Online Gather.town Pitches
Advanced MRI Techniques for Clinical Body Applications
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
3141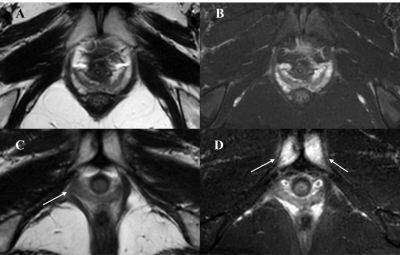 |
1 | The relationship between pubic bone and pubococcygeus muscle injury in transvaginal delivery primiparas using MRI Video Permission Withheld
Cheng Zhang1, Yujiao Zhao1, Cong You1, Zhiwei Shen2, and Wen Shen1
1Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China, 2Philips healthcare, Beijing, China As transvaginal delivery may led to bony and soft birth canal injury, this study aimed to explore the possible relationship between the pelvic bones injury and the pelvic floor support muscles injury. In this study, we found that the pubic injury with significant clinical symptom may suggest the occurrence of pubococcygeus muscle injury with hidden symptoms. With the increased severity of the pubic bone injury, the higher the rate and severity of pubococcygeus muscle injury could be detected, which could be used to guide the clinical evaluation of abnormalities and corresponding rehabilitation treatment in time. |
||
3142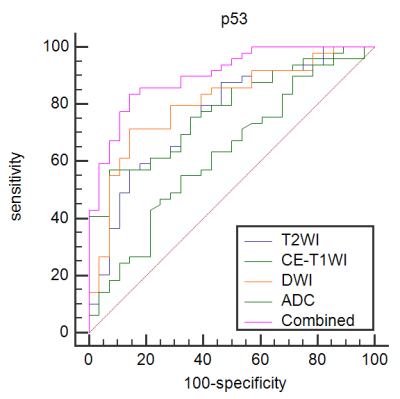 |
2 | The value of Combining ADC value with Texture Analysis to Preoperatively Predict the Expression Levels of Ki-67 and p53 of Endometrial Carcinoma
xueyan jiang1
1Anhui Provincial Cancer Hospital, Hefei, Anhui, hefei, China
In conclusion, a combination of ADC values and TA based on three MRI sequences was developed to provide a noninvasive method for preoperatively predicting the expression levels of Ki-67 and p53 in EC. To some extent, this noninvasive imaging marker can compensate for the limitation of endometrium curettage biopsy and adverse impact of tumor heterogeneity, and it provide an objective imaging basis for clinical and accurate individualized treatment.
|
||
3143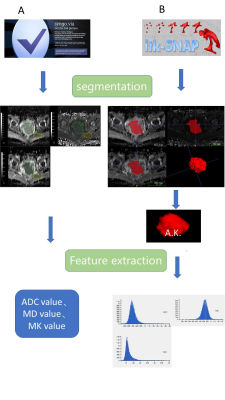 |
3 | Evaluation of Endostar and chemoradiotherapy combination efficacy on cervical cancer bydiffusion kurtosis imaging histogram analysis Video Not Available
Lanhui Qin1, Jin-ting Que1, Xin-shu Li1, Wei-hui Xu1, Sheng-lian Wen1, Huiting Zhang2, Fang Wu1, and Jin-yuan Liao1
1First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Nanning, China
This study explored the feasibility of whole tumor diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) histogram analysis (HA) to assess concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) combined with Endostar for locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC) before and during treatment. In terms of predicting efficacy, DKI whole tumor HA showed higher sensitivity and specificity, and higher the area under the ROC curve in the CCRT plus Endostar than in the CCRT group. During the treatment of LACC using Endostar, compared with the mean value of ADC, MD, MK and tumor diameter, DKI whole tumor HA showed excellent potential in monitoring treatment response and predicting early efficacy.
|
||
3144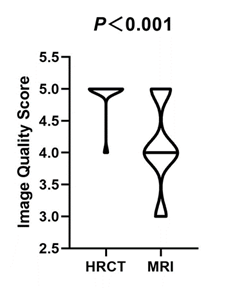 |
4 | Comparison of Ultrashort Echo Time MRI with High-Resolution CT for the Assessment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Xiaoyan Yang1, Min Liu1, Jing An2, Thomas Benkert3, Huaping Dai1, and Chen Wang1
1China-Japan friendship hospital, Beijing, China, 2Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd., Shenzhen, China, 3Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
This study investigated the feasibility of ultrashort echo time (UTE)-MRI to evaluate the radiologic findings of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, using high resolution CT (HRCT) as the reference standard. UTE-MRI is inferior to HRCT in identifying the details of lung parenchyma. The results suggest that UTE-MRI is equivalent to HRCT. In addition, inter-method agreement between UTE-MRI and HRCT were equal to inter- and intra-observer agreement for UTE-MRI for evaluating disease findings. Moreover, performance analyses demonstrated that UTE-MRI efficacy for detecting radiologic findings of pulmonary fibrosis, such as reticulation, traction bronchiectasis, and honeycombing were similar to that of HRCT.
