Power Pitch
Pitch: Body: Image-Guided Treatment: Assessment, Response & Prediction
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| 15:45 |
0714.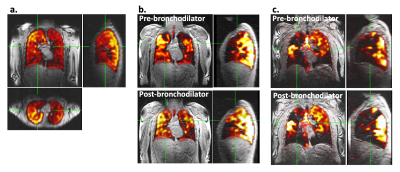 |
19F-MRI of pulmonary ventilation: Assessment of response to
treatment in asthma and COPD
Mary A Neal1,2,
Charlotte Holland1,2,
Benjamin J Pippard1,2,
Ian Forrest3,
Graham Burns3,
Rod Lawson4,
Holly F Fisher5,
John NS Matthews5,
A John Simpson2,
Jim M Wild6,
and Peter E Thelwall1,2
1Newcastle Magnetic Resonance Centre, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, 2Translational and Clinical Research Institute, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, 3Department of Respiratory Medicine, Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, 4Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield, United Kingdom, 5Institute of Health and Society, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, 6POLARIS, Imaging Sciences, Department of IICD, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom Keywords: Lung, Non-Proton, fluorine, 19F, ventilation 19F-MRI is an emerging technique which holds promise for direct, quantitative imaging of pulmonary ventilation without recourse to ionising radiation or use of specialist hyperpolarised gases. We aimed to assess the sensitivity of 19F-MRI to treatment response by imaging inhaled perfluoropropane in patients with asthma and patients with COPD before and after administration of a bronchodilator, at two research sites. Significant increases in percent ventilated lung volume were measured from the 19F-MR images following bronchodilator administration in both patient groups, and a positive correlation with spirometry was measured, demonstrating good technique sensitivity and clinical validity. |
| 15:45 |
0715.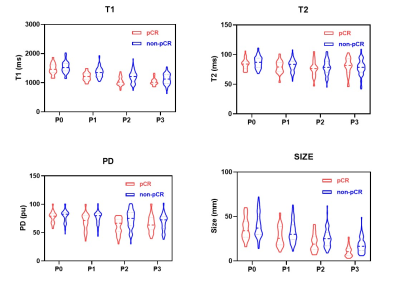 |
Time Course Changes of Synthetic Relaxation Time during
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer.
Ruimeng Zhao1,
Siyao Du1,
Si Gao1,
Lizhi Xie2,
Jing Shi3,
and Lina Zhang1
1Department of Radiology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China, 2MR Research, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 3Department of Medical Oncology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China Keywords: Breast, Cancer, neoadjuvant chemotherapy; pathological complete response This study investigated the time course changes of synthetic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) parameters (T1/T2 relaxation time [T1/T2], proton density [PD]) during neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and evaluate their value as predictors for pathological complete response (pCR) in locally advanced breast cancer. The results showed that median synthetic T1/T2/PD and tumor diameter generally decreased throughout NAC. And the Change of synthetic T1 after the first cycle of NAC may be an early predictor for NAC response in locally advanced breast cancer during whole treatment cycles. However, its predictive ability is significantly affected by histological grades. |
| 15:45 |
0716.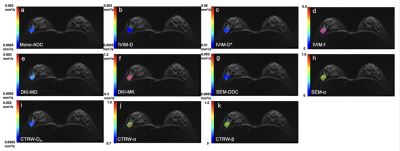 |
Various parameters derived from mono-exponential DWI, IVIM,
SEM, DKI and CTRW in breast cancer diagnosis and the
prediction of prognostic factors
Yanjin Qin1,
Yunfei Zhang2,
Yongming Dai2,
and Tao Ai1
1Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2MR Collaboration, Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China Keywords: Breast, Cancer In the present study, we compared the potential of various diffusion parameters derived from five models in distinguishing breast lesions, including the mono-exponential model (Mono), intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model, diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) model, stretched exponential model (SEM), and continuous-time random-walk (CTRW) mode. We found that diffusion-related parameters by the SEM and CTRW models are superior to ADC in discriminating breast lesions. Multiple diffusion parameters by all five diffusion models are related while the information provided is diverse. |
| 15:45 |
0717.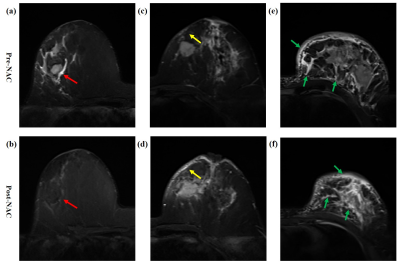 |
Do Breast Edema and Shrinkage pattern Provide Additional
Evaluation Value for Treatment Response and Recurrence in
Luminal Breast Cancer
Shiyun Sun1,
Yajia Gu1,
