Traditional Poster
RF Heavy
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

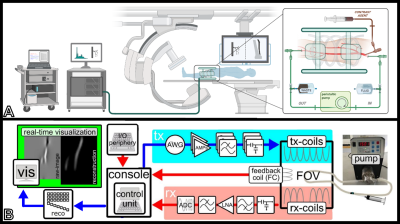 |
4988. Magnetic
Particle Imaging angiography in a human cadaveric perfusion
model
P. Vogel, M. Rückert, J. Günther, T. Reichl, T. Kampf, P.
Gruschwitz, A. M. Augustin, J-P Grunz, F. Kleefeldt, D.
Peter, S. Ergün, T. Bley, V. Behr, S. Herz, V. Hartung
University of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
Impact: MPI offers a radiation-free alternative for
real-time vascular imaging, improving patient safety,
especially in sensitive populations. With its
high-resolution, dynamic imaging capabilities the
integration into clinical settings could reduce/remove
ionizing radiation and associated risks in interventional
radiology.
|
|
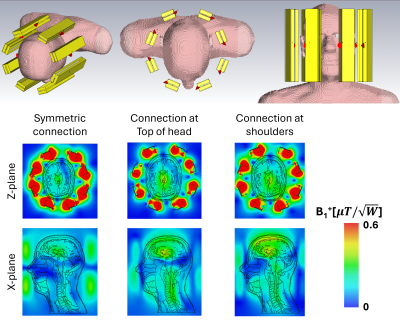 |
4989. Neither
loop nor dipole – mirrored box antenna as a candidate for
pattern reconfigurable transmit and/or receive coil for imaging
at (9.4T) UHF MRI
J. Vliem, L. Budé, I. Zivkovic
Technical University of Eindhoven, Eindhoven, Netherlands
Impact: Proposed antenna design can be used as
transcieve element alone or in time interleaved fashion for
efficient brain imaging at UHF. Obtained spatial diversity
can be employed in receive configuration for SNR enhancement
by minimizing the g-factor.
|
|
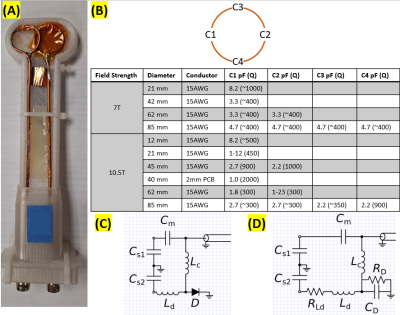 |
4990. Quality
factor measurement and enhancement techniques for ultra-high
field surface loop receiver coils
R. Lagore, A. Sadeghi-Tarakameh, M. Waks, K. Ugurbil, G.
Adriany
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: Bench measurements and simulation results of
Q-ratio and SNR fraction vs coil size shared herein provide
a useful guide to coil builders in understanding potential
sources of SNR losses and estimating those losses in
ultra-high field RF coil development.
|
|
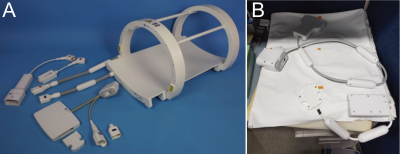 |
4991. Coil
evaluation for abdominal imaging of hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate
M. McLean, J. Birchall, I. Horvat-Menih, J. Kaggie, T. Lanz,
A. Morris, F. Robb, M. Wylot, A. Grimmer, E. Latimer, M.
Zamora-Morales, M. Graves, F. Gallagher
University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Impact: This body multi-channel array setup enables 13C
studies of diseases which may otherwise not be evaluable
with clamshell coils. For example, ovarian cancer is widely
disseminated through the abdomen and obesity is a strong
risk factor.
|
|
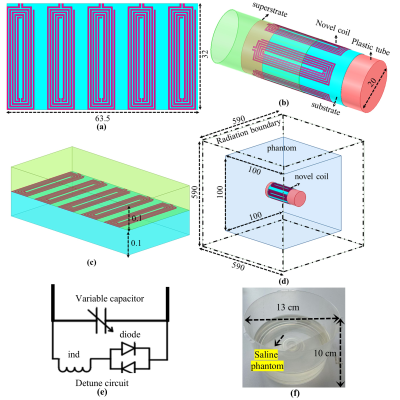 |
4992. A
Novel Self-Tuned and Self-Decoupled Wireless Prostate Array for
Enhanced Imaging Resolution and SNR at 3T MRI
S. Hayat, E. Xiao, W. Liao, Z. Mo, F. Du, N. Li, Q. Chen, X.
Zhang, Y. Li
Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China
Impact: The proposed 5-channel wireless array offers a
compact, self-decoupled, and efficient design that enhances
SNR and field uniformity for prostate imaging, improving
diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes while addressing
limitations of current coils.
