNR of DTI
images which likely improve the quantification accuracy for
better assessing depression severity. Therefore, the
application of DLR would be beneficial for depression
assessment and management.
|
|
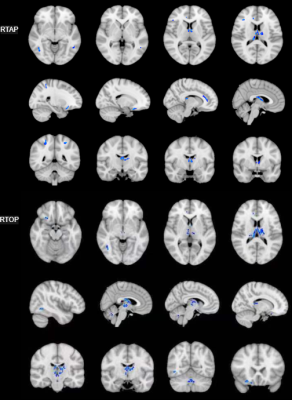 |
5071. Mean
Apparent Propagator Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of White
Matter Microstructural Changes in Neuropsychiatric Lupus
z. li, h. liu, y. jiang
The First Hospital of China Medical University, 辽宁, China
Impact: Application of mean apparent propagator MRI for
patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus
may help identify early biomarkers of the disease, which is
crucial for timely intervention and treatment strategies.
|
|
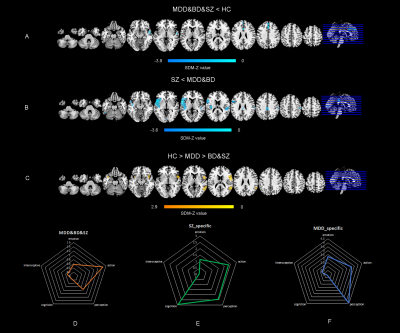 |
5072. Common
and specific gray matter abnormalities and epicenter
distribution across major psychiatric disorders
P. Zhu, K. Qin, W. Chen
Department of Radiology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
Impact: Due to the highly overlapping symptoms of MDD,BD
and SZ, there are often misdiagnoses. Therefore, this study
explores the potential structural change patterns of the
three diseases through structural similarities and
differences, and provides reliable diagnostic basis for the
clinic.
|
|
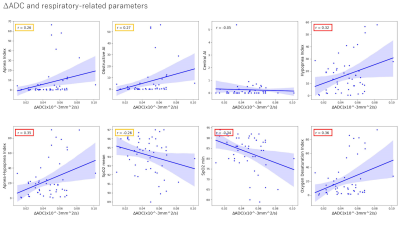 |
5073. Neurofluid
and Microstructural Evaluation by Time-Dependent Diffusion
Analysis and White Matter Parameters in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
T. Taoka, K. Iwamoto, S. Miyata, R. Ito, R. Nakamichi, T.
Nakane, H. Fujishiro, K. Ichikawa, A. Kamiunten, N.
Ichinose, M. Ikeda, S. Naganawa
Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan
Impact: ΔADC could serve as an indicator of brain
microstructural changes linked to respiratory function, with
implications for evaluating neurofluid dynamics.
|
|
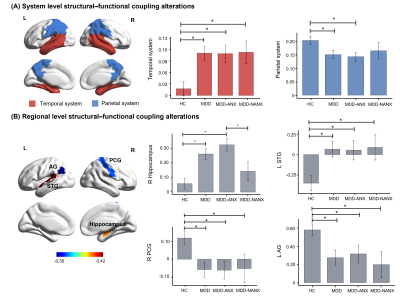 |
5074. Temporoparietal
structural-functional coupling abnormalities in drug-naïve
first-episode major depressive disorder
Q. Zhang, A. Zhang, G. Kemp, Y. Zhao, Q. Gong
Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Department of Radiology, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Impact: Our findings revealed disrupted topology-related
interplay between structural and functional connectivity in
temporoparietal regions in MDD, advancing understanding of
MDD-related multimodal network abnormalities and
highlighting the role of right hippocampal coupling
alterations in identifying the anxious depression subtype.
|
|
| 5075. WITHDRAWN | ||
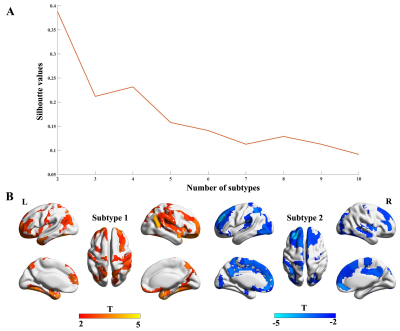 |
5076. Individualized
gray matter morphological abnormalities unveil two
neuroanatomical obsessive-compulsive disorder subtypes
B. Wen, Q. Tao, Y. Tian, W. Shi, Z. Liu, J. Sun, Y. Zhang,
J. Cheng, S. Han
the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Impact: Two subtypes manifest opposite gray matter
morphological abnormalities. Subtype exhibit divergent
structural covariance network-informed disease epicenters.
