Digital Poster
Vessel Wall & Lumen Imaging II
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1684. | WITHDRAWN | ||
1685.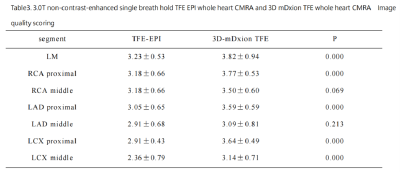 |
41 | Whole-heart NCMRA Using Single-Breath-Hold TFE EPI at 3T:Comparison with 3D-mDixon TFE Coronary MRA on Healthy Volunteers
Mengyue Han1, Jian Wang1, Jian Yao1, Xiao Du1, Ruopeng Wang1, Tiantian Yang1, Zheng Jing1, Yingcui Zhu1, Baijie Li1, Chenglin Xu1, Deyue Yan1, and Xiuzheng Yue2
1Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Heart, Cardiovascular Non-contrast-enhanced whole-heart coronary MRA(NCMRA) is a noninvasive modality for the detection of coronary artery disease. 3D-mDixon with compressed SENSE has been used in clinical practices but was limited to its scanning time of approximately 5-15 minutes. The EPI technique could shorten the scan time in MRI acquisition. The study aimed to evaluate the image quality of single breath-hold TFE-EPI NCMRA and 3D-mDIXON NCMRA with compression SENSE in healthy volunteers. The results showed there was no significant difference in image contrast between the LM, RCA proximal, and LAD proximal. The single breath-hold TFE-EPI sequence might have its own unique advantages. |
|
1686.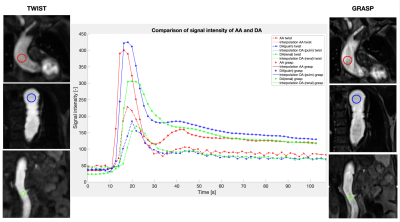 |
42 | Contrast-enhanced MRA with GRASP outperforms the conventional TWIST in aortic dissection patient cohort
Camilla Giulia Calastra1, Fabian Haupt1, Elena Kleban1, Adrian Huber1, Daniel Becker 2, Hendrik von-Tengg Kobligk1, and Bernd Jung1
1DIPR (Department of Interventional and Pediatric Radiology), Inselspital, Bern, Switzerland, 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Inselspital, Bern, Switzerland Keywords: Vessels, Cardiovascular, Magnetic Resonance Angiography This work compares the application of two magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) sequences on an aortic dissection patient cohort: the conventional cartesian-sampling-based, TWIST sequence, and the new radial-sampling-based GRASP sequence. The 1.5T MRA data from six patients with aortic dissection were assessed qualitatively and quantitatively to investigate overall image quality and spatial and temporal blurring. GRASP outperformed TWIST in temporal SNR, vessel sharpness and reduction in image blurring; streaking artifacts were clearly visible, but did not affect the diagnostic image quality. |
|
1687.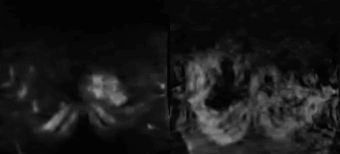 |
43 | Simultaneous 3D Whole-Heart Bright-Blood and Black-Blood Imaging with iNAV-based Non-Rigid Motion-Corrected Reconstruction at 0.55T
Carlos Castillo-Passi1,2,3, Michael G. Crabb1, Camila Muñoz1, Donovan Tripp1, Karl P. Kunze1,4, Radhouene Neji 1,4, Pablo Irarrazaval2,3,5, Claudia Prieto1,3,5, and Rene M. Botnar1,2,3,5
1School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Institute for Biological and Medical Engineering, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile, 3Millennium Institute for Intelligent Healthcare Engineering, Santiago, Chile, 4MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Limited, Camberley, United Kingdom, 5Electrical Engineering Department, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile Keywords: Heart, Low-Field MRI In this work, we demonstrate the feasibility of free-breathing whole-heart simultaneous bright-blood and black-blood imaging at 0.55T. We implemented an image navigator (iNAV)-based non-rigid motion-corrected 2 heartbeat sequence with 100% respiratory scan efficiency and high-dimensional patch-based low-rank (HD-PROST) denoising. The research sequence was validated on one healthy subject, showing simultaneous 3D visualization of cardiovascular anatomy on bright and black blood images at 0.55T in under 12 minutes scan time. |