|
||
3145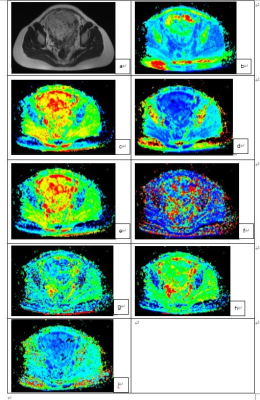 |
5 | Monoexponential, bi-exponential, and diffusion kurtosis MR imaging models in the diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum disorders
Tao Lu1, Yishuang Wang1, and Shaoyu Wang2
1Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, shanghai, China
This study investigated the diagnostic value of monoexponential, biexponential, and diffusion kurtosis MR imaging (MRI) in differentiating placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) disorders. The results showed that D mean and D max differed significantly among all the studied parameters for differentiating PAS disorders. A combined use of these two parameters yielded an AUC of 0.93 with sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 83.08%, 88.89%, and 83.70%, respectively. This suggested the quantitative evaluation of PAS disorders with different DWI models and PAS disorders can be differentiated effectively with the combined use of the different DWI parameters.
|
||
3146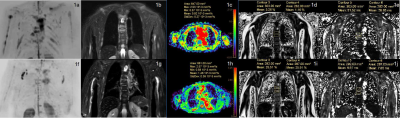 |
6 | Monitoring the response to induction therapy of multiple myeloma by diffusion weighted and mDIXON Quant whole body imaging
Mengtian Sun1, Jingliang Cheng1, Cuiping Ren1, Jie Ma2, and Liangjie Lin3
1MRI, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
This study aims to investigate the value of whole-body DWIBS and mDIXON Quant imaging in monitoring the response to induction therapy of multiple myeloma focal lesions (FLs). Significant differences in the number of multiple myeloma focal lesions (FLs), the maximum diameter of FLs, ADC, FF, T2* values, ADC change rate, FF change rate and T2* change rate were observed between the deep remission group and the non-deep remission group. The FF change rate was the best discriminator of the deep remission.
|
||
3147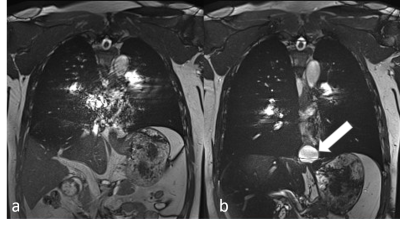 |
7 | Real-time MRI for assessment of patients with esophageal hiatal hernia: a feasibility research
Chao Wu1, Peng Zhang1, Chen Zhang2, Yajun Li1, and Haoran Sun1
1Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China, 2Siemens Healthcare, Beijing, China
The purpose of this study was to observe the swallowing process of hiatal hernia patients using real-time magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and to evaluate the transport of contrast agents through the gastroesophageal junction and the induction of sliding hernia during Valsalva. Results showed that hiatal hernia was detected in all patients enrolled in the study. Therefore, real-time MRI imaging of sliding hiatal hernia has great potential for clinical application.
|
||
3148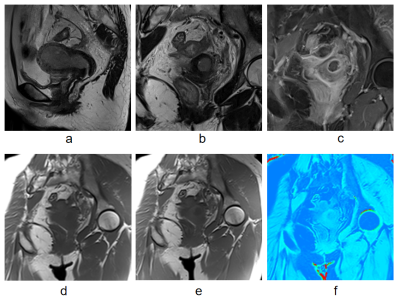 |
8 | Preliminary Application of Magnetization Transfer Imaging in EndometrialCarcinoma and Cervical Cancer Video Permission Withheld
Qiu Bi1, Qing Li1, Yunzhu Wu2, Shaoyu Wang2, and Kunhua Wu1
1the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming, China, 2Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China
Magnetization transfer imaging (MTI) is sensitive to reveal macromolecules in tumor tissues. This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) and histological features and risk stratification in endometrial carcinoma and cervical cancer. We found that MTR value could differentiate endometrial carcinoma from cervical cancer and facilitate preoperative risk stratification of endometrial carcinoma. It could provide a preoperative basis for cancerous histologic origin and risk assessment in uterus.
