Online Gather.town Pitches
Multiparametric MR: Liver & Kidney Cancer
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
3760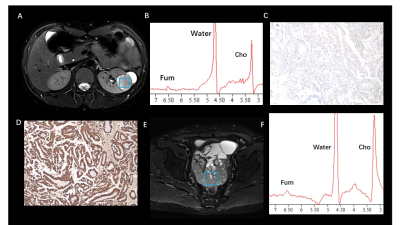 |
1 | Fumarate Metabolic Signature for Detecting Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome-associated Renal Cell Carcinoma
Guiqin Liu1, Guangyu Wu1, Yongming Dai2, and Ke Xue2
1Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2United Imaing Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Non-invasive in vivo detection of abnormal fumarate accumulation is important for identify fumarate hydratase (FH) deficiency in hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC). However, until now, no study has been reported to successfully identify fumarate accumulation in HLRCC-associated RCC. In our study, we achieved an 100% accuracy in primary HLRCC-associated RCC, as well as all of the HLRCC PDX models. For our best knowledge, it is the first time that, MRS can be successfully used to in vivo detected in FH-deficient renal lesions, which is a crucial innovation of conventional imaging diagnostic technology.
|
||
3761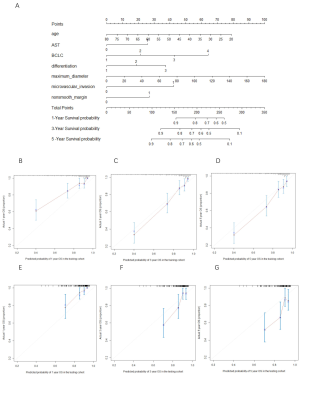 |
2 | A clinicopathological-radiological nomogram for prognosis of postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma
Lidi Ma1, Kan Deng2, Haixia Li2, Cheng Zhang1, and Chuanmiao Xie1
1Department of Radiology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Diagnosis and Therapy, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Few studies both focus on the prognosis for patients with early recurrence and five years overall survival (OS) for patients with BCLC 0-C. Here, we established nomograms for predicting 5-year overall survival and early recurrence after curative resection of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) based on clinicopathological-radiological model and investigated whether different treatment methods have influenced on OS for patients with early recurrence. The results demonstrate that the nomogram, based on clinical, pathological and radiological factors, had good accuracy in estimating OS and recurrence respectively. Further, reoperation maybe the best option for patients with recurrence in good condition.
|
||
3762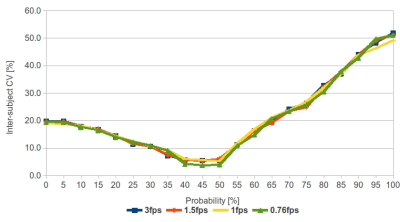 |
3 | Reliability of the volumetric positional probability distribution of liver tumor using volumetric 4D-MRI: effect of temporal resolution Video Permission Withheld
Oi Lei Wong1, Jing Yuan1, Darren Ming Chun Poon2, Yi Hang Zhou1, Siu Ki Yu3, and Kin Yin Cheung3
1Research Department, Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2Comprehensive Oncology Center, Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 3Medical Physics Department, Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
This study aims to evaluate the impact of temporal resolution on the positional probability distribution. Based on our results, PPV was independent of the fps setting and was most reliable at the probability of occurrence >35 - 50%. Thus, PPV is potentially useful to minimize the registration error during daily positional verification.
|
||
3763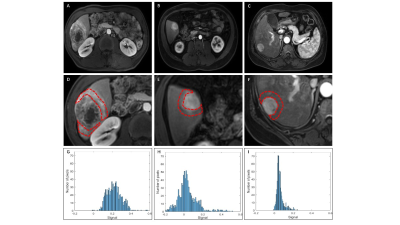 |
4 | Histogram Peritumoral Enhanced Features on 3.0T MRI Arterial Phase Can Predict the Microvascular Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Xinxin Wang1, Yunfeng Sun1, Xueyan Zhou2, Hongxia Zhang1, Jianxiu Lian3, and Yang Zhou1
1Department of Radiology, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin, China, 2Harbin University, Harbin, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Preoperative microvascular invasion (MVI) prediction plays an important role in therapeutic decision-making of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We aimed to investigate the value of histogram based on the arterial phase (AP) of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with extracellular contrast agent compared with radiological features for predicting MVI of solitary HCC. Results showed that peritumoral AP enhanced degree on MRI showed an encouraging predictive performance for preoperative prediction of MVI, especially in sHCCs (AUC=0.798, sensitivity =54.84%, specificity =100% ). Corona enhancement thickness≤8 mm may be used as a predictive marker for MVI when compared with the group with thickness>8 mm.
