Digital Poster
Image Reconstruction & Signal Models: Low Rank, Sparse, Rapid & Artifact Free - II
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Computer # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
1696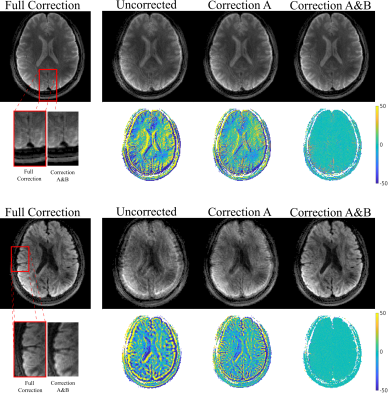 |
65 | Correcting for gradient non-linearity in concurrent field monitoring
Paul I Dubovan1,2, Kyle M Gilbert1,2, and Corey A Baron1,2
1Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Centre for Functional and Metabolic Mapping, Western University, London, ON, Canada
Concurrent field monitoring (FM) via integration of field probes in a radiofrequency coil provides advantages over sequential field monitoring that include patient-specific corrections, as well as improvements to user workflow. However, specific design considerations can require placing field probes far from isocentre where gradient fields are no longer linear, reducing data integrity when fitting high order spatially varying terms. We propose a three-part correction algorithm that seeks to correct these errors and compare FM data, as well as reconstructed images, before and after correction. Correction improved integrity of FM data and enhanced quality of anatomical and diffusion weighted images.
|
||
1697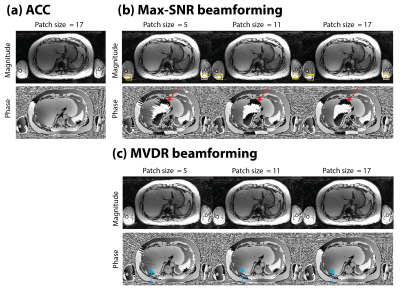 |
66 | A Beamforming-Based Coil Combination Method to Reduce Streaking Artifacts and Preserve Phase Fidelity in Radial MRI
Shu-Fu Shih1,2 and Holden H. Wu1,2
1Department of Radiological Sciences, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Department of Bioengineering, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Radial acquisition can be sensitive to hardware imperfections such as gradient non-linearity and B0 field inhomogeneity. This usually becomes accentuated in areas more distant to the isocenter and can lead to streaking artifacts even when nominally fulfilling Nyquist criteria. Previous work demonstrated beamforming-based methods for radial streaking reduction, but did not explicitly consider phase and did not evaluate the artifact-suppression performance on phase explicitly. In this work, we developed a new beamforming formulation based on minimum-variance distortionless response (MVDR) that can suppress streaking artifact while preserving accurate phase information
|
||
1698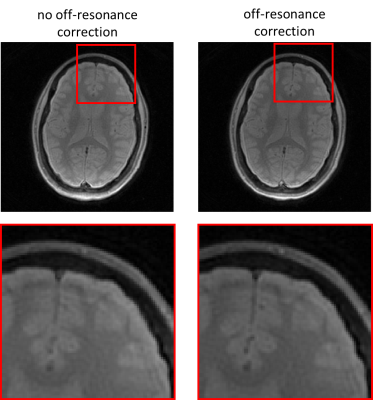 |
67 | Fast Multi-Parametric Mapping with an Extended Spiral and Off-Resonance Readout Correction
Willem van Valenberg1, Gyula Kotek1, Mika W. Vogel2, Juan A. Hernandez-Tamames1, and Dirk H. J. Poot1
1Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2GE Healthcare, Hoevelaken, Netherlands
Single-shot quantitative methods with spiral sampling can increase the readout duration to reduce undersampling artifacts in the images and their propagation to the parameter maps. However, a longer readout increases blurring due to the off-resonance field if not accounted for in the reconstruction. We propose an efficient reconstruction that 1. corrects for blurring due to the off-resonance field, and 2. reduces undersampling artifacts by constraining the signal variation in each voxel to a predetermined subspace. The reconstruction method is shown to enable accurate multi-parametric mapping of a single-shot MP-b-nSSFP acquisition with submillimeter resolution in 1.8s.
