Digital Poster
DTI & DWI III
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3954.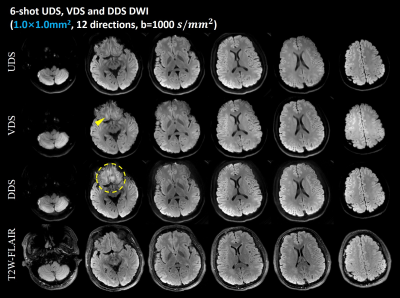 |
21 |
Comparison of uniform-density, variable-density and dual-density
spiral samplings for multi-shot diffusion-weighted imaging
Guangqi Li1,
Xiaodong Ma2,
Sisi Li1,
Xinyu Ye1,
Peter Börnert3,4,
Xiaohong Joe Zhou5,
and Hua Guo1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 3Radiology, C.J. Gorter Center for High-Field MRI, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands, 4Philips Research, Hamburg, Germany, 5Center for MR Research and Departments of Radiology, Neurosurgery, and Biomedical Engineering, University of Illinois College of Medicine at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion Tensor Imaging Different multi-shot spiral sampling schemes have been developed for high-resolution DWI. However, the performances of these sampling strategies such as variable-density spiral (VDS), dual-density spiral (DDS) and uniform-density spiral (UDS) have not been compared comprehensively. In this study, we compare multi-shot UDS, VDS and DDS in brain DWI in terms of inter-shot phase error correction, overall image quality and SNR performance. Both theoretical analysis and in-vivo results demonstrate that UDS exhibits the best off-resonance performance among the three spiral sampling patterns. Additionally, UDS achieves the highest SNR in diffusion imaging over the VDS and DDS acquisitions. |
|
3955.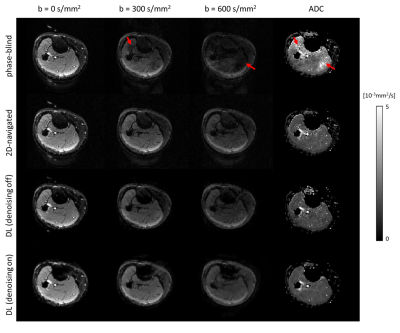 |
22 |
Deep Learning Based Self-Navigated Diffusion Weighted Multi-Shot
EPI with Supervised Denoising
Yiming Dong1,
Kirsten Koolstra2,
Laurens Beljaards3,
Marius Staring3,
Matthias J.P. van Osch4,
and Peter Börnert4,5
1LUMC, Leiden, Netherlands, 2Philips, Best, Netherlands, 3Division of Image Processing, Department of Radiology, LUMC, Leiden, Netherlands, 4C.J. Gorter MRI Center, Department of Radiology, LUMC, Leiden, Netherlands, 5Philips Research, Hamburg, Germany Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Advanced diffusion weighted self-navigated multi-shot MRI can run at high scan efficiencies resulting in good image quality. However, the model-based image reconstruction is rather time consuming. Deep learning-based reconstruction approaches could function as a faster alternative. Tailored network architectures with appropriately set physical model constraints can help to shorten reconstruction times, resulting in good image quality with reduced noise propagation. |
|
3956.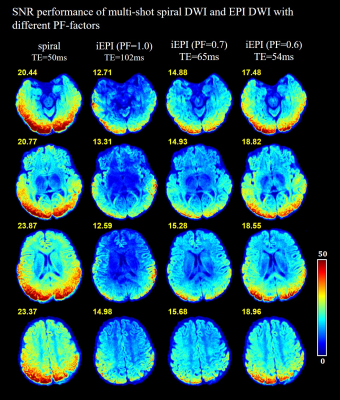 |
23 |
A comparison of navigator-free multi-shot spiral and EPI in
high-resolution DWI
Guangqi Li1,
Sisi Li1,
and Hua Guo1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Navigator-free multi-shot spiral and EPI acquisitions have been developed to achieve 2D high-resolution diffusion imaging. In this study, we investigated the off-resonance effects of spiral and iEPI samplings with different partial Fourier factors based on a signal model. Moreover, the SNR performances of the two multi-shot acquisitions at different resolutions and TEs were also explored. In summary, compared with iEPI, spiral provides superior SNR in multi-shot navigator-free DWI at various resolutions and TEs, even when the TE of spiral acquisition is slightly longer than that of iEPI. However, off-resonance correction for spiral sampling with ultra-long readout durations is more challenging. |
|
3957.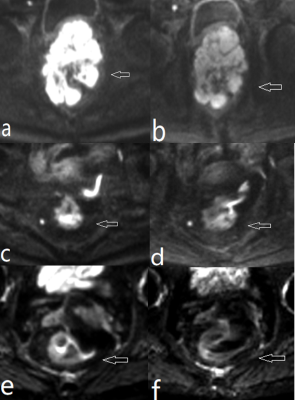 |
24 |
Feasibility of high resolution Readout-segmented echo planar
imaging with simultaneous multi-slice in the assessment of