|
|
 |
4993. A
Flexible Multinuclear RF Frequency Extension for a Low-Cost,
Accessible Spectrometer
C. Bauer, B. Malone, J. Ruff, J. Hou, S. Wright
Texas A&M University, College Station, United States
Impact: This spectrometer aims to advance multinuclear
magnetic resonance research by employing direct waveform
generation and sampling to simplify architecture. Its
low-cost, open-source design offers accessible tools for
researchers exploring innovative approaches in multinuclear
spectroscopy and imaging.
|
|
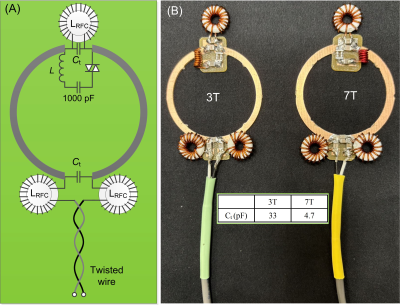 |
4994. Passive
RF and Active DC (PRAD) Coil for Enhancing Local SNR and
Correcting B0 Inhomogeneity in MRI
M. Lu, X. Chang, X. Yan
Vanderbilt University medical center, Nashville, United States
Impact: This versatile coil design provides a practical
method for improving MRI image quality without extensive
hardware modifications, potentially enhancing diagnostic
capabilities.
|
|
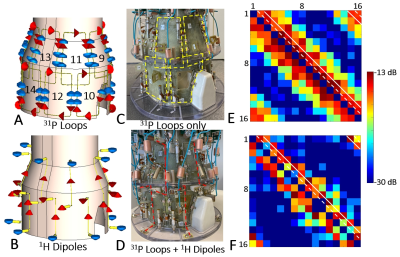 |
4995. Towards
Optimization of SNR at Both Frequencies of an UHF Double-Tuned
Array: 7T 32-Element Transceiver 31P/1H Loop/Dipole Human Head
Array.
N. Avdievich, G. Solomakha, F. Glang, T. Platt, S. Orzada,
D. Bosch, M. Ladd, A. Korzowski, K. Scheffler
Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tübingen, Germany
Impact: We demonstrated the feasibility of constructing
and decoupling of a densely-populated 32-element
double-tuned transceiver 7T human head array. First results
show reasonable transmit and receive performance at both
frequencies. The developed design can be even more
beneficial at higher fields.
|
|
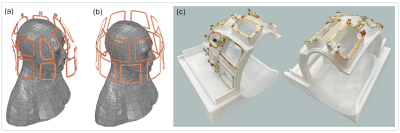 |
4996. Design
Considerations Towards Size-Adaptive pTx Arrays for 7T Brain
Imaging
A. Ghotra, S-L Hansen, Y. Aksu, M. Mahmutovic, M. Shrestha,
B. Keil
TH Mittelhessen University of Applied Sciences, Gießen, Germany
Impact: The novel 16-channel size-adaptive transceiver
array for 7T enhances transmission efficiency with
maintaining consistent SAR performance. Its four-segment
design, featuring three adjustable segments (two lateral and
one anterior), ensures precise head size customization with
superior parallel imaging and safety.
|
|
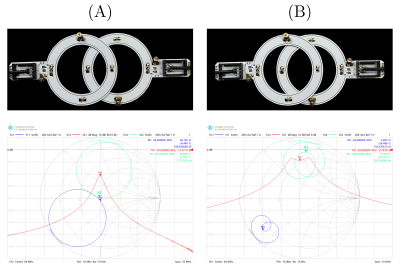 |
4997. Understanding
RF Coil Coupling in MRI Arrays: Insights from S11 and Z11
Analysis
M. Mahmutovic, M. Shrestha, S-L J. Hansen, A. Ghotra, M.
Poniatowski, B. Keil
Institute of Medical Physics and Radiation Protection, TH Mittelhessen University of Applied Sciences, Giessen, Germany
Impact: This study provides a deeper understanding of
coupling effects, offering a practical tool for diagnosing
decoupling issues in high-density array coils. These
insights could streamline coil designs, ultimately improving
MRI image quality.
