Weekend Course
MR Physics & Engineering II: Lost in k-Space?
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Imaging Principles | |||
| 13:00 | Spatial Encoding in MRI
Andrada Ianus
This talk will cover the basics of spatial encoding in MRI.
|
||
| 13:30 | Signal & Noise
Olaf Dietrich
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in MRI:
|
||
| RF Pulses | |||
| 14:00 | RF Pulses
Zhiyong Zhang
The goal of the talk is educational for basis concepts of RF pulse design including the basic properties of RF pulses (the flip angle, duration, and amplitude) as well as the concepts to understand the theory and implementation of RF pulses using the small tip angle tip angle approximations. The talk covers topics such as spatial localization, SLR pulses, adiabatic pulses, multi-band pulses and spatial-spectral pulses.
|
||
| 14:30 | Interactive Session |
||
| 15:00 | Break & Meet the Teachers |
||
| Pulse Sequences | |||
| 15:30 | 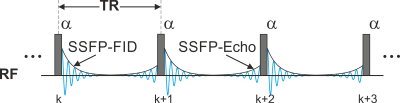 |
Design of Gradient-Echo Sequences
Rahel Heule
Signal generation in magnetic resonance imaging is driven by either of two fundamental mechanisms: spin echoes or gradient echoes. This lecture introduces the basic concepts and properties of gradient echo formation in comparison to spin-echo imaging. The influence of acquisition parameters on the produced contrast is described and typical artifacts are discussed. Special focus is on the design of rapid gradient-echo sequences based on the principle of steady-state free precession (SSFP), including three main classes: radiofrequency-spoiled gradient-echo, nonbalanced SSFP, and balanced SSFP imaging.
|
|
| 16:00 | Forming Echoes with RF Pulses
Jakob Assländer
Any sequence of radio frequency (RF) pulse forms echoes, such as spin echoes or stimulated echoes. This lecture will cover the underlying principles of such echoes. I will discuss why and when echoes occur, provide an understanding of how “to generate, recognize, use or avoid them,” to use Juergen Hennig’s words. To this end, I will explain two helpful and mutually related tools to simulate echoes: Bloch simulations and the extended phase graph formalism. Last, but not least, I will give some practical examples of how echoes are used in routine MR imaging.
|
||
| Contrast Generation | |||
| 16:30 | Magnetization Preparation: How to Generate Contrast
Martina Callaghan
|
||
| 17:00 | Interactive Session | ||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.