rectal cancer
Mi zhou1,
Meining Chen2,
and Yuting Wang1
1Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, chengdu, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques DWI has an important role in the staging and treatment response assessment of patients with rectal cancer, but its resolution is much lower than dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and T2W images. We achieved a high-resolution scan of the rectal cancer using SMS HR rs-EPI sequences with a resolution of 1.1×1.1×2 mm3. The SMS HR rs-EPI provided a significantly better image quality and more valuable ADC than conventional HR rs-EPI when assessing rectal cancer. The pretreatment ADC values of HR rs-EPI could be utilized to distinguish well and poorly differentiated rectal cancer. |
|
3958.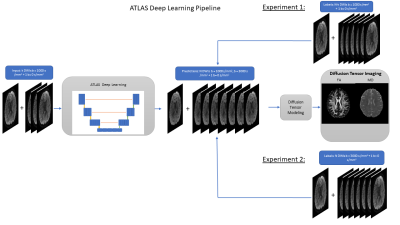 |
25 |
AcceleraTed deep-LeArning for model-free and multi-Shell (ATLAS)
DWI
Phillip Andrew Martin1,
Maria Altbach2,3,
and Ali Bilgin1,2,3,4
1Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States, 3Department of Medical Imaging, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States, 4Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques In this work, we aim to accelerate diffusion weighted MRI (dMRI) by predicting diffusion -weighted images (DWIs) across different shells using deep learning (DL), while remaining independent of a diffusion-model constraint. The proposed approach enables the predictions of unacquired DWIs in multiple shells from a small set of acquired DWIs from a given shell. This relaxes the need for applying multiple diffusion gradient weightings for obtaining a fully-acquired dataset over multiple shells. Without the constraint of a diffusion model, accurate diffusion metrics over multiple diffusion models can potentially be obtained by acquiring a small number of DWIs.
|
|
3959.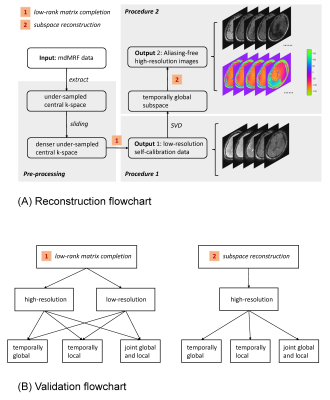 |
26 |
Self-Calibrated Subspace Reconstruction using Temporally Local
Matrix Completion for Multidimensional MR Fingerprinting
Zhilang Qiu1,
Siyuan Hu1,
Walter Zhao1,
Ken Sakaie2,
Mark A. Griswold3,
Derek K. Jones4,
and Dan Ma1
1Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3Radiology, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States, 4Cardiff University Brain Research Imaging Centre (CUBRIC), School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques We propose a new reconstruction method, named self-calibrated subspace reconstruction, for multidimensional MR fingerprinting (mdMRF), in order to correct the artifacts due to inter-shot (segment) magnitude and phase variations, without the need for extra navigator or calibration data. Different options for utilizing the low-rank property and the signal structure of mdMRF data are investigated and the optimal scheme is determined. Such that aliasing-free high-resolution image reconstruction and high-quality quantification, can be achieved. |
|
3960.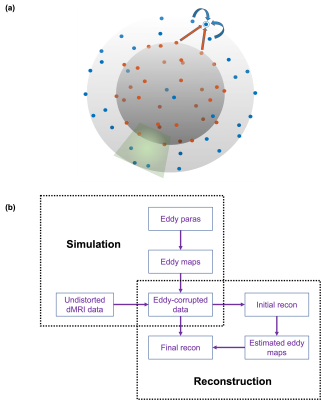 |
27 |
Extended multi-shell diffusion acceleration with Gaussian
processes estimated reconstruction (ems-DAGER)
Xinyu Ye1,
Karla Miller1,
and Wenchuan Wu1
1Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, FMRIB, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, UK, Oxford, United Kingdom Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Signal modelling Diffusion-weighted MRI suffers from relatively long acquisition time, especially for high spatial- resolution and/or high angular- resolution acquisitions. Thus, methods to increase the acquisition speed are urgently needed. Recently, increasing attention has been paid to utilize the relations between k- and q-space points for further acceleration. Here, we extend the Diffusion Acceleration with Gaussian process Estimated Reconstruction (DAGER) to leverage shared information in multi-shell acquisitions and incorporate eddy-induced distortion correction. |
