Digital Poster
Stretch, Rotate & Twist: New RF Coil Designs I
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3721. |
141 |
A tailored coil for sensitive detection of MRI signals in
modulating the rat’s blood-brain barrier by focused ultrasound
and microbubbles at 7T
Sheng-Kai Wu1,2,
Alessandro De Maio1,2,
Hsin-Ju Lee1,2,
Kullervo Hynynen1,2,
Meaghan O'Reilly1,2,
and Fa-Hsuan Lin1,2
1Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada Keywords: Multimodal, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides Imaging-guided focused ultrasound using MRI can modulate the permeability of blood-brain barrier with high spatial accuracy. However, many MRI-guided FUS studies rely on either a body coil or head coil poorly suited to the FUS system geometry. We developed a tailored receiver coil to improve the sensitivity of 7T MRI for rats. The tailored geometry allows for a 30% SNR increase in a study modulating the blood-brain barrier permeability with microbubbles. |
|
3722.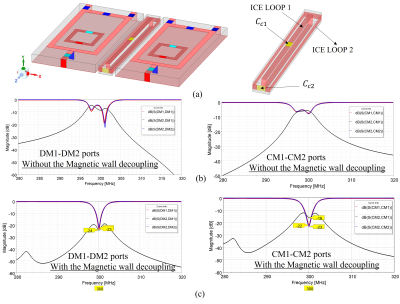 |
142 |
Quadrature Transceiver RF Arrays Using Double Cross Magnetic
Wall Decoupling for Ultrahigh field MR Imaging
KOMLAN PAYNE1,
Aditya Ashok Bhosale1,
Leslie Lei Ying1,
and Xiaoliang Zhang1
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, United States Keywords: Hybrid & Novel Systems Technology, RF Arrays & Systems Circularly polarized or quadrature transceiver coils can significantly increase overall signal reception and reduce the excitation power over linearly polarized RF transceivers. Due to the wave propagation of two modes owing to their electromagnetic field properties, it is challenging to achieve sufficient decoupling in multichannel quadrature coil arrays. In this work, we proposed a double cross magnetic wall decoupling for quadrature transceiver RF arrays based on a common-mode differential-mode (CMDM) resonator at UHF 7T. The proposed method comprised of two orthogonal decoupling elements is able to reduce the mutual coupling between the multi-modes in a pair of CMDM resonators. |
|
3723.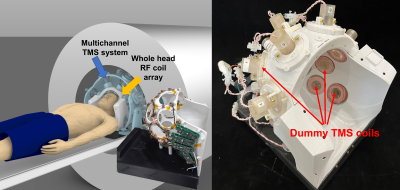 |
143 |
Analysis of the interactions between a TMS coil and a standard
receive-only RF loop for MR imaging at 3T
Lucia Navarro de Lara1,2,
Qinglei Meng1,2,
Jason P Stockmann1,2,
Sergey Makarov1,2,3,
Mohammad Daneshzand1,2,
Larry L Wald1,2,
and Aapo Nummenmaa1,2
1Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging/MGH, Charlestown, MA, United States, 2Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 3Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester, MA, United States Keywords: Hybrid & Novel Systems Technology, Hybrid & Novel Systems Technology, TMS/fMRI Specialized MR hardware is needed to combine non-invasive brain stimulation methods (e.g., TMS) and concurrent acquisition of functional MR images. Such integrated hardware systems enable studying causal relationships between the cortical and subcortical nodes of large-scale brain networks. For best possible imaging performance, all interactions of the stimulation coils on the transmit, encoding and receive system of the MR system should be analyzed on detail. The presented approach enables quantitatively assessing the influence of the TMS coils on MR imaging receive hardware. Understanding the effects could lead to improved design strategies for integrated TMS/MRI systems. |
|
3724.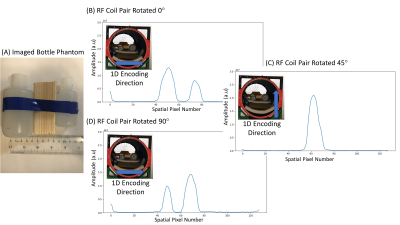 |
144 |
A Rotatable Twisted Solenoid TRASE Phase Gradient Head Coil
Christopher J Sedlock1,
Aaron R Purchase1,
Boguslaw Tomanek 1,
and Jonathan C Sharp1
1University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada Keywords: Hybrid & Novel Systems Technology, RF Arrays & Systems, TRASE TRASE is an MR encoding sequence that utilizes phase gradients of the RF transmit field for k-space encoding. A promising RF coil for TRASE imaging is the twisted solenoid due to its compact design and efficient B1 field. In this work we present the first TRASE head coil, consisting of a geometrically decoupled parallel-transmit (pTx) rotatable twisted solenoid pair. No RF switching hardware is required. The encoding direction of this coil pair is set by rotation angle, allowing for 2D radial k-space acquisitions. This method is compatible with the addition of a static B0 slice selection gradient for multi-slice.