|
1688.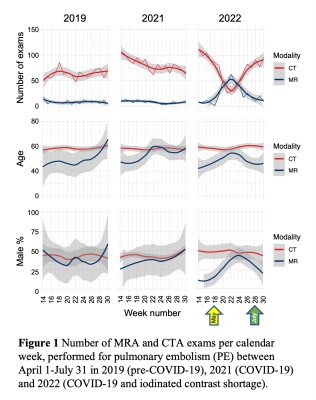 |
44 | MRA for Pulmonary Embolism to Conserve Iodinated Contrast Media During an Acute Supply Chain-related Shortage
Jitka Starekova1, Sheena Y Chu1, David A Bluemke1,2, Thomas M Grist1,2,3, Joanna E Kusmirek1, Scott K Nagle1, Mark L Schiebler1, Meghan G Lubner1, Prashant Nagpal1, and Scott B Reeder1,2,3,4,5
1Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Biomedical Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 4Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 5Emergency Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States Keywords: Vessels, MR Value The closure of GE Healthcare’s Shanghai facility in April 2022 during the COVID-19 lockdown in China led to a major supply chain disruption of iodinated contrast media in North America. In response, our department instituted measures to conserve iodinated contrast, including the use of MRA as an alternative to contrast enhanced CTA to evaluate for pulmonary embolus (PE). Over the period of April through July of 2022, this strategy conserved an estimated 27 liters of iohexol 350 mg/ml. We report our experience on the use of MRA for diagnosis of PE in the general population during this period. |
|
1689.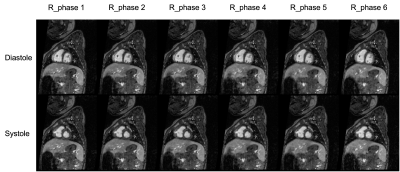 |
45 | Ferumoxytol-Enhanced 5D ROCK-MUSIC with Low-rank Tensor Reconstruction: Initial Feasibility in Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease
Zixuan Zhao1, Hsu-Lei Lee2, Guowen Shao1, Zhengyang Ming1, Fei Han3, Dan Ruan1, Anthony Christodoulou2, J. Paul Finn1, and Kim-Lien Nguyen1,4
1University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Siemens Health Solutions, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Los Angeles, CA, United States Keywords: Heart, Cardiovascular, Congenital Heart Disease, Ferumoxytol ROCK-MUSIC is a 4D whole heart MRI pulse sequence that has shown promise for fast imaging in pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) without dependence on the ventilator respiratory gating signal. Recent research in cardiac multitasking with low rank tensor (LRT) reconstruction allows for decomposition of cardiorespiratory motion. In this preliminary work, we showed that LRT reconstruction can be applied to the ROCK-MUSIC acquisition to enable higher temporal resolution with cardiorespiratory resolved imaging. When compared to L1-ESPIRiT, the LRT approach is able to achieve comparable image quality. |
|
1690.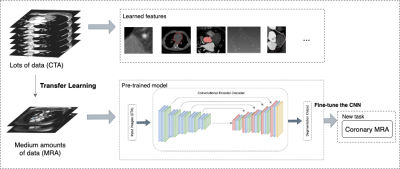 |
46 | Deep Learning-Based Automatic Segmentation of Non-contrast Coronary Magnetic Resonance Angiography Images
Lu Lin1, Difei Jiang2, Yueting Xiao2, and Yining Wang1
1Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2Shukun (Beijing) Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing, China Keywords: Heart, Cardiovascular Coronary Magnetic Resonance Angiography (CMRA) is the only non-invasive coronary artery imaging method without radiation exposure and contrast media, and its application in clinical practice has been increasing. However, image post-processing for clinical diagnosis is time-consuming and requires expertise for radiologists. We proposed a three-dimensional U-Net-based automatic method for CMRA images by transfer learning from a pre-trained model of coronary computed tomography angiography(CCTA) to obtain accurate segmentation of coronary arteries. |
|
1691.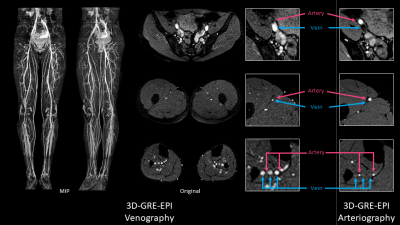 |
47 | Improved non-contrast-enhanced MR Venography of lower extremities using non-triggered 3D-GRE-EPI.