|
||
3149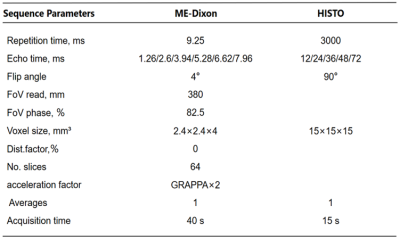 |
9 | Assessment of lumbra osteoporosis using MRI fat content quantitative technology:comparison with QCT
Chumin Huang1, Zisan Zeng1, and Huiting Zhang2
1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthnieers, Hubei, China
The purpose of this study is to explore the feasibility of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 3D multi-echo-Dixon (ME-Dixon) and T2-corrected multi-echo single-voxel (HISTO) spectroscopy sequences to evaluate osteoporosis by comparison with quantitative computed tomography (QCT). The results show that the proton density fat fraction (PDFF) values of bone marrow measured by these two MRI methods have high and significantly negative correlation with bone mineral density (BMD) values measured by QCT at lumbar.
|
||
3150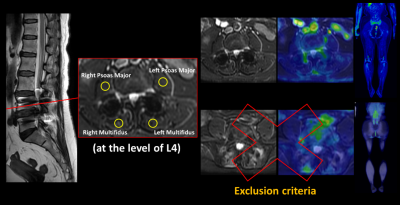 |
10 | The Effect of Implant for Lumbar Assessment in Simultaneous TOF PET/MR: A Preliminary Report
Wei-Min Hung1, Ching-Wei Gu1, Guo-Shu Huang1, Charng-Chyi Shieh2, Chia-Wei Li2, Yen-Chang Chen2, and Yi-Chih Hsu1
1Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan, 2GE Healthcare, Taipei, Taiwan
This study focused on the accuracy of standardized uptake value (SUV) reconstructed using the corrected MR attenuation correction (MRAC) images with time-of-flight (TOF) information by PET in patients with metallic implants. We compared the SUV of both paraspinal and psoas muscles in patients with and without implant for TOF reconstructed PET images. In the result, there was no significance in the SUV measurements obtained from MRAC between no-implant and with-implant patients. And therefore, our study demonstrated that SUVs measured from TOF PET/MR of lumbar implant indicated good reliability and robust of MRAC.
|
||
3151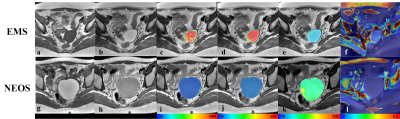 |
11 | Multi-Parametric MRI in Diagnosing Ovarian Endometrioma: a Feasibility Study
Fang Wang1, Dawei Ding2, Weiqiang Dou3, Dmytro Pylypenko3, Qing Wang1, and Dexin Yu1
1Department of Radiology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2Department of Radiology, Qilu Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
This study aims to investigate the feasibility of multi-parametric MRI in distinguishing endometrioma from other ovarian cystic lesions. A total of 50 patients with clinically suspected endometriosis were recruited in the study. Quantitative MRI, including T1, T2 mapping, T2* mapping and CEST, was used. A positive correlation was found between R2* and iron levels in fluid of endometrioma. The AUC of R2*, T1, T2 and MTR_asym were 0.941, 0.996, 0.980 and 0.806, respectively. Therefore, multi-parametric quantitative MRI can be considered an effective method in differentiating endometriomas from various ovarian cystic lesions.
|
||
3152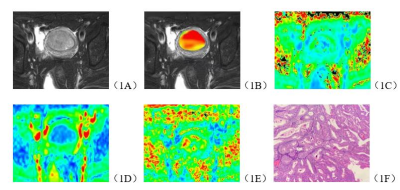 |
12 | Amide proton transfer and diffusion kurtosis imaging technology in differentiation stage Ia endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp Video Not Available
Shifeng Tian1, Ailian Liu1,2, Changjun Ma1, Lihua Chen1, Nan Wang1, Liangjie Lin3, Jiazheng Wang3, and Zhigang Wu3
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Dalian Medical Imaging artificial intelligence engineering technology research center, Dalian, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Endometrial polyps (EP) is a common disease of uterine body, with a prevalence rate of about 8~25% in female population. Its clinical symptoms can be like those of endometrial carcinoma (EC), with vaginal bleeding, but there are obvious differences in prognosis and treatment between them. The purpose of this study is to investigate the value of differential diagnosis for staging Ia EC and EP by using amide proton transfer (APT) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI). It shows that APT and DKI can be used to distinguish between stage Ia EC and EP. effectively and quantitatively
|
||
3153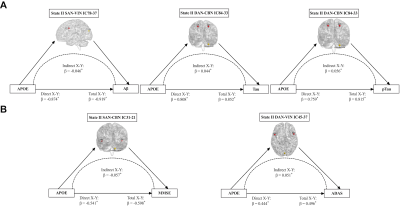 |
13 | Dynamic functional network connectivity and its association with lipid metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease Video Permission Withheld
Feifei Zang1, Xinyi Liu1, Dandan Fan1, Cancan He1, Zhijun Zhang2, and Chunming Xie2
1Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2Southeast University Affiliated ZhongDa Hospital, Nanjing, China
Brain networks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) represent the fluctuating functional connectivity with time. Using the sliding-window method, this study identified two different functional connectivity states at the large-scale network level in AD spectrum. The AD patients took more time in the tense-connected state II than the non-AD populations. Moreover, lipid metabolism-related factors affected the dynamic network connectivity across the AD spectrum populations. These results provide insights into the neural biological underpinnings of the dynamic networks reorganization for AD pathophysiology.