|
|
3725.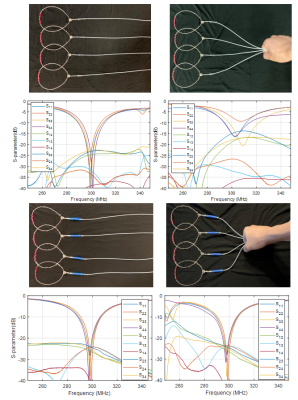 |
145 |
Miniature and flexible Bazooka balun for MRI RF coils
Shuyang Chai1,2 and
Xinqiang Yan1,2
1Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 2Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States Keywords: New Devices, New Devices Flexible receive coil design has been researched on for a long time. However, several challenges is still presenting. One of them is the still bulky and rigid balun. Here we exhibit a novel flexible bazooka balun. It can be built on any coaxial cable and is formed by heat shrinks and braided wires. The flexible balun is smaller than conventional balun in length and size. |
|
3726.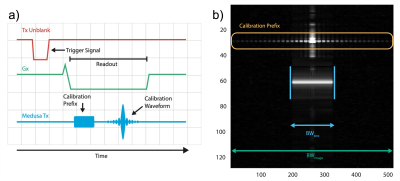 |
146 |
In-bore Preamplifier Nonlinearity Calibration
Chris Vassos1,
John Pauly1,
Fraser Robb2,
Shreyas Vasanawala3,
and Greig Scott1
1Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Aurora, OH, United States, 3Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States Keywords: Hybrid & Novel Systems Technology, System Imperfections: Measurement & Correction Present MRI preamplifiers are very linear but use 10s of mA bias current and over 150mW power. For wireless arrays, low power alternatives based upon SiGe transistors are needed. These achieve the needed gain and noise figure, with order of magnitude power reduction, but at the cost of increased nonlinearity. Using pilot tone technology, we present a calibration system for preamplifier nonlinearity correction targeted to low power SiGe preamplifiers. This system integrated a phase-locked SDR into a form of prescan to demonstrate that in-bore preamplifier linearity calibration and correction are possible. |
|
3727.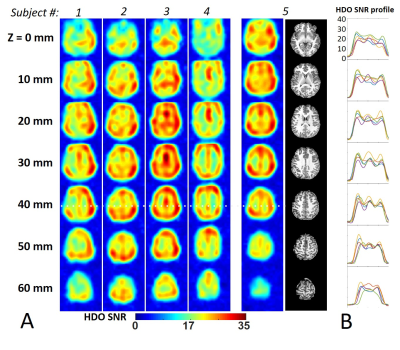 |
147 |
Comparing 8-channel and 4-channel head array coils for 7T human
brain Deuterium MRS imaging (DMRSI) applications
Xin Li1,
Soo Han Soon1,
Matt Waks1,
Hannes M. Wiesner1,
Xiao-Hong Zhu1,
and Wei Chen1
1Department of Radiology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, Non-Proton Deuterium MRS imaging (DMRSI) has emerged as an important neuro-metabolic imaging tool. We compared the performance of 4-channel and 8-channel deuterium head array coils for 7T human brain DMRSI through electromagnetic simulation, phantom and in vivo measurements. Both simulation and phantom studies show that the 4-channel array coil produced more than twice the RF magnetic field (B1) than the 8-channel array coil. Whole-brain DRMSI data with high spatial (0.7 cc nominal voxel) and temporal (2.5 min) resolutions was collected from five healthy subjects using a 4-channel head array coil, showing excellent SNR throughout the human brain. |
|
3728.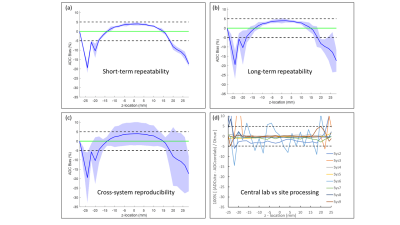 |
148 |
ADC Repeatability and Reproducibility of NCI CIRP Network
Pre-Clinical MRIs
Dariya Malyarenko1,
Ghoncheh Amouzandeh1,2,
Stephen Pickup3,
Rong Zhou3,
Henry Charles Manning4,
Seth T Gamon4,
Kooresh I Shoghi5,
James D Quirk5,
Renuka Sriram6,
Peder Larson6,
Michael T Lewis7,
Robia G Pautler7,
Paul E Kinahan8,
Mark Muzi8,
and Thomas L. Chenevert1
1Radiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, United States, 2neuro42, San Francisco, CA, United States, 3Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 4Cancer Systems Imaging, The University of Texas MDACC, Houston, TX, United States, 5Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, United States, 6Department of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States, 7Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, United States, 8Radiology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States Keywords: System Imperfections: Measurement & Correction, Precision & Accuracy The goal of this work was to assess ADC repeatability, reproducibility, and bias of Co-Clinical Imaging Research Resource Program (CIRP) network MRIs using standardized procedures for comparison to corresponding performance of clinical MRIs. A temperature-controlled phantom provided an absolute reference standard and means to assess spatial uniformity of these metrics. Seven institutions participated in the study where DWI were acquired over multiple days on 10 pre-clinical scanners, from 3 vendors at 6 field strengths. Technical level repeatability and reproducibility metrics, and spatial uniformity patterns are comparable to that observed on human systems using similar phantoms and test procedures. |
|
3729.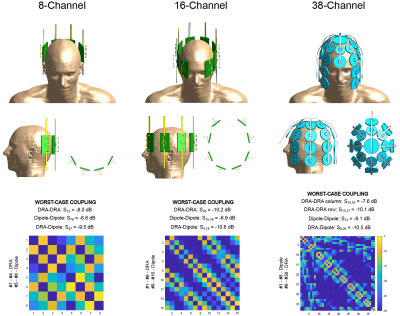 |
149 |
Can a 38-channel dipolectric antenna array compete with a
32-channel commercial head coil at 7T?
Thomas Dardano1,2,
Lijing Xin1,2,
and Daniel Wenz1,2
1CIBM Center for Biomedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Animal Imaging and Technology, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems In this work we explore a concept of dipolectric antenna array up to 38 receive channels. We constructed and evaluated an 8-channel version of dipolectric antenna array for human brain MRI at 7T and benchmarked its receive performance against a commercial 1Tx/32Rx head coil. In vivo data obtained for 8-channel array along with simulations (16- and 38-channel) indicate that a 38-channel dipolectric antenna array could provide significantly higher SNR than the current state-of-the-art solutions for human brain at 7T. |
|
3730. |
150 |
Twisted pair coils as flexible receive elements for 7 T - SNR
and active detuning efficiency
Raphaela Czerny1,
Roberta Frass-Kriegl1,
Veronika Cap1,
Elmar Laistler1,
and Lena Nohava1
1High Field MR Center, Center for Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Flexible RF Coils Form-fitting coil designs demand highly flexible coils such as twisted pair or coaxial transmission line resonators. Both of these designs and respective interfacing circuits were investigated as receive-only coils at 7 T. Similar signal-to-noise ratio and active detuning performance compared to a standard copper wire coil were demonstrated in bench and MRI experiments. |
|
3731.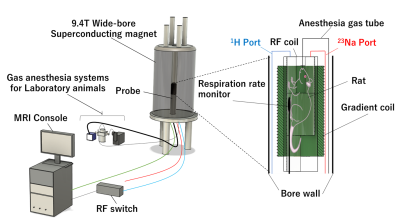 |
151 |
Development of 1H/23Na dual-tuned RF probe using inductive
coupling for 9.4T vertical wide-bore superconducting MRI for
rat’s kidney
Naoto Momiyama1,
Tomoyuki Haishi2,
and Yasuhiko Terada1
1Graduate School of Science and Technology, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan, 2Department of Radiological Sciences, International University of Health and Welfare, Narita, Japan Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Non-Proton A superconducting magnet for vertical NMR, commonly used as a high-field magnet, is effective for the MRI of X nuclides with low detection sensitivity. Even in a narrow magnetic field space, an inductively coupled RF coil with a simple structure can be used to image small animals one size larger. In this study, to visualize 23Na distribution in the kidney region of anesthetized rats, we developed 1H/23Na dual-tuned RF coils using inductive coupling with a 9.4T wide bore magnet (room temperature bore diameter 89 mm) and performed in vivo imaging. |
