Digital Poster
Muscle & Tissue
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Computer # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
2821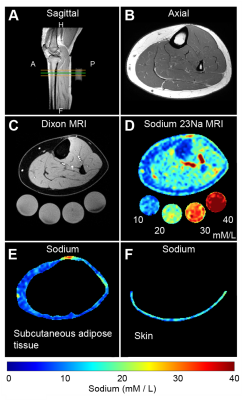 |
101 | Multi-nuclear MRI of tissue sodium provides novel measure of treatment response to physical therapy in women with lipedema
Paula Donahue1, Rachelle Crescenzi2,3,4, Kalen Petersen5, Maria Garza6, Niral J Patel7, Chelsea A Lee7, Sheau-Chiann Chen8, and Manus J Donahue6,9
1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 2Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 3Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 5Department of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO, United States, 6Department of Neurology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 7Department of Pediatrics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 8Department of Biostatistics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 9Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States The overall goal of this work is to apply multi-nuclear sodium MRI to evaluate the therapeutic effect of physical therapy in women with lipedema. Lipedema is a fat disorder affecting approximately 11% of women and since it is largely refractory to diet and exercise, objective measures of condition severity and treatment response are required. We applied sodium MRI to evaluate whether abnormal tissue sodium accumulation in the legs, a previously established lipedema biomarker, reduced following physical therapy in persons with lipedema. Results show reduction of skin and subcutaneous sodium, which corresponds with reduced pain and increased function. |
||
2822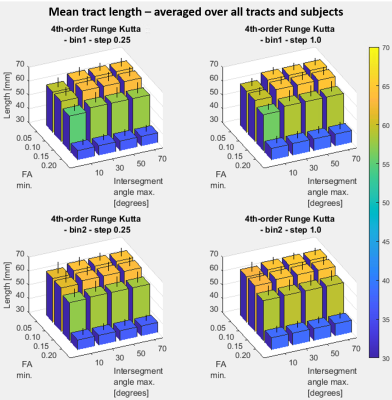 |
102 | Impact of tract propagation stop criteria on skeletal muscle DTI fiber tract completeness and characteristics
Carly Anne Lockard1,2, Melissa T Hooijmans3, Xingyu Zhou2,4, and Bruce M Damon1,2
1Stephens Family Clinical Research Institute, Carle Health, Urbana, IL, United States, 2Carle Clinical Imaging Research Program, Carle Health, Urbana, IL, United States, 3Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Amsterdam Movement Sciences, Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 4Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States
Diffusion-tensor MRI tractography has been applied to characterize skeletal muscle architecture and diffusion characteristics. Ideally, tracking would occur completely for accurate length, angle, curvature, and diffusion property estimation of a bundle of fibers. In practice, it is desirable to end tracts early if poor quality data is encountered and tract termination settings can influence the balance between tract completeness and desirable exclusion of inaccurate tract regions. This work examines the effect of applying a range of fractional-anisotropy and intersegment-angle tract-termination thresholds on muscle architecture and diffusion estimates, and fiber polynomial fit residuals.
|
||
2823 |
103 | Octopus rubescens as a model for the development and validation of muscle DTI tractography
Noel Naughton1, Luisa Ciobanu2, Shreyan Majumdar 1, Mattia Gazzola3, and Brad Sutton1
1Beckman Institute, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States, 2NeuroSpin, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 3Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States
We present data from a pilot study of an Octopus rubescens arm demonstrating it is possibly to identify the complex structural arrangement of its musculature using MRI and DTI tractography. All major muscle groups of the octopus arm are able to be identified and extracted using DTI tractography. Overall, this pilot study establishes cephalopod arms as an appealing testbed for the development of muscle MRI segmentation and tractography algorithms.
|
||
2824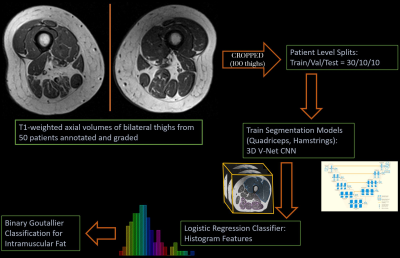 |
104 | Deep-learning based 3D segmentation of thigh muscle and classification of intramuscular fat on T1-weighted axial MRI
Upasana Upadhyay Bharadwaj1, Amir M. Pirmoazen1, Zehra Akkaya1, John A. Lynch2, Gabby B. Joseph1, Sharmila Majumdar1, Valentina Pedoia1, and Thomas M. Link1
1Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
Intramuscular fat is an important biomarker for knee osteoarthritis. Quantitative analysis on routine clinical imaging (T1-weighted MRI) is not feasible without pixel-level annotation, leading to the adoption of Goutallier classification, a semi-quantitative grading system that is time-consuming and has variable reproducibility. This study automates binarized Goutallier classification on patients (n=50) from the Osteoarthritis Initiative cohort with a two-staged process: deep-learning 3D segmentation of quadriceps and hamstrings (dice scores of 0.89[0.88,0.90] and 0.84[0.83,0.87], respectively) followed by histogram features for classification of intramuscular fat (0.93[0.92,0.95] AUROC). With model-reader kappa (0.64[0.61,0.68]) comparable to inter-reader kappa (0.61[0.59,0.64]), our approach shows promise for end-to-end automation.