Gray matter morphological abnormalities of subtypes exhibit
distinct associations with neurotransmitter
receptors/transporters. Novel insights are offered into
nosology and heterogeneous nature of OCD.
|
|
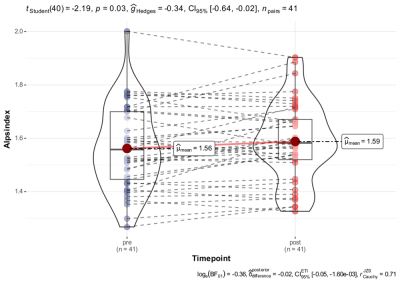 |
5077. Bariatric
Surgery Alters Brain Glymphatic Function in Obese Patients: A
DTI-ALPS Study
J. Duan, Y. Liao, P. Wu, J. Peng, P. Rong
The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China
Impact:
This research suggests bariatric surgery can alter the brain's glymphatic system, highlighting its potential influence on cognitive health and opening avenues for further exploration of obesity-related neurological impacts. |
|
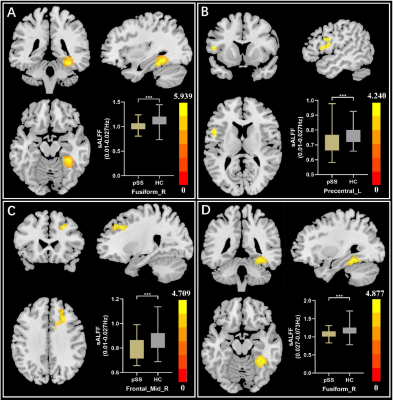 |
5078. Frequency-Dependent
and Temporal Variability of Low-Frequency Fluctuations in
Primary Sjögren's Syndrome Patients
C. Hu, L. Wang, P. Wei, Y. Shang, X. Zhang, X. Du, H. Cao,
C. Gao, X. Ge, Z. Ding, Z. Han, J. Huang
Hangzhou First People's Hospital, Hangzhou, China
Impact: This study reveals that ALFF indicators
demonstrate aberrant alterations in pSS, exhibiting
characteristics of both frequency dependence and temporal
variability, complementing traditional metrics and
suggesting that ALFF could serve as a novel tool for
investigating the neurological underpinnings of pSS.
|
|
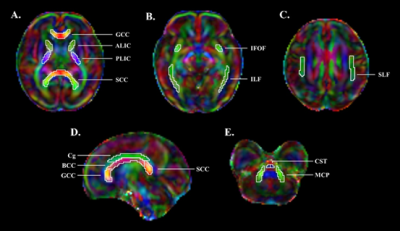 |
5079. Application
of Zoomit-DTI in Assessing Fetal Brain White Matter Development
in Pregnancies Complicated by Maternal Diabetes
Q. Zhu, M. Liu, L. Deng
ZheJiang SirRunRun Hospital, Hangzhou, China
Impact: This study reveals the microstructural
differences in fetal brain white matter development in
pregnant women with GDM. Zoomit - DTI may be helpful for the
early diagnosis and intervention of the neurodevelopmental
risks of fetuses in pregnant women with GDM.
|
|
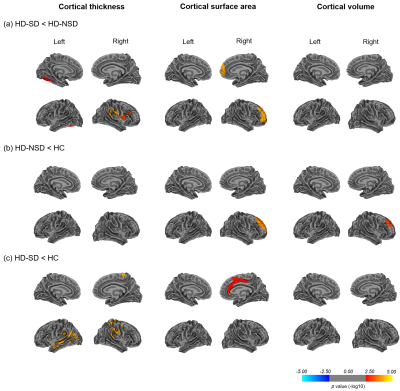 |
5080. Cortical
and subcortical gray matter bases of sleep disturbance in
patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis
Y. Jiang, Z. Zhang, Y. Miao, J. Wu
Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Dalian University, Dalian, China
Impact: Cortical and subcortical gray matter
abnormalities are associated with sleep quality in HD
patients, with a more widespread pattern observed in
patients with SD. Our findings highlight the importance of
distinguishing HD patient subgroups based on sleep quality.
|
|
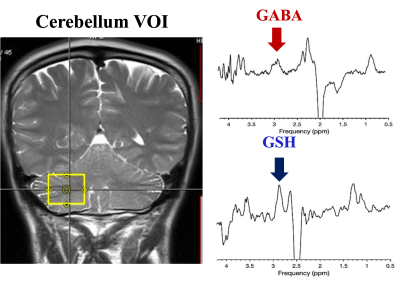 |
5081. MRS
Insights into Cerebellar Alterations and Motor Variations in
Welders Exposed to Manganese
J. George, B. Bozymski, G. Nossa, C. Mizimakoski, C. Lee, J.
Park, R. Harold, D. Foti, U. Dydak
Purdue University, West Lafayette, United States
Impact: This study examines the cerebellum’s response to
Mn overexposure, linking elevated Mn to disrupted
glutamatergic signaling and potential oxidative
stress. Findings could support stricter occupational health
guidelines and further research on Mn’s effects on motor
control and neurodegenerative risks.
|
|
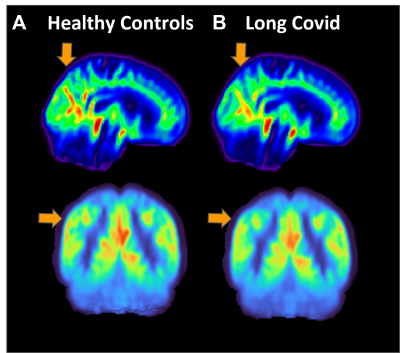 |
5082. Cerebral
Hypoperfusion and Vascular Impairment in Long COVID Patients
with Cognitive Symptoms
S. Cataldo, M. Belzunce
ECyT, UNSAM, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Impact: Our results indicate that cerebral
hypoperfusion may serve as a biomarker to evaluate new
treatments for long COVID, reinforcing the hypothesis that
vascular dysfunction underlies its cognitive symptoms. This
could improve diagnostic accuracy and guide targeted
interventions.