|
3732. |
152 |
Stretchable Coil for Small Animal MRI
Thejas Vishnu Ramesh1,
Folk W. Narongrit2,
and Joseph V. Rispoli1,2,3
1Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, United States, 2Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, United States, 3Radiology and Medical Imaging, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Small Animal MRI This work demonstrates a simple, easy to use, stretchable coil system for small animal MRI at 7T. Phantom images obtained using the stretchable coil were analysed for coil SNR. The SNR of the stretchable coil was compared with SNR of a standard commercial coil. Ex-vivo imaging of a mouse and rat brain was also performed. Current work involves minimizing SNR reduction due to coil stretch. Future work involves developing a 4-channel stretchable coil array for in-vivo imaging of a rat brain. |
|
3733.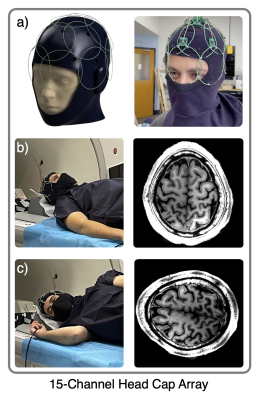 |
153 |
15-Channel Head Cap Array using Twisted-Pair Elements for MRI
Julian Adolfo Maravilla1,
Colin Taylor Knizek2,
Nazem Khairallah1,
Ana Claudia Arias1,
and Michael Lustig1
1EECS, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States, 2University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems, Flexible RF Array, Conformal RF Array, fMRI Sleep Studies, TMS/EEG/fMRI A tight fitting and wearable 15-Channel Head Cap Array using Twisted-Pair Elements was designed and characterized for potential use in a multimodal imaging system. The RF Array was characterized in terms of safety and SNR. The elements in the array (Twisted-Pair coil) show >40dB isolation for active detuning with no significant component heating under harsh RF conditions (ΔT<4°C). SNR evaluations revealed a 3x increase in peripheral SNR and retainment of SNR under parallel imaging conditions when compared to a commercial head array. An array of this caliber can be used for fMRI sleep studies and simultaneous TMS/EEG/fMRI. |
|
3734.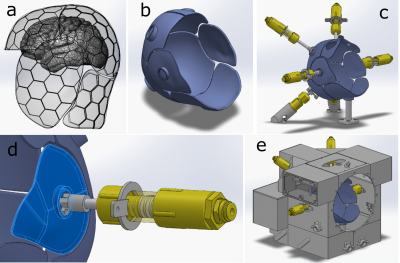 |
154 |
Toward a Size-Adaptable 128-Channel Receive RF Coil for Human
Head Imaging at 3T Using a Flexible Plate Approach
William Mathieu1,
Charbel Matta1,
Milica Popović1,
and Reza Farivar2
1Electrical and Computer Engineering, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2Ophthalmology, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems We present a size-adaptable flexible-plate 128-channel receive coil design with initial results. Our approach allows for increased element density as elements can be placed closer to the surface of the scalp. Arrays are built on semi-flexible plates with boundaries roughly following cranial sutures. The aim is to accommodate at least 99% of head shapes and sizes. Our 18-channel “occipital” plate array (1 of 8 plates) was compared to the posterior portion (40-channels) of the Siemens 64 Head/Neck coil using SNR maps. Results show that our design improves average and max SNR by 1.9- and 7.4-fold, respectively. |
|
3735.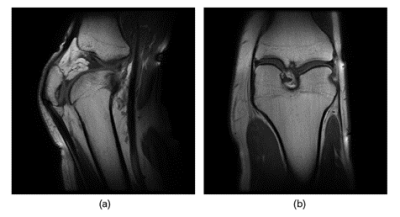 |
155 |
Stretchable conductive-thread MRI receive array coils for the
knee
Folk W. Narongrit1,
Thejas Vishnu Ramesh2,
and Joseph V. Rispoli1,2,3