|
3961.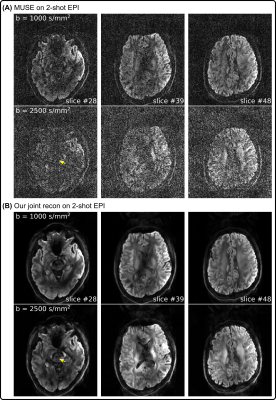 |
28 |
In Vivo Diffusion MRI at 7 T: High Spatial-Angular-Temporal
Resolution Pursuit
Frank Z Tan1,
Patrick Alexander Liebig2,
Robin Martin Heidemann2,
Frederik Bernd Laun3,
and Florian Knoll1
1Artificial Intelligence in Biomedical Engineering, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany, 2Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 3Institute of Radiology, University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Ultra high field, multi-shell, q-space, crossing fiber The pursuit of high-spatial-angular-temporal resolution for in vivo diffusion MRI at 7T is challenging, but also receives continuous interest. We hereby propose shift-encoded interleaved EPI and a joint reconstruction technique with LLR regularization. Preliminary results achieve up to 8.7-fold acceleration per shot in 2-shot EPI acquisition with 1.4 mm isotropic nominal resolution. Moreover, with the integrated joint reconstruction for noise reduction, high-quality diffusion-weighted images render more spatially-continuous fiber anisotropy maps and clearer fiber crossing in the fiber orientation distribution function. |
|
3962.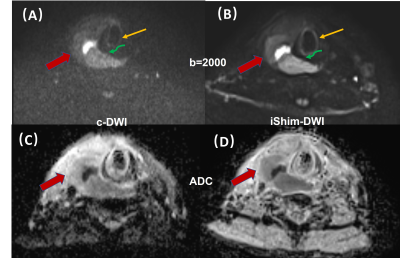 |
29 |
Integrated shimming technique can improve ultrahigh-b-value DWI
in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma:
comparison with conventional volume shimming
Yan Wen1,
Liling Long1,
Chenhui Li1,
Huiting Zhang2,
and Alto Stemmer3
1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Wuhan, China, 3MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany Keywords: Data Analysis, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques This study aimed to investigate the value of integrated shimming (iShim) technique in the ultrahigh-b-value DWI images in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by comparing with the conventional volume shimming technique. Our results showed that the ultrahigh-b-value DWI images with iShim technique had significantly higher image quality based on subjective (edge, artifact, and confidence) and objective (signal-to-noise ratio, contrast, and contrast-to-noise ratio) assessments compared with conventional single-shot-EPI DWI images with volume shimming. Therefore, ultrahigh-b-value DWI images with iShim technique can be well applied in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal SCC examination. |
|
3963.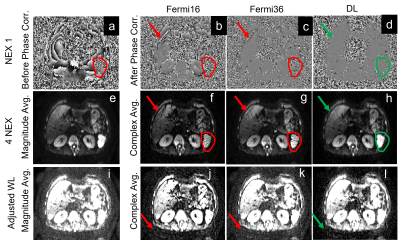 |
30 |
Robust Complex Signal Averaging for Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Xinzeng Wang1,
Daniel Litwiller2,
Arnaud Guidon3,
Patricia Lan4,
and Tim Sprenger5
1GE Healthcare, Houston, TX, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Denver, CO, United States, 3GE Healthcare, Boston, MA, United States, 4GE Healthcare, Menlo Park, CA, United States, 5GE Healthcare, Stockholm, Sweden Keywords: Data Processing, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques In the past decade, complex signal averaging has been investigated for diffusion weighted imaging to address the well-known noise floor issue. The robustness of complex signal averaging highly depends on the performance of phase correction to remove the shot-to-shot background phase variations. To achieve optimal phase correction, parameters (kernel size, regularization terms, etc.) need to be tuned for different anatomies, SNR levels and/or image size. In this work, we evaluated a deep-learning based phase correction method for various DWI applications, including brain, liver, prostate and showed improved complex signal averaging with lower noise floor and less artifacts. |
