Oral Session
Low-Field MRI: System Development
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| 09:15 | 0060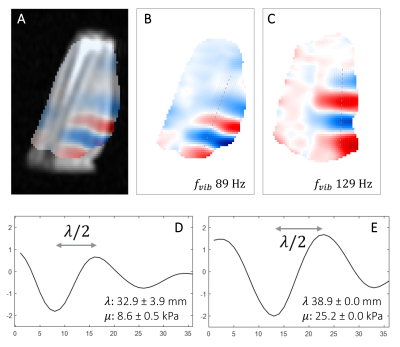 |
Fast 3D acquisition of wave displacement in vivo for low-field MRE: application in the human forearm
Maksym Yushchenko1, Mathieu Sarracanie1, and Najat Salameh1
1Center for Adaptable MRI Technology (AMT Center), Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Basel, Allschwil, Switzerland We describe a method to capture wave displacement in vivo in the human forearm for magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) at low magnetic field (0.1 T). Taking advantage of the inherently low spatial frequency nature of propagating waves, the proposed method samples a very low fraction (10%) of the 3D k-space, combined with efficient motion-encoding, processing schemes, and an optimized RF quadrature volume coil. For the first time, acquisitions are demonstrated in humans at a field below 1.5 T within only a few minutes (1-3 min). |
|
| 09:27 | 0061 |
Numerically Optimized Magnet Designs for a Portable, Low-Field Neonatal MRI Brain Scanner
Jacob M White1,2, Monika Śliwiak2, Sara V Bates3,4, Jason P Stockmann2,3, Lawrence L Wald1,2,3, and Clarissa Z Cooley2,3
1Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology, Cambridge, MA, United States, 2A. A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 3Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 4Division of Newborn Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States Point-of-care MRI scanners sited in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) can provide immense benefits for diagnosing and monitoring neonatal brain injury. While NICU sited systems can address some of the transport concerns, a truly portable “isolette-side” imager with a neonate-specific design could further improve imaging access. We present a neonate-specific lightweight MRI permanent magnet design for use at the bedside in the NICU. We examine two magnet designs demonstrating the feasibility of realizing a sufficiently homogeneous main magnet with mean B0 of 125mT weighing under 15kg, both with and without a built-in gradient of 10mT/m. |
|
| 09:39 | 0062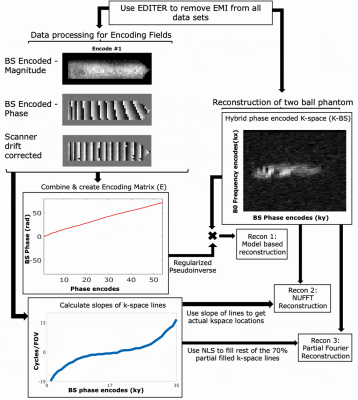 |
EMI-Suppressed Gradient-Free Phase-Encoded Imaging at 47.5mT Using an Optimized Square-Root Solenoid for Encoding and a Saddle Coil for Imaging
Sai Abitha Srinivas1,2, Christopher E Vaughn1,2, Jonathan B Martin1,2, and William A Grissom1,2,3,4
1Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States, 2Vanderbilt University Institute of imaging science, Nashville, TN, United States, 3Radiology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States, 4Electrical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States
Traditional B0 gradients have several drawbacks including high acoustic noise, PNS, bulkiness, and high cost. To address this, we demonstrate the use of Bloch-Siegert (BS) RF encoding for phase encoding using an optimized square root solenoid with a Bucking coil for high efficiency encoding and a nested uniform saddle coil for the imaging Tx/Rx coil at 47.5mT, a field strength that is especially attractive due to its low SAR and accessibility. The coil performance was evaluated in simulation and experimentally, and 2D BS phase encoded imaging and reconstructions were performed using optimized ‘U’ shaped BS pulses.
|
|
| 09:51 | 0063 |
A New Approach to Shimming Halbach Arrays Using Higher Order Halbach Array Inserts
Thomas O'Reilly1, Wouter Teeuwisse1, and Andrew Webb1
1Radiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands
Halbach arrays are an appealing magnet design for low field MRI due to their low weight and cost typically suffer from relatively high B0 inhomogeneity. In this work we show a new approach to shimming Halbach arrays using higher order Halbach inserts which can be designed to target specific spherical harmonic terms. We demonstrate the principle by correcting for the x2-y2 spherical harmonic, improving B0 homogeneity of a 31cm diameter bore Halbach array by 50% and show that in simulations homogeneities of 280 ppm can be achieved over a 20 cm sphere by correcting up to 5th order spherical harmonics.
|
|
| 10:03 | 0064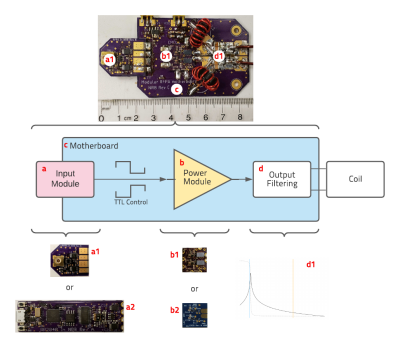 |
Low-cost Modular RFPA Platform for Gradient-Free Quantitative Imaging
N Reid Bolding1, Christopher Vaughn2, Colin Blades-Thomas3, William A Grissom2, and Mark A Griswold3
1Physics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States, 3Radiology, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States
This work presents a $75 phase modulated 2.07MHz radiofrequency power amplifier (RFPA) measuring 8.5x4.5cm for Selective Encoding through Nutation and Fingerprinting (SENF). By eliminating the need for a gradient system and imaging in a low B0, SENF shows great potential to reduce the cost, size, and accessibility of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment. Here we present the development of a transmit stage of a SENF coil unit. Special consideration has been given to simplifications that can be made in RFPA design in this specific application.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.