1Elmore Family School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, United States, 2Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, United States, 3Radiology and Medical Imaging, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, New Devices, Coils, Stretchable We report on the development of an 8-channel stretchable array coils for 3T knee MRI which was rapidly designed using embroidered conductive threads on athletic fabric. The coil is omnidirectionally stretchable and conforms to the anatomy. Phantom testing shows the coil’s signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and image quality are comparable to a commercial flexible coil. In vivo imaging was done on a healthy volunteer illustrates the potential of rapidly developed stretchable coils. |
|
| 3736. | WITHDRAWN | ||
3737.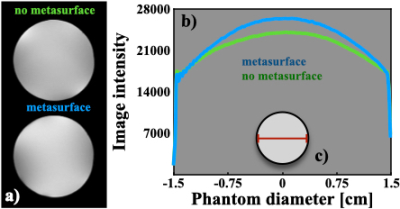 |
156 |
B1 improvement of a birdcage coil using a flexible metamaterials
at 7 T
Sergio Solis-Najera1,
Jelena Lazovic2,
Rodrigo Ruiz1,
Fabian Vazquez1,
and Alfredo Odon Rodriguez3
1Departamento de Fisica, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico, 2Department of Physical Intelligence, Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Stuttgart, Germany, 3Electrical Engineering, UAM Iztapalapa, Mexico City, Mexico Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems This work presents a flexible metasurface to improve the B1 and the image SNR of a transceiver quadrature birdcage coil for preclinical MRI applications at 7 T. The metasurface was not tuned so no passive components were used. The imaging phantom was entirely covered with the metasurface and produced an improvement of both B1 and the SNR. This easy-to-implement approach offers an alternative to improve the B1 field for preclinical applications at high field.
|
|
3738.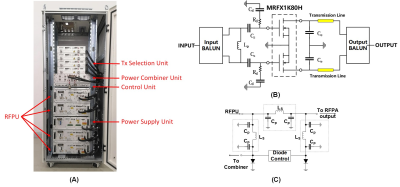 |
157 |
Design of a high power RF amplifier with configurable number of
channels
Jifeng Chen1,2,
Ye Li1,2,
Zhenhua Shen3,
Bin Liu3,
Xiaoliang Zhang4,
Bin Cao3,
Xin Liu1,2,
Xu Chu3,
and Hairong Zhen1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, 3Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, New York, NY, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, Parallel Transmit & Multiband, RF power amplifier UHF (Ultra high field) MRI requires high RF power from RF Power Amplifier (RFPA), especially for whole-body imaging1. Some studies on body imaging reported limitation on available RF power. In this study, we present works to provide RFPA with highest peak power capability known for UHF MRI with configurable number of transmit channels so as to meet different RF coil requirements. Feasibility and performance of the new method in UHF MRI was demonstrated on the bench and 5T whole-body scanner. |
|
3739.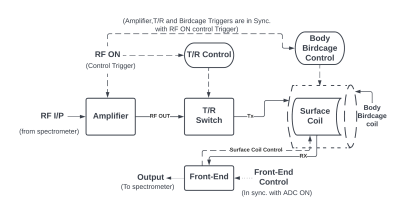 |
158 |
RF FRONT-END RECEIVER USED IN 1.5T MRI
Anvesh Inamdar1,
Sanket Gothankar1,
Bhaskar Niak1,
and Rajesh Harsh1
1Medical Systems Division, SAMEER, Mumbai, India Keywords: RF Pulse Design & Fields, RF Pulse Design & Fields, RF Front-end In an MRI, the receiver coil produces moderately low signals that are difficult to detect in a noisy environment. As a result, there was a requirement for a customised RF front end that could tolerate high power leakage from coils, provide adequate isolation, low noise figure, and have a good gain factor. The developed RF front end complies with the requirements and produces images with low noise |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.