Toshiki Takumi1, Hiroshi Hamano1, Tomohiro Mochizuki1, Yasutomo Katsumata2, Masami Yoneyama1, Shouichi Andou3, Ken Ohno3, and Takashi Namiki1
1Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 2Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan, 3Kawanishi City Medical Center, Hyogo, Japan Keywords: Vessels, Blood vessels, Venography MRI is one of a promising diagnostic of lower extremity arterial and venous disease, and non-contrast-enhanced MR angiography has an array of specific applications for numerous clinical indications. In this study, we demonstrated non-contrast-enhanced non-triggered 3D gradient-echo echo-planer-imaging (3D-GRE-EPI) can provide high quality MR Venography in lower extremities. Consequently, 3D-GRE-EPI was provided high sharpness, contrast and could distinguish veins and arteries. |
|
1692.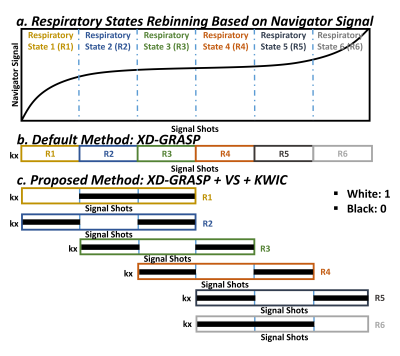 |
48 | Incorporation of View-Sharing and KWIC Filtering into XD-GRASP Reconstruction Improves Spatial Resolution in Thoracic NC-MRA
Lexiaozi Fan1,2, Jeanette N. Akuamoah2, Kyungpyo D Hong2, Joshua D. Robinson2,3,4, Cynthia K. Rigsby2,3,5, and Daniel Kim1,2
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, United States, 3Department of Pediatric, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, United States, 4Division of Cardiology, Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States, 5Department of Medical Imaging, Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States Keywords: Vessels, Image Reconstruction Conventional thoracic non-contrast magnetic resonance angiography (NC-MRA) often produces suboptimal image quality in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) and results in lengthy scan times. We recently developed a NC-MRA pulse sequence using a stack-of-stars k-space sampling pattern with XD-GRASP reconstruction and evaluated its performance in adults. In this study, we sought to improve our NC-MRA pulse sequence by incorporating view-sharing (VS) and k-space weighted image contrast (KWIC) filtering to reduce blurring, which is critical for pediatric patients who have smaller hearts and faster heart rates than adults. We evaluated it performance against contrast-enhanced MRA in pediatric patients. |
|
1693.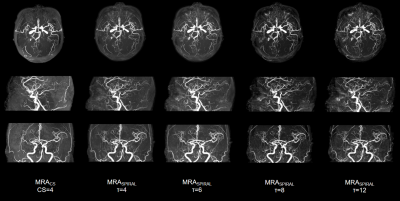 |
49 | Acceleration of brain MRA with Spiral, compared with Compressed SENSE
Yujie Yu1, Maoxue Wang1, Xiance Zhao2, and Weibo Chen2
1The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China Keywords: Vessels, Brain, TOF The purpose of this study is to quantitively and qualitatively evaluate the clinical feasibility of spiral-based TOF-MRA (MRAspiral) in terms of acceleration of data acquisition and imaging performance, with reference to the routine use of TOF-MRA with C-SENSE=4. The results showed that MRAspiral with τ=8 (2min7s) can significantly reduce the acquisition time by 44.3% with a balanced image quality and scan time for arteries visualization and clinical diagnosis. |
|
1694.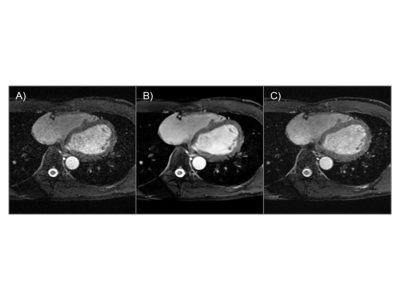 |