|
|
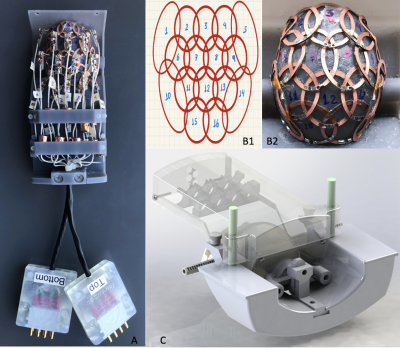 |
4998. Design
and construction of a 16-channel receive-only array for high
resolution MRI of marmosets’ brain at 9.4 T.
D. Papoti, B. Zhang, D. Szczupak, D. Schaeffer, A. Silva
University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, United States
Impact: Higher SNR anatomical images may decode new
features for the longitudinal evaluation of different stages
of Alzheimer’s disease progression.
|
|
 |
4999. A
double-layer 1H/23Na transceiver array for human brain imaging
at 7T
F. Lou, C. Duan, Z. Quan, J. Qu, C. Guo, A. Nagel, X. Lou,
X. Zhang
School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Impact: This coil design provides an integrated solution
for 23Na and clinically acceptable 1H structural imaging.
Without the necessity to change coils, it could
significantly reduce unnecessary scanning procedures and
eliminate the need for image registration.
|
|
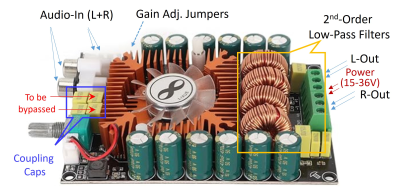 |
5000. Low-Cost,
Low-Power Gradient Amplifier for MRI Array Coils Using Modified
Audio Class-D Amplifiers and Custom Analog Feedback
M. Takrimi, M. C. Işık, F. G. Uyar, M. E. Öztürk, M.
Ghasemzadeh, E. Aydın, E. Atalar
Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey
Impact: Gradient array coils offer tunable magnetic
field profiles and adjustable ROIs but require multiple
power amplifiers. This work demonstrates an affordable
(<90$) solution using commercially available Class-D audio
amplifiers combined with tunable analog feedback system to
feed multi-channel gradient arrays.
|
|
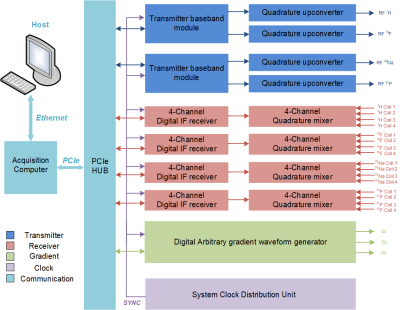 |
5001. A
Scalable Digital Distributed Console for Simulcast X-nuclei MRI
Z. Zhang, L. Chen, X. Cheng, J. Wang, Q. Bao, K. Wang, X.
Sun, F. Chen, C. Liu
State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China
Impact:
The Simulcast-X MRI study has been successfully implemented by our developed console on a 3T MRI platform. The potential of this technology lies in reducing scan time in multinuclear MRI, offering opportunities to investigate the complex interactions among different nuclei. |