and Chao You1
1Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Keywords: Breast, Breast, breast edema; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); treatment response; recurrence This study aims to develop an accurate and convenient prediction model for luminal breast cancer based on conventional MRI. First, we evaluated conventional MRI features and their changes during NAC (pre, early and post) and identified stable imaging markers that predicted multiple treatment responses and prognosis. Second, we comprehensively explored the shrinkage pattern, breast edema and changes during NAC. We found that both of them can provide added value to traditional MRI features. Finally, we constructed a combined model with multi-parameter MRI features and clinicopathological information, which showed good prediction performance in treatment response and prognosis of luminal breast cancer. |
| 15:45 |
0718.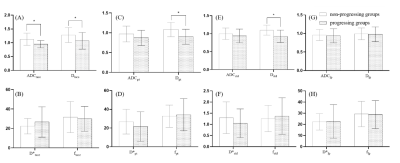 |
Prediction of the recurrence and invasion of hepatocellular
carcinoma after TACE using intravoxel incoherent motion
Xinyao Zhao1,
Qingqing Wen2,
Weiqiang Dou2,
and Junying Wang3
1Department of Radiology, Yantaishan Hospital, Yantai , Shandong Province, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, 3Shandong Province Qianfoshan Hospital, Jinan, Shandong Province, China Keywords: Liver, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, IVIM The accurate evaluation of tumor response after Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) treatment is important for tumor prognosis and subsequent treatment. In this study, we comprehensively investigated the feasibility of IVIM parameters in the TACE treatment area, peritumoral area, and hepatic parenchymal to predict tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after TACE treatment. ADC and D of TACE-treated area, and D of the peritumoral area can predict the intralesional and peritumoral recurrence after TACE treatment with high accuracy, indicating that IVIM might be a useful tool in predicting the therapeutic response and the peritumoral invasion. |
| 15:45 |
0719.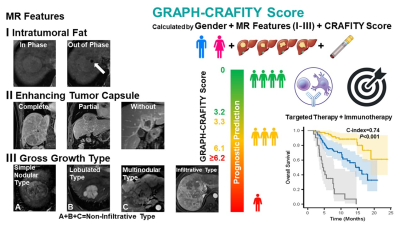 |
The GRAPH-CRAFITY Score: a novel prognostic tool for
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with targeted
therapy and immunotherapy
Ying Xu1,
Lu Li1,
Yi Yang1,
Lizhi Xie2,
Sicong Wang2,
Feng Ye1,
and Xinming Zhao1
1Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China Keywords: Liver, Treatment, Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, Prognostic Prediction · One-hundred and sixty-six patients (55.6±10.4 years) treated with lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibody were included in training cohort and 77 patients (55.4±10.7 years) treated with lenvatinib or bevacizumab plus anti-PD-1 antibody were included in validation cohort. Based on independent risk factors (Gender, intRatumoral fAt, enhancing tumor caPsule, gross growtH type and CRAFITY Score) identified by the multivariate analysis, a novel prognostic tool named GRAPH-CRAFITY Score was developed to predict OS. GRAPH-CRAFITY Score by integrating Gender, MR features and laboratory tests is an effective and user-friendly tool to predict OS of HCC patients treated with targeted therapy and immunotherapy. |
| 15:45 |
0720.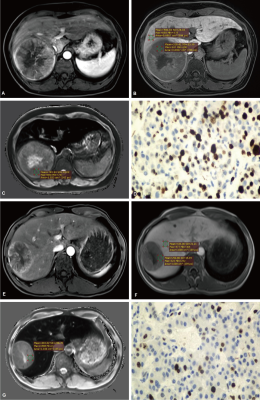 |
Preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression of
hepatocellular carcinoma using T1 mapping on gadoxetic
acid-enhanced MRI
Yue Zhao1,
Xiuhong Guan1,
Yongzhou Xu2,
Xinqing Jiang1,
and Ruimeng Yang1
1Department of Radiology, Guangzhou First People’s Hospital, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China Keywords: Liver, Cancer The cell proliferation index, Ki-67 labeling index (LI) indicates the status of cell proliferation activity which corresponds with tumor biological behavior, treatment efficacy and prognosis. If the preoperative Ki-67 expression status in HCC can be accurately predicted noninvasively, it may provide important information for clinical decision-making. T1 mapping is useful for preoperative prediction of Ki-67 LI of HCC. The nomogram Combining T1 mapping on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and clinical indicators has good predictive efficacy for preoperative prediction of Ki-67 LI, which can promote the individualized risk stratification and further treatment decision of HCC patients. |