|
||
2825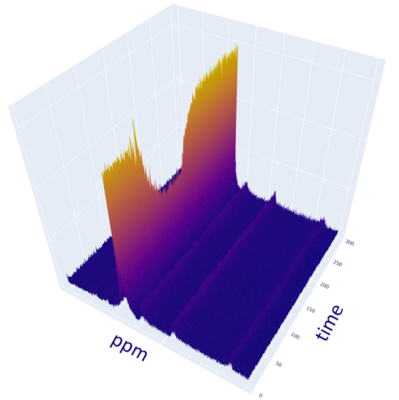 |
105 | Assessing Skeletal Muscle Metabolism with PCr, NAD+NADH, and pH measurement with Dynamic 31P MRS at 7T
Sai Krishna Merugumala1, Huijun Liao1, Wufan Zhao1, and Alexander P Lin1
1Department of Radiology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
A supine leg extension ergometer targeting the quadriceps femoris was built to be MR compatible and dynamic 31P-MR spectroscopy was acquired during an exercise challenge in a 7 Tesla MRI system. With the higher field strength, PCr and PCr recovery could be measured with a high confidence of fit without the need for additional smoothing and filtering steps. The increased spectral dispersion at 7T shows sufficient separation between the NAD+NADH resonance in addition to increased SNR. pH estimation in the active skeletal muscle was also performed.
|
||
2826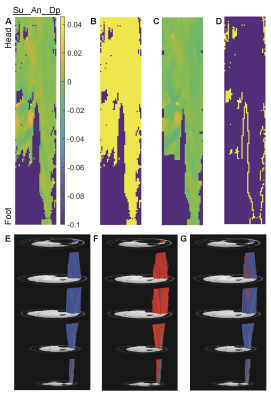 |
106 | Restoration of Missing or Erroneous Muscle Fiber Tracking Data Using Smoothed Polynomial Coefficients
Bruce Damon1,2, Melissa Hooijmans3, Carly Lockard1,2, and Xingyu Zhou2,4
1Stephens Family Clinical Research Institute, Carle Health, Urbana, IL, United States, 2Carle Clinical Imaging Research Program, Carle Health, Urbana, IL, United States, 3Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 4Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States
Diffusion-tensor tractography is used to quantify functionally relevant muscle architectural variables, including fiber tract length, orientation, and curvature. However, image noise and artifacts cause positional errors in the fiber tracking points and may cause tracts to terminate prematurely. The effect of the points’ positional errors on estimates of muscle fiber curvature can be mitigated through the use of polynomial fitting. Here we test several approaches for smoothing the spatial field of polynomial fitting coefficients and reconstructing missing or shortened-length fiber tracts. We show that median filtering of the polynomial coefficients retains additional fiber tracts without altering the median architectural properties.
|
||
| 2827 | 107 | Separation of Intra- and Extra-cellular Sodium Using A Rotation of Spiral Disc (RSD) Sequence with Multiple Echoes
Kwan-Jin Jung1, Hsin-Yu Fang2, Kenneth Wilund2, and Brad Sutton3
1Biomedical Imaging Center, Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, USA, IL, United States, 2Department of Kinesiology and Community Health, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, USA, IL, United States, 3Department of Bioengineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, USA, IL, United States An efficient sequence to acquire sodium image, i.e., rotation of the spiral disc, was developed last year. This sequence is further developed to separate the sodium signal into intra- and extra-cellular sodium by collecting multiple echoes and bi-exponential curve fitting. This method is confirmed on agarose phantom for T2* mapping and on human lower-leg muscle with an isometric plantar flexion exercise for separation of intra- and extra-cellular sodium. In the calf muscle experiment, it was found that the intracellular sodium was increased more than the extra-cellular sodium. This method finally allows studying separately the intra- and extra-cellular sodium in muscles. |
||
| 2828 | 108 | The potential value of whole-body MRI for the rheumatologist’s assessment and management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients
Varvara Choida1,2, Rachel Tattersall3,4, Jessica J Manson5, Debajit Sen1,5, Coziana Ciurtin1,5, and Margaret Hall-Craggs2,6
1Centre for Adolescent Rheumatology Versus Arthritis, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Centre for Medical Imaging, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Department of Rheumatology, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, Sheffield, United Kingdom, 4Sheffield Children's NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield, United Kingdom, 5Department of Rheumatology, University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom, 6Department of Radiology, University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
The impact of musculoskeletal inflammation detected by whole-body MRI (WBMRI) in adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) on rheumatologists’ clinical decisions was investigated. Anonymised clinical information collected for 30 patients before undergoing research WBMRI scans was examined by two rheumatologists who recorded independently their disease activity ratings, investigations, and treatment plans before and after reviewing the WBMRI reports. WBMRI findings changed rheumatologists’ disease activity ratings in half the patients and treatment plan in one-third, approximately. WBMRI detected inflammation in sites recommended for regional imaging pre WBMRI in less than half of cases and in other sites in more than one-half.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.