|
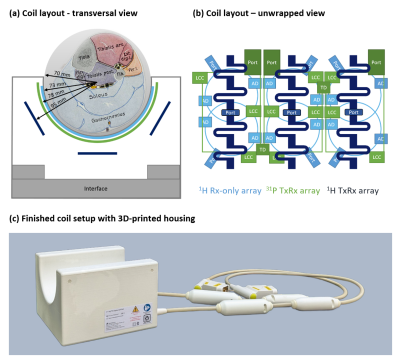 |
5002. A
9-channel 1H, 3-channel 31P RF coil for metabolic calf muscle
studies at 7 T
V. Cap, M. Meyerspeer, V. dos Santos, O. Soanca, E.
Laistler, R. Frass-Kriegl
Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Impact:
The developed coil will enable advanced metabolic calf muscle studies, as it combines excellent 1H performance with the possibility of acquiring high-quality 31P spectra. Combining dipoles and loops is a powerful approach for building high-density coil arrays at ultra-high field. |
|
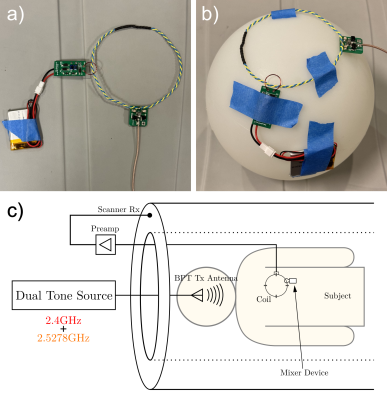 |
5003. External
RF Mixer for Platform-Independent Motion Sensing with Beat Pilot
Tone
J. Kang, S. Anand, M. Lustig
University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, United States
Impact: Our hardware augmentation removes dependence on
platform-specific nonlinearities by externalizing the BPT
intermodulation process to a well-characterized device. This
allows BPT, a novel and effective motion detection scheme,
to be widely applied across scanner platforms.
|
|
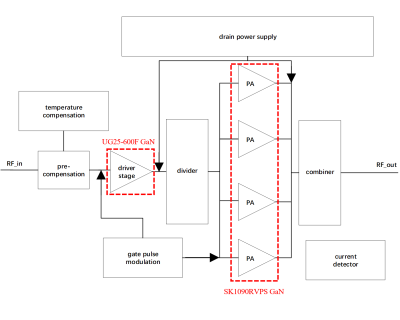 |
5004. A
multi-octave GaN HEMT radio frequency power amplifier with high
efficiency and high linearity for 5T multinuclear MRI
S. Gao, X. Yang, J. Wang, X. Rong, S. Hayat, G. Yang, P. He,
X. Zhang, H. Zheng, Y. Li
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, shenzhen, China
Impact: GaN RFPA with higher bandwidth, linearity and
efficiency can be applied to high-field multinuclear MRI
transmitting systems with different field strengths, which
brings improvements for scanning sequences with long pulse
widths and high linearity requirements.
|
|
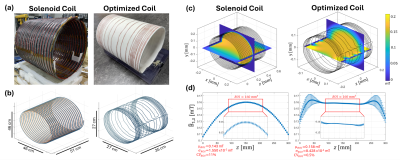 |
5005. Optimized
z-Direction RF Coil for Multiphoton Excitation with Improved
Homogeneity
H. Kempfert, V. Han, T. Ipek, C. Liu
University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, United States
Impact: Our
numerically optimized z-directed transmit coil provides
improved spatial homogeneity and field strength for
multiphoton MRI applications. This advancement supports our
future experimental requirements as we further explore the
applications of multiphoton MRI.
|
|
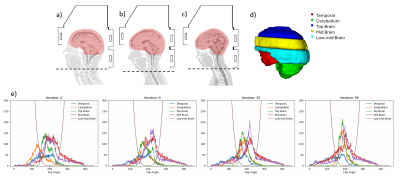 |
5006. RF
shimming methods for optimizing B1+ homogeneity and SAR
reduction for a high channel density transmit array at 7T
A. Sajewski, J. Li, T. Santini, T. Campos, L. Wang, T.
Ibrahim
University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, United States
Impact: Multi-ROI RF shimming using histogram loss is
successful at optimizing B1+ throughout
the brain. By performing B1+-restrictive
RF shimming with SAR-heavy cost functions, the
electromagnetic fields of a multichannel transmit array are
manipulated to maintain B1+ conditions
while reducing SAR.
|
|
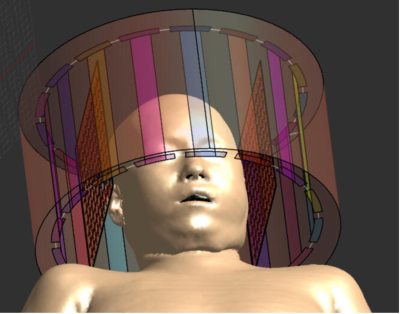 |
5007. Enhancing
B₁⁺ Field Homogeneity in 7T MRI Using Metasurfaces: Balancing
Image Quality and Safety
P. Narvekar, P. Jacobs, R. Reddy
University of Pennsylvania , Philadelphia, United States
Impact: This study's findings could lead to improved MRI
diagnostics. It opens new avenues for investigating
metasurface optimization and safety protocols, ultimately
advancing high-field MRI applications and patient outcomes
in neuroimaging.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.