|
3964.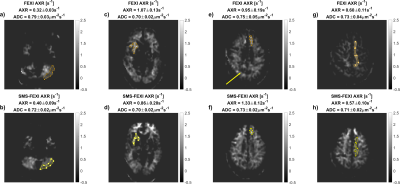 |
31 |
Whole Brain Simultaneous MultiSlice Filter EXchange Imaging in
less than 15 minutes: Initial Results
Frederik Testud1,
Arthur Chakwizira2,
and Markus Nilsson2
1Siemens Healthcare AB, Malmö, Sweden, 2Department of Medical Radiation Physics, Lund University, Lund, Sweden Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Neuro, Microstructure Filter EXchange Imaging (FEXI) is sensitive to the rate of diffusional water exchange, which depends among other factors on the cell membrane permeability. FEXI maps the so-called apparent exchange rate (AXR), however, previous FEXI protocols were limited to few slices because of very long acquisition times. In this proof-of-concept work, Simultaneous MultiSlice was included in the FEXI sequence and with protocol optimization allowed for a 12-minute whole-brain scan. FEXI accelerated with or without SMS showed similar AXR values. |
|
3965.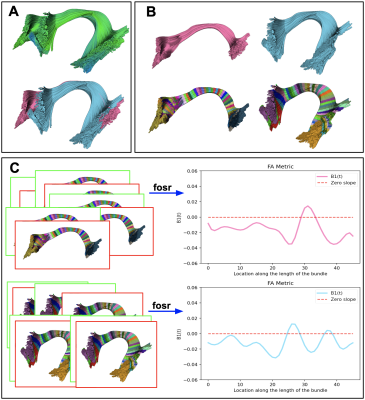 |
32 |
BUAN 2.0, streamlines as functions, nonlinear registration, and
subdivision of bundles for advanced tractometry
Bramsh Qamar Chandio1,2,
Sophia I Thomopoulos1,
Paul M Thompson1,
Jaroslaw Harezlak3,
and Eleftherios Garyfallidis2
1Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Marina del Rey, CA, United States, 2Department of Intelligent Systems Engineering, Luddy School of Informatics, Computing, and Engineering, Indiana University Bloomington, Bloomington, IN, United States, 3Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Indiana University Bloomington, Bloomington, IN, United States Keywords: Software Tools, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Tractography, tractometry, bundle segmentation, white matter tracts, group analysis We propose BUAN 2.0, which adds new advancements to its predecessor BUAN. It sub-segments bundles with varying substructures in them. It uses nonlinear registration of bundles to find accurate correspondences among bundle segments across subjects. The number of horizontal segments is decided based on the bundle and data specifications. More importantly, in BUAN 2.0, instead of treating each point on the streamline as an independent observation, we treat each streamline as a complete entity, as a function. Streamlines are analyzed by deploying functional data analysis (FDA) methods for studying group differences in populations along the length of the tracts. |
|
3966.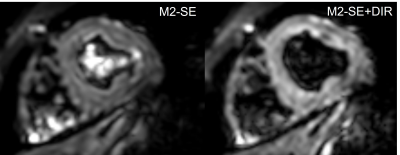 |
33 |
Black Blood Cardiac Diffusion Imaging using Second Order Motion
Compensation and Double Inversion Recovery
Yishi Wang1,
Zhen Zhang2,
Rui Wang2,
Xiuzheng Yue1,
Fang Wang2,
Rongrong Zhu2,
and Ruoshui Ha2
1Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 2Medical Imaging Center, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China Keywords: Pulse Sequence Design, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Cardiac Diffusion, Black Blood, Motion Compensation Second-order motion-compensated diffusion imaging is a robust solution for cardiac diffusion imaging but prone to bright blood signals due to motion compensation itself. In this work, we incorporated black blood module into second-order motion-compensated sequence to achieve cardiac diffusion imaging with blood signal suppressed. |