|
||
3764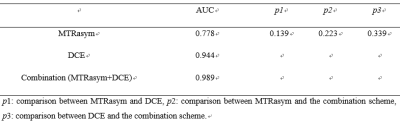 |
5 | Differentiation of Primary and Secondary Liver Cancer with Amide Proton Transfer-weighted imaging and Dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging Video Not Available
Xue Ren1, Jiazheng Wang2, Peng Sun2, Lihua Chen1, Qingwei Song1, Renwang Pu1, Ying Zhao1, Tao Lin1, Qihao Xu1, and Ailian Liu1
1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Liver cancer has become one of the most frequent fatal malignancies around the world. And the early precise diagnosis of different types of liver cancer is very critical for treatment strategy design. This retrospective study evaluated the diagnostic efficacy of amide proton transfer weighted (APTw) and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) imaging for the differentiation between primary and secondary liver cancer. Results showed that a combination of APTw and DCE significantly improved the diagnosis of liver cancer.
|
||
3765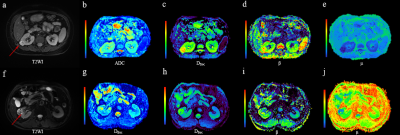 |
6 | To characterize clear cell renal cell carcinoma using diffusion weighted imaging with a fractional order calculus model Video Not Available
Bowen Shi1, Ke Xue2, Yili Yin1, Qing Xu1, Binbin Shi1, Dongmei Wu3, Yongming Dai4, and Jing Ye1
1Department of Medical Imaging, Clinic Medical School, Yangzhou University, Northern Jiangsu Province Hospital, Yangzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Central Research Institute, Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co.,Ltd, Shanghai, China, 3Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, School of Physics and Electronics Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 4MR Collaboration, Central Research Institute, Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Accurately characterizing ccRCC grades with a non-invasive method would be vital for guiding treatment and prognosis. This study evaluated and compared the performance of conventional ADC and the FROC parameters, Dfroc, β, μ, in differentiation of low- and high-grade ccRCC. All the FROC parameters showed better diagnostic performance than ADC in characterizing ccRCC grades, among which β yielded the highest AUC value. This implied the clinical potential of the FROC model in evaluating renal tumor aggressiveness and the dominant role of β in probing tumor heterogeneity and microstructural complexity.
|
||
3766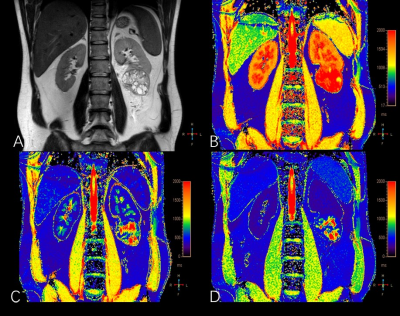 |
7 | Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced T1 Mapping: Repeatability, Reproducibility, and Differentiating Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma from Non-ccRCC
Shuai Wang1, Binghui Zhao1, Jilei Zhang2, and Weibo Chen2
1Radiology, Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China T1 mapping is a quantitative MR technique that can be used to measure the longitudinal relaxation time of tissues. Previous studies demonstrated that it is potentially able to differentiate benign and malignant tumors and identify histopathological grade. In this study, the dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) T1 mapping exhibited the robust reproducibility and repeatability and thus may have potential be used for quantitative renal tumor evaluation in cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Furthermore, we found that clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) had higher native and enhanced T1values than non-ccRCC. Thus, DCE T1 mapping is promising in differentiating ccRCC from non-ccRCC. |
||
3767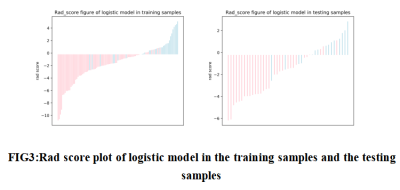 |
8 | Prediction of Lymphatic Vessel Space Invasion of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Enhanced MRI Radiomics Method
Haixia Yu1 and Jianping Ding1
1Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China
Cervical Cancer Lymph-vascular space invasion (LVSI) is a type of cancer cells that invade into lymphatics and blood vessels.The typical symptoms are closely related to the distant metastasis of cervical cancer.The selection of treatment strategies for early cervical cancer is particularly important.This study established and verified the radiomics based on enhanced MRI to predict the preoperative LVSI status of cervical squamous cell carcinoma, which can be used as a noninvasive biomarker to better predict the LVSI status of patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
|
||
3768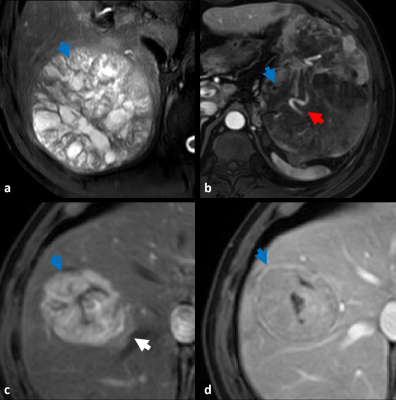 |
9 | A MRI-based model using Graph Convolutional Network combine Nomogram to predict Microvascular invasion diagnosis
Yang Zhou1, Ziqian Zhang1, Wenjuan Zhao1, Xinxin Wang1, Kun Wang2, Kuan Luan2, Jianxiu Lian3, and Mengchao Shi3
1Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin 150010, Harbin, China, 2Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, Harbin, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Accurate preoperative assessment of microvascular invasion (MVI) can help clinicians choose more reasonable treatment options, reduce the recurrence of HCC patients after surgical treatment, and improve the survival rate of patients. In this study, Graph convolutional network (GCN) was used to build a preoperative diagnostic model for MVI for mining the correlation between radiomic features. The results revealed that the value of the predicted MVI nomogram established was 0.884 in the validation when the radiographic characteristics of the patients were combined with graph convolutional network Score(GS).
|
||
3769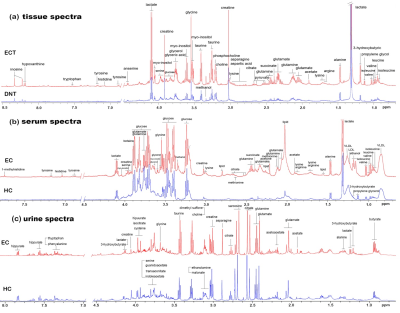 |
10 | Investigating the visual predicting model of metabolic biomarkers in biofluids for esophageal cancer detection using NMR-based metabolomics
Yan Lin1, Ting Ouyang1, Huanian Zhang1, Rongzhi Cai1, Peie Zheng1, Zhijie Fu1, Han Zhou1, and Renhua Wu1
1Radiology Department, Second Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou City, China
Constructing an optimal metabolic model by combining biomarkers in biofluids may improve its non-invasive screening efficiency for esophageal cancer (EC). In this study, urine and serum specimens representing the healthy and EC individuals were examined using high-resolution 600 MHz 1H NMR technique. Furthermore, the paralleled patient-matched metabolites of EC tumor tissues and their adjacent non-cancerous tissues were investigated, which was used as references to determine biofluids metabolic biomarkers. The visual nomogram prediction model through a combination of creatine and glycine in both serum and urine was constructed using multiple regression analysis, which improves the diagnostic efficiency for EC.
|
||
3770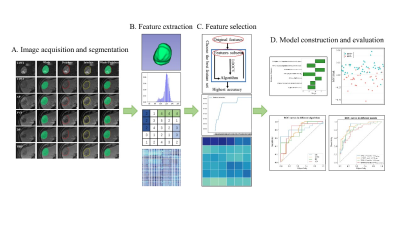 |
11 | Preoperatively Predict Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma - via Multi-region Radiomic Analysis in Multi-sequence MRI
Zewen Han1, Xiaojie Chen2, Lanmei Gao2, and Yueming Li2
1The School of Medical Technology and Engineering, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China, 2Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Microvascular invasion (MVI) affects postoperative prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. Radiomics has shown great potential in providing valuable information for tumor pathophysiology. We aim to use multi-sequence MRI radiomics focused on not only intratumoral and peritumoral areas, but also the HCC-liver interface to predictive MVI status preoperatively. The radiomics and clinico-radiological indicator-based fusion model can well predict MVI status in HCC patients.
