Digital Poster
Vascular Imaging: Angiography
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Computer # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
1833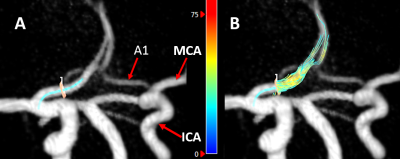 |
13 | A1-diameter asymmetry of the Circle of Willis induces blood-flow changes directed towards the anterior communicating artery
Rick J. van Tuijl1, Maud E.H. Ophelders1, Ynte M. Ruigrok2, Iris N. Vos1, Irene C. van der Schaaf1, Jaco J.M. Zwanenburg1, and Birgitta K Velthuis1
1Radiology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Neurology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
Asymmetry in diameter of the pre-communicating part (A1-segment) of both anterior cerebral arteries is common and is related to anterior communicating artery aneurysm formation. We used TOF-MRA and 4D phase-contrast 3T-MRI in 122 subjects without intracranial aneurysms, and found that blood-flow asymmetry between A1-segments increased linearly with increasing A1 diameter asymmetry. Asymmetry of >30% in A1-segment diameters resulted in statistical significant blood-flow differences compared to persons with symmetric A1-segments. Whether this >30% A1-diameter asymmetry is a good cut-off to define a risk factor for anterior communicating artery aneurysm formation requires further research.
|
||
1834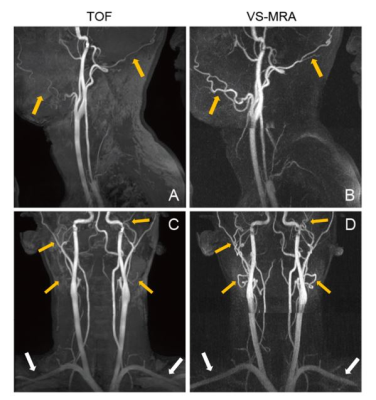 |
14 | Non-Contrast-Enhanced Whole Neck MR Angiography using Velocity Selective Saturation and Slab Selective Inversion
Chanjoo Park1, Zungho Zun2, Jaeseok Park3, Seung Hong Choi4, and Taehoon Shin1,5,6
1Division of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Radiology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea, Republic of, 4Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 5Graduate Program in Smart Factory, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 6Department of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States
Velocity-selective (VS) MRA is a promising non-contrast-enhanced angiography method allowing for high 3D spatial resolution and high angiographic contrast. This study proposes a VS-MRA protocol which includes field error compensation and slab-selective inversion for improved visualization of neck arteries. Initial in-vivo test shows that the proposed VS-MRA better depicts small vessels (such as facial and occipital arteries) and yields higher contrast enhancement ratio than clinical 3D TOF.
|
||
1835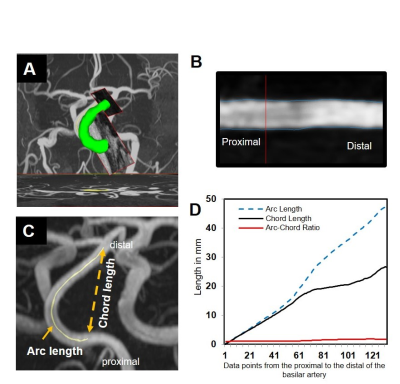 |
15 | MRI Measures of Non-atherosclerotic Brain Arterial Remodeling in a Population-based Study
Xinwei Zhou1, Melissa Caughey2, Arther Du3, Shang Zhou1, Yi-Pei Liu1, Shatorupa Ghosh2, Bruce Wasserman 1,4, and Ye Qiao1
1Radiology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States, 2Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of North Carolina & North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, United States, 3Gilman School, Baltimore, MD, United States, 4Radiology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Balitimore, MD, United States
We have reported reliable MRI measures of non-atherosclerotic brain arterial remodeling (NABAR), as assessed by outward and tortuous remodeling of the large intracranial arteries in older individuals. This will allow us to elucidate the predictors of prevalent and progressing NABAR, and its correlations with brain hypoperfusion and cognition function in an older community-based population.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.