|
3967.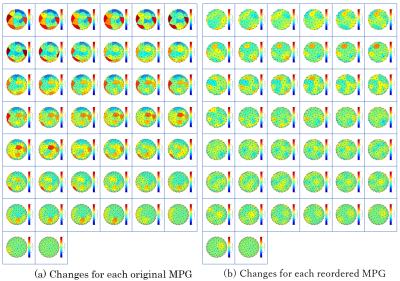 |
34 |
Investigation of motion probing gradient pulse for uniform
collection of temporal and spatial diffusion information
Yuichi Suzuki1,
Katsutoshi Murata2,
Hideyuki Iwanaga1,
and Osamu Abe1
1Radiology Center, The University of Tokyo Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 2Siemens Healthineers, Tokyo, Japan Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques We examined the application order of MPG pulses (called reordered MPG) that can uniformly collect spatial diffusion information even if the examination is interrupted, compare it with the an electrostatic repulsion method (conventional method, called original MPG), and verify its usefulness. In conclusion, The reordered MPG, which was rearranged based on the MPG direction of the original, could collect diffusion information more uniformly than the original MPG even if the inspection examination was interrupted. |
|
3968.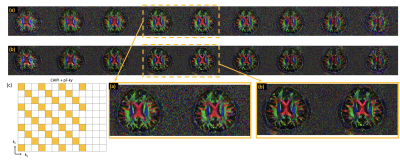 |
35 |
Accelerated High Resolution Diffusion Imaging using 3D
multi-shot EPI and Model-based Reconstruction
Chu-Yu Lee1 and
Merry Mani1
1University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States Keywords: Artifacts, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Diffusion weighted images are usually acquired using 2D EPI methods. This technique has the limitation of low spatial resolution and low SNR. 3D diffusion weighted images are attractive option for improved SNR, however the motion-induced phase inconsistencies pose a challenge for the reconstruction of such data. We present a navigator-free phase-compensated reconstruction, which can be implemented as a regular parallel imaging framework. This two-step method involves first estimating a low-resolution phase from the data itself and then integrating the phase information in the forward encoding operator. We show good phase compensation from accelerated datasets using the proposed approach. |
|
3969.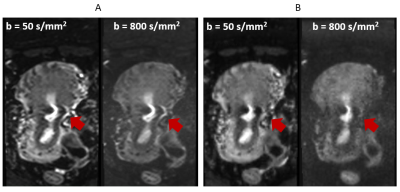 |
36 |
Readout-segmented EPI using 2D spatially-selective RF excitation
pulses for DWI with reduced FOV
Wei Liu1,
Thomas Benkert1,
and Elisabeth Weiland1
1MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany Keywords: Pulse Sequence Design, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques In this work, we propose to further minimize the distortion and T2* blurring in DWI by the combination of readout-segmented EPI and 2D spatially-selective RF excitation. We demonstrate its application to DWI of the temporal lobe and the uterus. The experimental results based on volunteer scans show substantial distortion reduction in the proposed method, compared to the conventional 2DRF based single-shot EPI with reduced FOV. |
|
3970.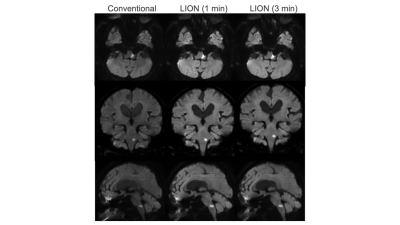 |
37 |
Volume isotropic thin-slice high-quality brain DWI with no
fat-suppression pre-pulse
Takayuki SAKAI1,
Masami Yoneyama2,
Diachi Murayama1,
Iain Ball3,
Tosiaki MIYATI4,
Shigehiro Ochi1,
and Atsuya Watanabe5,6
1Radiology, Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Chiba, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Australia & New Zealand, North Ryde, Australia, 4Faculty of Health Sciences, Institute of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 5General Medical Services, Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba, Japan, 6Orthopaedic Surgery, Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Chiba, Japan Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques We hypothesized that LIPO-only (LION) DWI might be one of the best solutions to