|
||
1699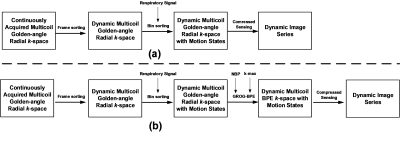 |
68 | BPE XD-GRASP: Using GROG-BPE for improved respiratory motion compensation in dynamic contrast enhanced golden-angle radial MRI
Yumna Bilal1,2, Ibtisam Aslam1,3, Muhammad Faisal Siddiqui1, and Hammad Omer1
1Medical Image Processing Research Group (MIPRG), Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, COMSATS University Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan, 2Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Gujrat, GUJRAT, Pakistan, 3Service of Radiology, Geneva University Hospitals and Faculty of Medicine, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland This work aims at incorporating the GROG facilitated Bunch Phase Encoding (BPE) in XD-GRASP reconstruction framework for improved motion compensation in free-breathing Dynamic Contrast Enhanced golden-angle radial MRI data. In the proposed method, the inherent randomness and added redundancy in the BPE data, is exploited by the Compressed Sensing (CS) algorithm resulting in images with higher quality and improved mitigation of respiratory motion artifacts as compared to the conventionally used XD-GRASP method. |
||
1700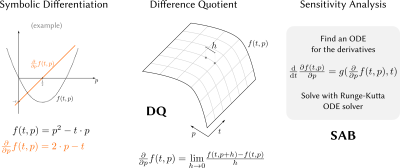 |
69 | Sensitivity Analysis of the Bloch Equations
Nick Scholand1,2,3 and Martin Uecker1,2,3
1Institute of Medical Engineering, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria, 2Department of Interventional and Diagnostic Radiology, University Medical Center Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 3German Centre for Cardiovascular Research, Göttingen, Germany
Algorithms for pulse optimization, quantitative MRI, or model-based reconstruction require knowledge about partial derivatives of the Bloch equations.While being available for specific analytical solutions, computing them becomes challenging in the general case. Difference quotient techniques can be used, but require perturbation tuning to avoid errors.
In this work, we investigate the use of direct sensitivity analysis to estimate the partial derivatives of the Bloch equations. We validate it with an analytical sequence model and compare it to the difference quotient in an example without analytical solution. In all cases, direct sensitivity analysis provided highly accurate estimates of the partial derivatives. |
||
1701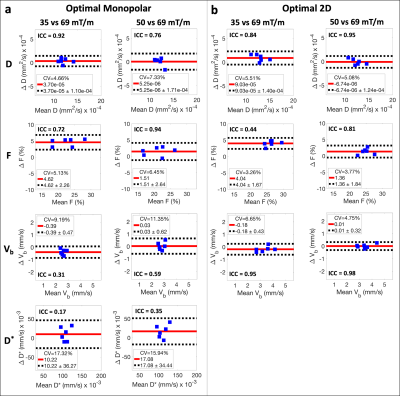 |
70 | Reproducibility of IVIM Quantification Across Diffusion Gradient Waveforms using Pseudo-Diffusion and Physical IVIM Signal Models
Gregory Simchick1,2 and Diego Hernando1,2
1Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States
The intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) DWI signal has been shown to depend on both b-value and the first motion moment (M1). However, traditional pseudo-diffusion IVIM signal models only include b-value dependence. In this work, monopolar and 2D (b-M1) IVIM acquisitions were acquired using diffusion gradient waveforms with different maximum amplitudes to emulate different gradient hardware. From each acquisition, IVIM estimates were obtained by fitting pseudo-diffusion and physical (M1 dependent) IVIM signal models. Estimated IVIM parameters were compared across acquisitions. Reproducible physical IVIM estimates were obtained using 2D IVIM-DWI acquisitions, while pseudo-diffusion IVIM estimates obtained using monopolar acquisitions demonstrated poor reproducibility.