|
||
3154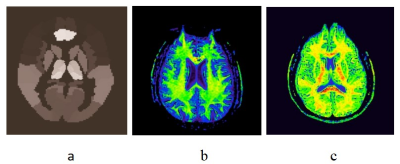 |
14 | The value of DKI technique in the study of brain Microstructural damage and Cognitive function in patients with OSAHS
Ning Zhang1, Kun Peng2, Ailian Xiao2, and Jinxia Guo3
1Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, 2The Sixth Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) can lead to cognitive dysfunction, and in severe cases, it may develop into dementia. Early, timely and accurate diagnosis is of great significance to delay the progression of the disease, improve the quality of life and improve the prognosis. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) based on non-Gaussian model to characterize the diffusion of water is regarded as a more sensitive technology to explore the microstructural tissue changes in compare with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). In this study, the mean kurtosis (MK) from DKI is used to assess the possible abnormality of brain regions in white and gray matter in moderate and severe OSAHS patients. And the correlation between MK values and cognitive function changes was also analyzed. The MK was found to be associated with changes in 9 brain regions including right postcentral gyrus gray matter, parietal lobe gray matter, insular gray matter, left precentral gyrus white matter, frontal lobe white matter and bilateral cingulate gyrus, left occipital lobe gray matter, and well correlated with attention, delayed recall, which can be helpful for understanding of the potential mechanism for neurocognitive function impairment and doing the evaluation.
|
||
3155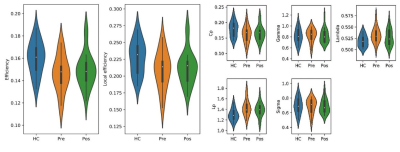 |
15 | Structural connectivity abnormality in trigeminal neuralgia with pain relief using graph theory analysis Video Permission Withheld
shanshan Shen1, shuqian Zhang1, yingmin Chen1, and Lizhi Xie2
1Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang, China, 2GE Healthcare, Shijiazhuang, China
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) characterized by recurring paroxysmal pain, severely affects the quality of life (QoL) of patients. In this study, we compared brain network frame remodeling in TN patients before and after percutaneous micro-balloon compression (PMC) operation with healthy controls (HCs) using graph theory analysis. Both TN pre-treatment patients (Pre) and HCs exhibited small-world network organization. Pre TN patients had abnormal global network construction, Pos recovered, but in local network index increased. Graph theory analysis could be a useful method to detect instant change after operation.
|
||
3156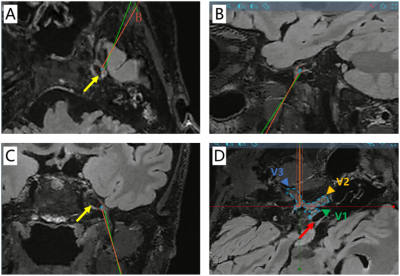 |
16 | Highly accelerated sub-millimeter 3D T2 FLAIR based on deep learning and its application in robot-assist PBC for trigeminal neuralgia Video Permission Withheld
Qiangqiang Liu1,2, Shuheng Zhang3, Jiwen Xu1,4, Jiachen Zhu3, Yiwen Shen5, Changquan Wang2, Wenzhe Chen2, Jun Yang3, and Jianmin Yuan6
1Department of Neurosurgery, Clinical Neuroscience Center, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2Clinical Neuroscience Center, Ruijin Hospital Luwan Branch, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, Shanghai, China, 3United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4Clinical Neuroscience Center, Ruijin Hospital Luwan Branch, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, 5Department of Radiology, Ruijin Hospital Luwan Branch, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, 6Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
With 3D T2 FLAIR imaging, trigeminal nerve is clearly demonstrated with CSF nulled, while low SNR and low spatial resolution is always the limitation. In this study, we introduced a 0.75mm isotropic resolution whole brain 3D T2 FLAIR imaging in 5min 40sec based on a novel deep learning framework, and evaluated on a small patient cohort who underwent MR-guided robot-assist percutaneous balloon compression (PBC). To our knowledge, this is the first clinical report of MR-guided robot-assist PBC surgery based on DL accelerated 3D scan.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.