improve the image quality of volumetric thin-slice DWI if it is further optimized to increase the robustness of fat suppression. We investigated the clinical usefulness of proposed LION fat suppression combined with thin-slice DWI for brain volumetric DWI in patients with acute stroke. LION-DWI has improved SNR compared to conventional DWI and has superior visual lesion detectability in patients with acute stroke. Therefore, it is possible to improve the image quality and shorten the imaging time of thin-slice DWI by changing the fat suppression to LION. |
|
3971.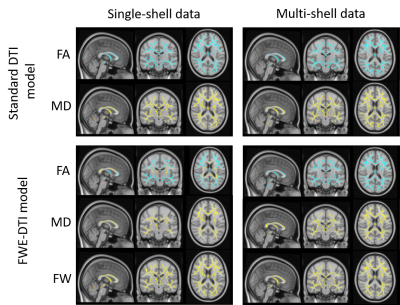 |
38 |
The Trouble with Free-Water Elimination using Single-Shell
Diffusion MRI Data: A Case-Study in Ageing
Marta M. Correia1,
Stefan Winzeck2,3,
Marc Golub4,
and Rita G. Nunes4
1MRC Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2BioMedIA Group, Department of Computing, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Division of Anaesthesia, Department of Medicine, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 4Institute for Systems and Robotics - Lisboa and Department of Bioengineering, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal Keywords: Data Analysis, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Ageing, Free-Water Two different algorithms for free-water elimination (FWE) were applied to single-shell and multi-shell diffusion MRI data. Positive correlations were found between age and fractional anisotropy (FA) estimated with the FWE algorithm for single-shell, but this was not replicated with multi-shell diffusion data. Because only the multi-shell FWE algorithm is well-posed, we postulated that the positive correlations between age and FA must be a false positive finding, resulting from inappropriate fitting using single-shell data. FWE estimates from single-shell modelling have been shown to be biologically plausible, but this does not imply specificity, and more work is required to validate these approaches. |
|
3972.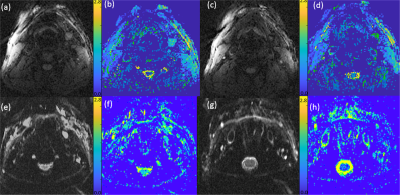 |
39 |
New Rapid 3D diffusion weighted imaging using 3D hybrid
Radial-Echo Planar Imaging (RAZER) sequence
Seong-Eun Kim1,
Henrick Carl Axel Odeen 1,
John A Roberts1,
and Dennis L Parker1
1UCAIR, Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States Keywords: Pulse Sequence Design, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, non-cartesian trajectory Non-Cartesian sampling schemes offer advantages over Cartesian schemes. Recently 2D radial and 3D hybrid radial-Cartesian approaches such as 3D stack of stars have gained popularity. Despite of many advantages, the current hybrid trajectory is presently limited by drawbacks including the degradation of sampling efficiency and the k-space coverage per unit time for diffusion application. For more flexible, rapid, and motion-robust 3D DWI, we implemented a 3D hybrid radial-EPI(RZAER) sequence and demonstrated the feasibility of 3D diffusion weighted RAZER sequence for carotid vessel wall.
|
|
3973.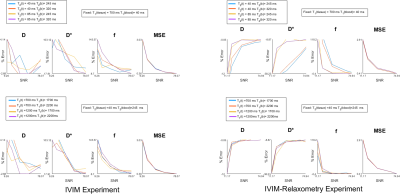 |
40 |
Incorporating Tissue and Blood Relaxometry For Estimating IVIM
Parameters: A Simulation Study
Yousef Mazaheri1
1Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States Keywords: Signal Representations, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, IVIM The aim of this aim of this study is to use numerical simulation to compare the performance of the standard bi-exponential IVIM model to an extended model which incorporates tissue and blood relaxometry for the estimation of IVIM parameters. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.