50 | Efficiency of 3D ky-kz centric acquisition in whole heart coronary MRA (WHCA) using high resolution deep learning reconstruction (HR-DLR)
Yoshiaki Morita1,2, Hideki Ota2, Takashi Nishina3, Sho Tanaka3, Yuichi Yamashita3, Yoshimori Kassai3, Ryuichi Mori2, Yuki Ichinoseki2, Tatsuo Nagasaka2, Mitsue Miyazaki4, Kei Takase2, and Tetsuya Fukuda1
1Department of Radiology, National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center, Suita, Osaka, Japan, 2Department of Radiology, Tohoku University Hospital, Sendai, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan, 4Department of Radiology, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, United States Keywords: Heart, Cardiovascular, coronary artery Whole heart coronary MRA (WHCA) using fast field echo (FFE) with 3D centric ky-kz trajectory was compared with conventional FFE on healthy subjects. The mean acquisition was almost within 5 minutes using a 30-mm threshold in real-time motion correction with a navigator echoes. High resolution deep learning reconstruction (HR-DLR) was also applied to improve the image quality. |
|
1695.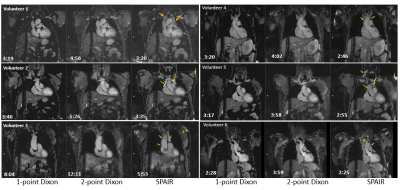 |
51 | Native MR angiography of the thorax using Compressed Sensing and 1-point Dixon at 3T: Comparison with standard fat suppression and 2-point Dixon
Michaela Schmidt1, Marcel Dominik Nickel1, and Daniel Giese1
1Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany Keywords: Vessels, Blood vessels For increased vessel contrast a robust fat suppression of adjacent fat is desirable in MR angiography. While spectral fat suppression can be insufficient, fat separation based on 2-point Dixon requires the acquisition of a second echo. A 1-point Dixon approach based on opposed-phase imaging is presented here that allows to suppress fat dominated voxels effectively while keeping scan efficiency. The approach is evaluated in volunteers and compared to conventional approaches regarding image quality, artifacts, fat suppression and vessel diameter. |
|
1696.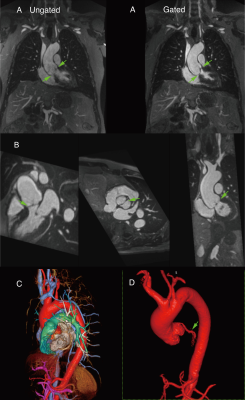 |
52 | Cardiac Gated, Ferumoxytol-Enhanced MR Angiography of the Aorta with a Flexible k-space Trajectory: Initial Results
J Paul Finn1,2,3, Takegawa Yoshida1,2, Arash Bedayat1,2, Kim-Lien Nguyen2,3,4, Xiaodong Zhong5, and Gerhard Laub6
1Department of Radiological Sciences, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Diagnostic Cardiovascular Imaging Laboratory, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4Division of Cardiology, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Los Angeles, CA, United States, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 5Siemens Healthineers, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 6DrLaubconsulting LLC, Los Angeles, CA, United States Keywords: Heart, Cardiovascular Contrast enhanced MRA of the aorta is typically performed without cardiac gating, greatly limiting its value in the aortic root and its more widespread utilization. We implemented a cardiac gated sequence for breath-held MRA of the thoracic aorta with flexible contrast during the steady-state distribution of ferumoxytol and compared it to ungated MRA with similar resolution. The resulting images were compared for definition of the aortic annulus, leaflets and ascending aorta. The gated sequence performed significantly better than the ungated sequence for all measured parameters and holds promise as a high quality alternative to gated CTA in appropriate clinical circumstances. |
