Digital Poster
Tumor Characterization & Treatment Response
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Computer # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
2894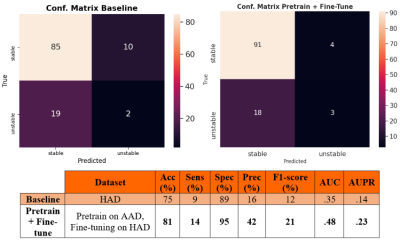 |
100 | Towards improving high-grade gliomas diagnostic surveillance on T2-weighted images using weak labels from radiology reports
Tommaso Di Noto1, Chirine Atat1, Eduardo Gamito Teiga1, Monika Hegi2, Andreas Hottinger3, Patric Hagmann1, Meritxell Bach Cuadra1, and Jonas Richiardi1
1Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Neuroscience Research Center, CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Lausanne University Hospital and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Manual annotations are a major bottleneck in supervised machine learning. We present a method that leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) to generate automatic weak labels from radiology reports. We show how weak labels can be used for the image classification task of high-grade-glioma diagnostic surveillance. We apply a convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify T2w difference maps that either indicate tumor stability or instability. Results suggest that pretraining the CNN with weak labels and fine-tuning it on manually-annotated data leads to better performance (though not statistically significant) when compared to a baseline pipeline where only manually annotated data is used.
|
||
2895 |
101 | Three IVIM-DWI models to predict survival risk in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma patients after (chemo)radiotherapy
Ya Zhang1, Dehong Luo2, Wei Guo3, Zhou Liu2, Dan Bao1, Haijun Xu1, Lin Li1, Meng Lin1, Yanfeng Zhao1, and Xinming Zhao1
1Radiology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medica, Beijing, China, 2Radiology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital & Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, China, 3Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China
To investigate the predicted survival risk power of three IVIM-DWI models in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LHSCC) patients after (chemo)radiotherapy, 45 patients were retrospectively enrolled. IVIM-DWI sequence scanning was performed using echo planner imaging (EPI) sequence with 12 b values (0, 10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 100, 150, 200, 400, 800 and 1000 s/mm2). Followed up for 2-72 months with median follow-up of 14 months. The pretreatment ADC, D, f value and D* value were significantly correlated with prognosis of local disease, and the pretreatment ADC, D* value were independent biomarkers for survival risk prediction.
|
||
2896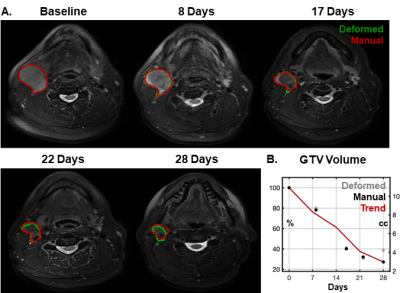 |
102 | Anatomic changes during head and neck radiotherapy observed with automated MRI tracking
Eric Aliotta1, Yu-Chi Hu1, Peng Zhang1, Phil Lichtenwalner1, Amanda Caringi1, Natasha Allgood1, Jillian Tsai2, Kaveh Zakeri2, PengPeng Zhang1, Nancy Lee2, Laura Cervino1, and Michalis Aristophanous1
1Medical Physics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiation Oncology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
Longitudinal MRI is an ideal tool for tracking anatomic changes that occur during head and neck radiotherapy. We have implemented an image tracking system that monitors volumetric changes in gross tumor volumes (GTV) and parotid glands to identify and alert of major changes early in treatment. In a cohort of 91 patients, this system identified systematic shrinkage of GTVs (9.2±8.3% per week) and parotids (3.1±3.7% per week) during treatment. Importantly, GTV changes observed in the first week of treatment were strongly predictive of larger changes that would occur later in the course (P<1x10-5, two-tailed t-test).
|
||
2897 |
103 | The value of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion in Differentiating Renal Tumors with Low Signal Intensities on T2-weighted MR image
Jinghong Liu1 and Ailian Liu1
1The first hospital of Dalian medical university, Dalian, China
Clear cell carcinoma of kidney usually presents with high signal intensity on T2WI imaging, while some clear cell carcinoma presents with low signal intensity on T2WI imaging.Other rare renal tumors, such as papillary renal cell carcinoma and lipid-deficient angiomyolipoma, are characterized by low signal intensity on T2WI. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) is a model built on the basis of DWI, reflecting the structural changes and physiological state of cells from the microscopic level. Our objectivie si to evaluate the feasibility of the IVIM in differentiating renal tumors with low signal intensities on T2WI.
|
||
2898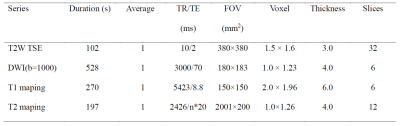 |
104 | Early response evaluation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer using T1 and T2 mapping Video Not Available
Xiaoling Gong1, Yu Shen2, Daguang Wen3, Mingtian Wei2, Xiaoxiao Zhang4, Xiaoyong Zhang4, Ziqiang Wang2, and Bing Wu3
1Departments of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Cheng du, China, 2Department of Clinical, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 3Departments of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 4Philips Healthcare, China, Chengdu, China Neoadjuvant chemotherapy can improve oncologic outcomes and overall survival rate. However, not all patients respond well during treatment, and continuous treatment will be painful, costly, and even increase risk of progression. Thus, early stratification of treatment response and screening of patients who may not be effective in treatment is very important. We investigated the value of T1 and T2 mapping MRI in response evaluation and found that T2 value showed a significant difference between groups of pre and 1-week post-treatment, while the T1 value had no statistical difference. T2 mapping may be a useful functional biomarker for early responses evaluation. |
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.