ISMRT Oral
1st, 2nd, & 3rd Place Clinical Abstract Winner Presentations
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| 11:30 |
5429. |
The clinical benefit of high-resolution 3D proton density at 3T
in the discrimination between intracranial aneurysm and normal
variants
Angela Borella1,
Glenda McLean1,
and Lee-Anne Slater1
1Diagnostic Imaging, Monash Health, Melbourne, Australia At 3T, a three-dimensional proton density (3D PD) weighted sequence plays a supplementary role to the time-of-flight MR angiography (TOF MRA) to improve diagnosis and significantly decreases indeterminate findings for aneurysm. This leads to better patient care and a measurable decrease in the likelihood for the patient to undergo surveillance or more invasive tests that use ionising radiation and intravenous contrast media like Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA). The anxiety and stress that patients experience due to inconclusive findings and ongoing surveillance has been significantly alleviated since the inclusion of the 3D PD to the protocol. |
| 11:40 |
5430.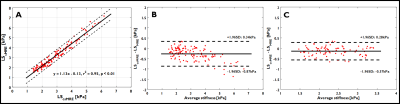 |
Comparison of compressed sensing accelerated MR elastography to
standard breath-hold gradient recalled echo MRE for estimating
liver stiffness
Scott Hipko1,
Dmitriy Akselrod2,
and Jiming Zhang3 1University of Vermont, Burlington, VT, United States, 2Radiology, University of Vermont Medical Center, Burlington, VT, United States, 3Radiology Oncology & Medical Physics, University of Vermont Medical Center, Burlington, VT, United States
The standard MRE(sMRE) uses four breath-hold, each of 14–22
s, to stage liver fibrosis. The long breath-hold time
challenges most children and adult patients with limited
breath-hold capability. The compressed sensing (CS)
technique was used to accelerate the MRE (csMRE) acquisition
to shorten the breath-hold duration (~10s). The preliminary
results showed that the LS estimated from csMRE strongly
correlated to sMRE and showed strong agreement in the normal
to mild liver fibrosis stage. However, it underestimates the
liver stiffness in the elevated liver stiffness. The
confident available area for LS estimation in csMRE
increased 38% compared to sMRE.
|
| 11:50 |
5431.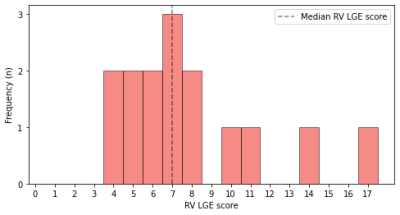 |
Prognostic role of right ventricular late gadolinium enhancement
in patients with Tetralogy of Fallot undergoing pulmonary valve
replacement
Moreno Zanardo1,
Caterina Beatrice Monti1,
Davide Capra1,
Emilia Giambersio1,
Giulia Lastella2,
Gianluca Guarnieri1,
Gaetano Amato1,
Francesco Secchi3,
and Francesco Sardanelli4
1Università degli Studi di Milano, Milan, Italy, 2ASST Nord Milano, Milan, Italy, 3Università degli Studi di Milano - IRCCS Policlinico San Donato, Milano, Italy, 4Università degli Studi di Milano - IRCCS Policlinico San Donato, Milan, Italy
Our purpose was to evaluate the correlations between right
ventricular (RV) late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) at
cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) in patients with Tetralogy
of Fallot (ToF) scheduled for pulmonary valve replacement
(PVR) and post-PVR functional data. After assessing a
semiquantitative LGE scoring for the RV, we observed a
correlation between such score and RV post-PVR outcomes
appraised at CMR. The assessment of RV LGE before PVR may
provide prognostic insights on post-PVR functional outcomes,
potentially facilitating a patient-tailored treatment
pathway.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.