|
1697.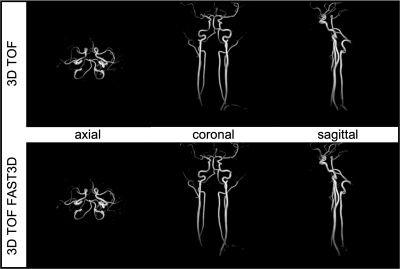 |
53 | Non-Contrast Carotid Artery Imaging using 3D TOF and Time-SLIP bSSFP with centric ky-kz k-space trajectory.
Vadim Malis1, Won Bae1,2, Yoshimori Kassai3, Marin A Mcdonald1, and Mitsue Miyazaki1
1Radiology, UC San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States, 2VA San Diego Healthcare System, San Diego, CA, United States, 3Canon Medical, Ōtawara-shi, Japan Keywords: Vessels, Vessels, Non-Contrast MRA Carotid artery stenosis (CAS) is one of the most common causes of acute ischemic stroke. MRA techniques are routinely used for the diagnostics of CAS, yet one of their drawbacks remains as a long scanning time. In this study we acquired and compared two sets of images of carotid arteries: 3D time-of-flight (TOF), time spatial labeling inversion pulse (Time-SLIP) balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) and their accelerated versions that utilize centric ky-kz acquisition pattern (FAST3D). |
|
1698.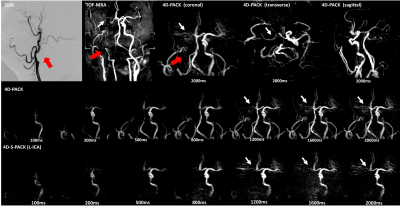 |
54 | Application of 4D-PACK and 4D-S-PACK in the internal carotid artery occlusion: initial experience
Jin Zhang1, Beibei Sun2, Shenghao Ding2, Yongjun Cheng3, Mengyou Ma3, Xinyang Wu3, Peng Wu3, and Huilin Zhao2
1Radiology, Renji hospital, Shanghai, China, 2Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China Keywords: Vessels, Blood vessels We recruited 4 patients with internal carotid artery occlusive diseases and assessed whether 4D-MR angiography can be used as a noninvasive alternative to intraarterial DSA. All patients were imaged with TOF-MRA, 4D-PACK, 4D-S-PACK, and DSA. 4D-PACK demonstrated a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 100%, 100%, and 100% respectively, as same as TOF-MRA, for diagnosing ICAO in reference to DSA. Moreover, 4D-PACK along with 4D-S-PACK could provide additional dynamic information on compensatory circulation after ICAO. Our results showed that non-contrast 4D-MR angiography has the potential to become an alternative imaging approach in diagnosing ICAO and initially assessing its blood supply pattern. |
|
1699.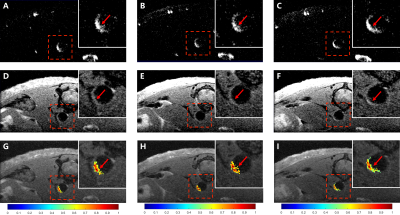 |
55 | High-Resolution Heart-Saturated TOF (HRHS-TOF): A novel MRI protocol for atherosclerotic plaque imaging on mice in vivo
Nan Gao1, Yuqing Wang1, Chengqin He2, and Xiaolei Song1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Inno Medicine, Beijing, China Keywords: Atherosclerosis, Atherosclerosis Time of flight (TOF) is the most commonly used bright blood MRI method for imaging the human vascular system. However, there were several challenges when TOF was used for imaging AS plaque in mice. This study proposed a novel MRI protocol, High-Resolution Heart-Saturated TOF (HRHS-TOF), imaging only AS plaque without background information. Moreover, this protocol could perform without measurement of the T1 value of blood in advance. ApoE−/− mice were scanned to investigate the feasibility and data interpretation of HRHS-TOF protocol. |