|
|
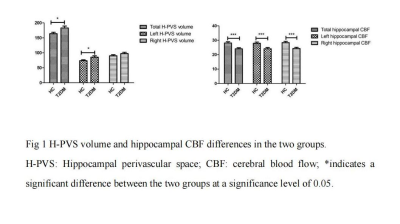 |
5083. Asymmetric
impairment of hippocampus in patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus related with cognitive function
P. Pan, J. Gao, A. Kai, X. Lei, X. Zhang
Shaanxi Provincial People's Hospital, Xi'an, China
Impact: Hippocampal injury in patients with T2DM is
asymmetry. H-PVS and hippocampal CBF are expected to be
imaging markers for identifying general cognitive
dysfunction. This may provide clinicians with important
information for planning treatment strategies and assessing
prognosis in T2DM patients.
|
|
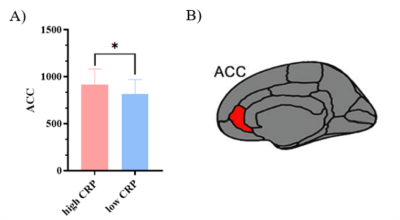 |
5084. Higher
CRP levels are related to increased grey matter volume in
anterior cingulate cortex and fatigue symptom in COVID-19
survivors in acute phase
R. Zhu, X. Niu, W. Bao, H. Li, X. Quan, G. Ye, Q. Zhu, M.
Zhang
the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China
Impact: This study provides direct evidence of an
association between immune biomarkers, ACC, and fatigue
symptoms. These results point towards a putative etiological
model of post-COVID-19 fatigue, in which elevated peripheral
proteins are associated with structural changes in the ACC.
|
|
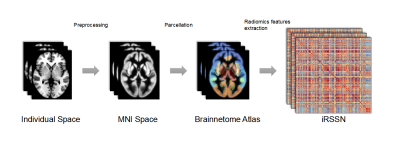 |
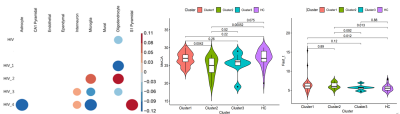
5085. Identifying
Depressive Disorder: Perspectives from an Individualized
Radiomics-Based Structural Similarity Network
J. Wen, Y. Hao, L. Gong, L. Gao, H. Guo, G. Wen
Department of Medical Imaging, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Impact: Individualized radiomics-based structural
similarity network shows great potential for serving as more
reliable features in MDD diagnosis.
|
|
 |
5086. The
Gray Matter Atrophy Pattern Associated with Abnormal Gait and
Cognitive Impairment in HIV-Infected Individuals.
J. Sun, Z. Zhuo, Y. Zhang, J. Weng, K. Zhang
Xuanwu Hospital Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Impact: This study provides insights into how infectious
and systemic diseases, such as HIV, affect the brain by
integrating multimodal data including imaging, behavioral
assessments, and gene transcription analysis. This
comprehensive approach enables a deeper understanding of
disease pathology and mechanisms.
|
|
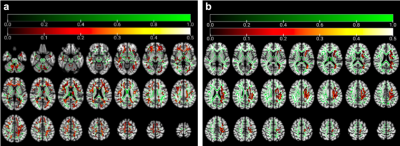 |
5087. Emotion-associated
white matter changes in thyroid eye disease: Comparative study
using diffusion kurtosis and tensor imaging
M. Jiang, H. Zhanghai, Y. Song, X. Song, X. Tao
Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study demonstrates that DKI is more
sensitive than DTI in detecting subtle white matter changes
in thyroid eye disease. Our findings highlight potential
neural mechanisms underlying emotional disturbances in this
condition.
|
|
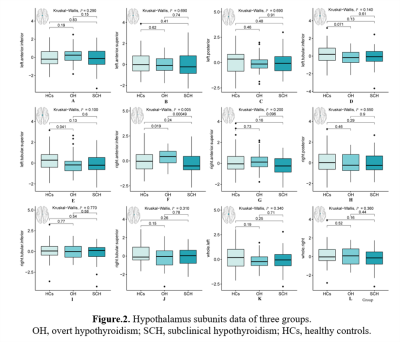 |
5088. Alterations
in hypothalamus subunits morphology and functional connectivity
in patients with adult-onset hypothyroidism
L. Wang, J. Cao, J. Tian, L. Zhao
The First Clinical Medical College of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine ( Gansu Provincial Hospital), Lanzhou, China
Impact: This work may find alterations in the
hypothalamus subunits at different phases of hypothyroidism,
which may help us better understood the mechanisms
underlying the brain damage caused by hypothyroidism.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.