Digital Poster
Contrast Agents
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Computer # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
1439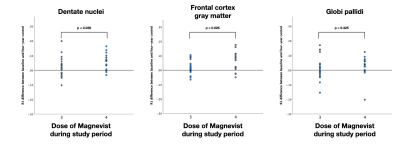 |
63 | Quantification of Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain Using Quantitative MRI
Angie Landgren Liu1, Ida Blystad1,2, and Anders Tisell2,3
1Department of Radiology, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2Center for Medical Image Science and Visualization (CMIV), Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 3Department of Medical Radiation Physics, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) used for MRI are known to cause gadolinium depositions in the brain. In this study we show that the using quantitative MRI we can detect gadolinium depositions after fewer doses of GBCAs than generally seen on conventional MRI. We included 43 patients that were earlier enrolled in a prospective longitudinal cohort study of early Multiple Sclerosis. All patients had received the linear GBCA Magnevist. Measurements of the longitudinal relaxation rate R1 showed a significant increase in dentate nuclei, globi pallidi and frontal grey matter.
|
||
1440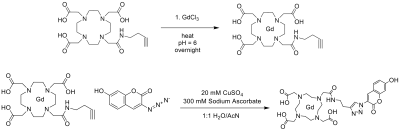 |
64 | Development of a fluorescent, MRI contrast agent (Gd-DOTA-coumarin) to improve measurement of Gd concentration
Ayesha Bharadwaj Das1, Jin Zhang1, Ching-Hsuan Tung1, James Kelly1, Youssef Zaim Wadghiri2, and Gene Kim1
1Radiology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
Measurement of gadolinium concentration in DCE-MRI is a significant step but remains challenging. In this study, we developed a novel Gd-based contrast agent Gd-DOTA-coumarin that can directly quantify gadolinium concentration through florescence measurement using a plate reader. The preliminary results shows that the longitudinal relaxivity in plasma at 7T is 8.6 mM-1s-1 and the limit of detection for the fluorescence measurement is 100 µM in blood. This new agent has also been successfully used for in vivo MRI experiments.
|
||
1441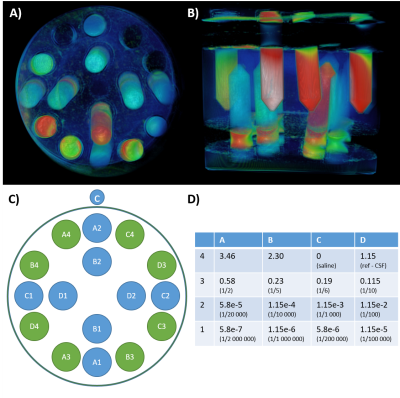 |
65 | A serial dilution study of four Gadolinium-based contrast agents for the detection of low-Gd concentration
Emilie Poirion1, Corentine Marie2, Dann Fournier1, Remy Carrion1, and Julien Savatovsky1
1Hospital Foundation A. de Rothschild, Imaging department, Paris, France, PARIS, France, 2Paris Brain Institute, Paris, France Gadolinium-enhanced imaging provides valuable information in clinical practice. Concerns raised by gadolinium depositions favors strategies reducing injected doses in patients requiring repeated scans. We designed four phantoms containing serial dilutions of four gadolinium-based contrast agents to compare their efficacy for low-Gd concentration detection in clinically used MR sequences, based on signal intensity and contrast-to-noise ratio. We performed a preliminary study comparing T1-TSE, FLAIR and FLAIR with optimized parameters on these phantoms. The optimized FLAIR sequence shows an efficient detection of low concentrations, in particular using gadobutrol or gadoteridol. |
||
1442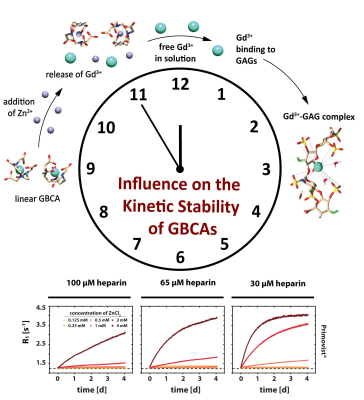 |
66 | Influence of Glycosaminoglycans on the Transmetallation and Transchelation Kinetics of Gadolinium from GBCAs in the Presence of ZnCl2 Video Permission Withheld
Patrick Werner1, Patrick Schuenke2, Matthias Taupitz3, and Leif Schröder1
1Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany, 2Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Berlin, Germany, 3Charite, Berlin, Germany
Relaxation rates in aqueous solutions containing 30-100 µM heparin as well as 150 µM GBCA were measured as a function of time. Different ZnCl2 stimuli with concentrations between 0.125-4 mM were used as competing ions that initiate a transmetallation and a transchelation process of the Gd3+ ion from GBCAs to glycosaminoglycans. The time resolved relaxometry measurements indicate that glycosaminoglycans play a concentration-dependent double role as competing chelator structures. They foster the thermodynamic instability of intact GBCA by sequestering Gd3+ from the contrast agent but simultaneously interact with competing ions and thus cause a reduced kinetic instability.
|
||
1443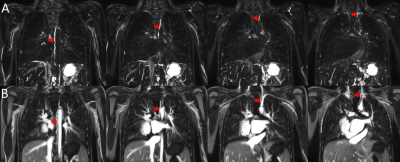 |
67 | Enhancement of the Lymphatic System Following Intravenous Administration of Ferumoxytol
Daniel F Young1,2, Surendranath Veeram Reddy1, Abhay Veeram Divekar 1, Sheena Pimpalwar1, Tarique Hussain1, and Joshua S Greer1
1Pediatrics, UT Southwestern, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Pediatrics, Children's Health Medical, Dallas, TX, United States
Lymphatic Imaging is increasingly important in the management of patients with Congenital Heart Disease. It is not known how the intravenous contrast agent ferumoxytol influences this imaging. This retrospective review of 120 patients suggests that intravenously given ferumoxytol rapidly enters the lymphatic system. The resultant shortening of T2 relaxation causes a degradation in T-2 weighted lymphangiography. Conversely, T1-weighted angiography shows clear depiction of the thoracic lymphatic duct immediately after ferumoxytol infusion. This enhancement depends on fasting status of the patient. The classic mechanism of macrophage uptake of iron oxide for MR lymphangiography does not explain the timing of these findings.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.