|
1700.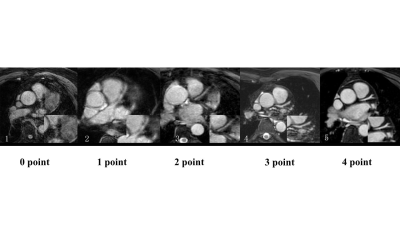 |
56 | Analysis of baseline and cardiac function factors affecting the image quality of contrast-free 3.0T MR coronary angiography
Gang Zhang1, Wei Xing1, Zhiwei Shen2, Jianxiu Lian2, and Ke Jiang2
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of CM, Henan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Heart, Cardiovascular Magnetic resonance coronary angiography (MRCA) imaging technology is still somewhat sophisticated, with numerous elements influencing image quality. This study found that for subjects with high BMI, high heart rate, and high systolic blood pressure, further optimization of imaging sequences and parameters is needed to explore individualized coronary MR imaging protocols. |
|
1701.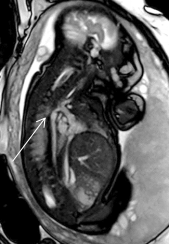 |
57 | Magnetic resonance imaging of fetal aorta
LIN GANG1
1Xijing Hospital, Air Force Military Medical University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China Keywords: Vessels, Cardiovascular Key words:fetal cardiovascular; coarctation of aortic arch;imaging technology Prenatal ultrasound diagnosis has always been the first choice of screening for perinatal birth defects. However, due to the influence of many factors, the difficulty of diagnosis is increased, even for experienced experts, so there is an urgent need to find better supplements and alternatives. With the development of the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, many congenital aortic diseases can be alleviated or cured by perinatal surgery or elective surgery, so early diagnosis can reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality.the author has made some innovative explorations in the MRI scanning method of fetal cardiovascular. |
|
1702.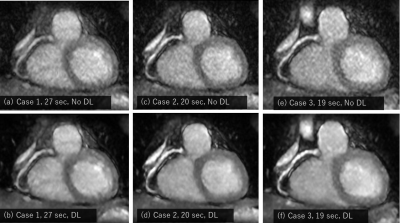 |
58 | Breath-hold Whole Heart Coronary MRA with Parallel Imaging, Compressed Sensing and Deep Learning reconstruction
Mitsuharu Miyoshi1, Atsushi Nozaki1, Shigeo Okuda2, Masahiro Jinzaki2, and Tetsuya Wakayama1
1Global MR application and workflow, GE Healthcare Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Radiology, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan Keywords: Heart, Cardiovascular, Coronary Artery For Breath-hold Whole Heart Coronary MRA, we developed the combination of Parallel Imaging and Compressed Sensing to accelerate scan time and Deep Learning reconstruction to improve the image quality. With the combination of these techniques, we could obtain Coronary MRA with 1.8mm isotropic acquisition voxel size in a possible breath-hold scan time. Deep Learning recon effectively improved the SNR and image quality. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.