|
||
1702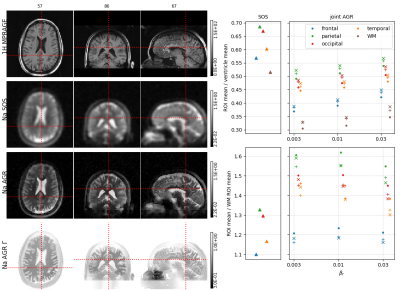 |
71 | Quantification of grey matter sodium content in joint sodium MR reconstructions using anatomical regularization and T2* estimation at 3T
Georg Schramm1, Yongxian Qian2, Johan Nuyts1, and Fernando Boada2
1KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2New York University School of Medicine, New York City, NY, United States
Sodium MR signal acquisition and image reconstruction are severely hampered by the fast relaxation properties of the sodium nuclei. Signal decay due to fast transverse relaxation during readout leads to loss of high frequency information and severe partial volume effects (e.g.signal spill over from CSF into GM). In this work, we apply a reconstruction framework including anatomical regularization and signal decay modeling and estimation to dual echo sodium data to three subjects to investigate its effect on cortical grey matter sodium quantification.
|
||
1703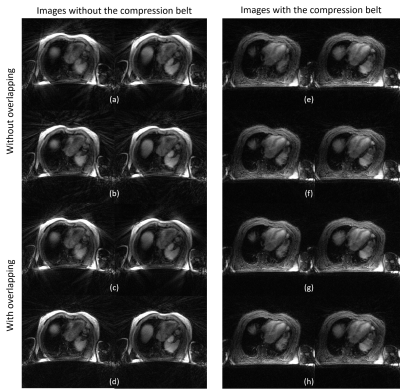 |
72 | Evaluating the impact of respiratory binning strategies on 4D-MRI reconstruction for an MR-Linac
Bastien Lecoeur1, Marco Barbone2, Sophie Alexander3, Jessica Gough3, Uwe Oelfke1, Wayne Luk2, and Andreas Wetscherek1
1Joint Department of Physics, The Institute of Cancer Research, London, United Kingdom, 2Department of Computing, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom, 3The Royal Marsden NHS Fundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
In the context of MR-guided radiotherapy, 4D-MRI is of particular interest for lung and abdominal cancer treatment, as it enables quantifying the extent of respiratory motion at the time of treatment, facilitating time-efficient midposition treatments. To reduce long reconstruction times of iterative compressed sensing-based reconstructions involving algorithms, such as XD-GRASP, we used a fast C++ implementation. We evaluated the impact of using overlapping respiratory bins and different self-gating signals on image quality and reconstruction time in multiple patients with and without abdominal compression belts.
|
||
1704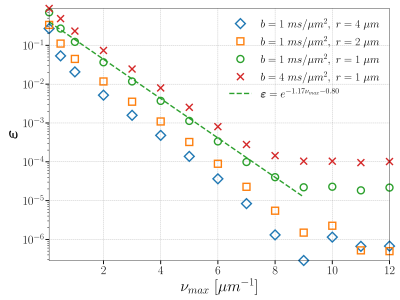 |
73 | A Fourier representation of the diffusion MRI signal
Chengran Fang1, Demian Wassermann1, and Jing-Rebecca Li1
1INRIA Saclay, PALAISEAU, France
The diffusion MRI community lacks a spectral perspective to investigate the intricate relationship between the diffusion MRI signals and cellular structures. Our study proposes a new simulation method that can provide a Fourier representation of the signal. Common spectral methods suffer from the singularity of the heat kernel, which requires infinite Fourier modes. We overcome the singularity by formulating the solution in a convolutional form and splitting the heat kernel into a singular part and a smooth part. Numerical experiments are performed to demonstrate the convergence of our method.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.