|
||
3771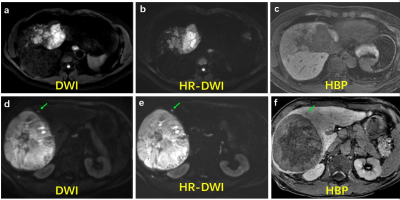 |
12 | High-resolution DWI for liver lesion detection in patient at-risk for HCC: prospective comparison with the HBP using gadoxetic acid
Zhen Zhang1, Hanyu Jiang1, Ting Duan1, Bin Song1, and Xiaoyong Zhang2
1Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Chengdu, China, 2Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Cheng du, China
Compared with conventional diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), high-resolution DWI (HR-DWI) can improve the image quality with higher image scores. In patients with increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma, gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI with HR-DWI showed comparable performance with conventional DWI + hepatobiliary phase for detecting potentially malignant liver lesions.
|
||
3772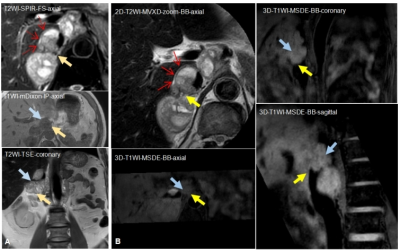 |
13 | Plain magnetic resonance imaging by black blood sequences to assess vascular invasion of complex retroperitoneal occupying
Ying Cui1, Yufei Zhao1, and Xingui Peng1
1Southeast University, Nanjing, China
This study aimed to investigate the value of plain conventional and black-blood magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for assessing the invasion of large and important vessels in patients with complex retroperitoneal tumors. The great advantages of vascular wall imaging are non-invasive and non-enhanced, as well as three-dementional, which provides a better presence and evaluation of wall structure, tumor contact of the vessel circumference, narrowing, and deformity. The researchers in the field of vascular imaging should be interested in this topic.
|
||
3773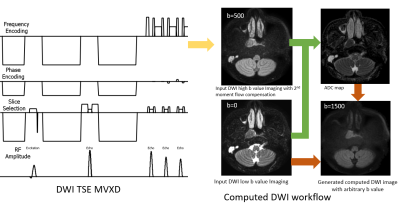 |
14 | Comparison of Computed DWI with actual scanned DWI for nasopharyngeal carcinoma detection using DWI TSE MVXD
Zhigang Wu1, Rui Chen2, Zaiyi Liu2, Fei Zeng1, Guangyi Wang2, and Huifeng Ye2
1Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 2Department of Radiology, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, China
Diffusion MRI provides unique information on the structure, organization, and integrity of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) non-invasively. Higher b-values diffusion-weighted imaging could improve the detection rate of malignancies. We use the combination of DWI TSE Multivane XD and computed DWI to generate the high b values diffusion for nasopharyngeal whithout distortion, with higher SNR and less scan time. A in vivo comparison between actual scanned DWI and cDWI study was also studied on both volunteer and patients with NPC. The image quality is comparable. It shows cDWI is a promising technique for the NPC diagnosis.
|
||
3774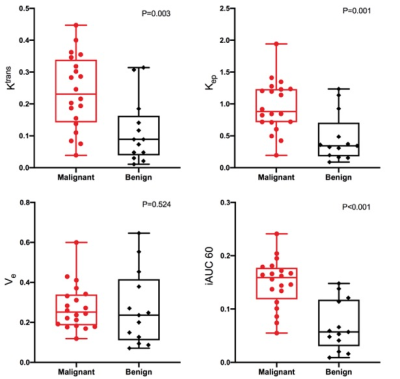 |
15 | Value of Qualitative and Quantitative DCE-MRI Analysis based on GRASP Acquisition in Diagnosing of breast lesions
Xin-zhu Zhou1, Hua Lai1, Lian-hua Liu1, Shuang He1, Hui-fang Yao1, Li-ping Chen1, Chen Deng1, Ya Yang1, Qiang Lei1, and Yun-zhu Wu2
1Department of Radiology, Chengdu Women's and Children's Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China
This study investigated the diagnostic capabilities of qualitative and quantitative parameters derived from high-resolution DCE-MRI with GRASP sequence. 31 patients (33 lesions, 13 benign and 20 malignant lesions) were prospectively included. The results showed that there were prominent discrepancies of quantitative and quantitative parameters between malignant and benign breast lesions. Ktrans, Kep, and iAUC(60) had excellent diagnostic efficiency for breast cancer.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.