| 15:45 |
0721.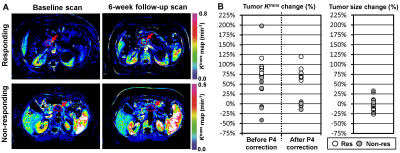 |
Quantitative DCE-MRI after P4-based error correction
provides a more accurate therapy response assessment of
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Martin D Holland1,
Ezinwanne Onuoha2,
Moh’d Khushman3,
Darryl Outlaw3,
Mehmet Akce 3,
Bassel El-Rayes 3,
Grant R Williams 3,
Salila Hashmi 4,
Sushanth Reddy 4,
J. Bart Rose 4,
Desiree E. Morgan 5,
Xiaoyu Jiang 6,
Dana Cardin 7,
Katherine Frederick-Dyer 6,
Junzhong Xu 6,
and Harrison D Kim5
1Interdisciplinary Engineering, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United States, 2Biomedical Engineering, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United States, 3Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United States, 4Surgery, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United States, 5Radiology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United States, 6Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 7Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States Keywords: Pancreas, Cancer, DCE-MRI, Pancreatic cancer, Therapy monitoring, Perfusion phantom, Quantification Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) measures tissue perfusion by monitoring the dynamic change of MRI contrast agents. However, the inter/intra-scanner variability in quantitative DCE-MRI (qDCE) measurement remains a concern. We developed a point-of-care portable perfusion phantom (P4) that can be imaged with a human subject in a standard MRI scanner to detect and correct the inter/intra-scanner variability of qDCE measurement. We demonstrated that the PDAC response to chemotherapy could be accurately assessed using quantitative DCE-MRI after our P4-based error correction method approximately seven weeks after starting therapy in two clinics. |
| 15:45 |
0722.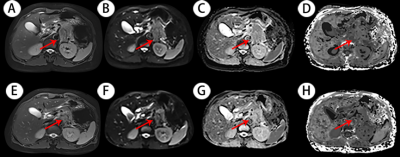 |
Value of diffusion kurtosis MR imaging for evaluating
response to first-line chemotherapy in unresectable
pancreatic cancer
Zehua Zhang1,
Caixia Fu2,
Robert Grimm3,
and Zhengrong Zhou1
1Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China, 2MR Application Development, Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China, 3MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany Keywords: Pancreas, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques This study firstly compared diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and traditional diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) in evaluating first-line chemotherapy in unresectable pancreatic cancer. The result demonstrated that higher efficacy was shown in DKI derived parameters than DWI by the ROC curve analysis. DKI has potential to become a new non-invasive tool for clinical efficacy evaluation and help clinicians select individualized treatment. |
| 15:45 |
0723.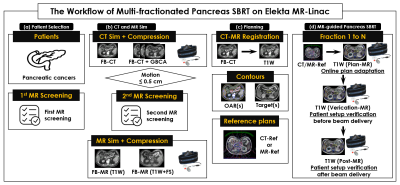 |
Stereotactic MR-guided Adaptive Radiotherapy for Pancreatic
Cancers on a 1.5 Tesla MR-linac system
Danny Lee1,2,
Seungjong Oh1,2,
Min-Sig Hwang1,2,
Daniel Pavord1,
Jason Sohn1,2,
Athanasios Colonias1,
Mark Trombetta1,
Alexander Kirichenko1,2,
and Paul Renz1
1Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 2Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, United States Keywords: Cancer, Pancreas, MR-guided pancreas SBRT on MR-Linac Ablative SBRT to pancreatic cancers on MRI-Linac is a novel and rapidly evolving technology allowing real-time visualization of tumor and nearby organs-at-risk (OAR). Reliable identification of pancreas tumors on MR-Linac has direct impact on radiotherapy planning and outcome. A novel workflow was clinically implemented for pancreas stereotactic body radiotherapy on Elekta Unity MR-Linac. Compared to T2W images, pancreas tumors on T1W images, were superiorly visible for accurate delineation during the entire treatment course. This study is the first to determine the impact of an optimized MR sequence for pancreas tumors and OARs during multi-fractionate MR-guided radiotherapy on 1.5T Elekta MR-Linac. |
| 15:45 |
0724.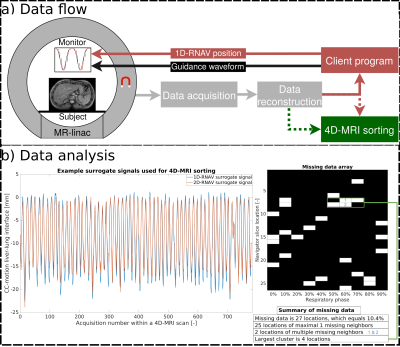 |
Comparing the effectiveness of 1D versus 2D navigated
respiratory-correlated 4D-MRI acquisitions for radiotherapy
guidance
Katrinus Keijnemans1,
Pim Borman1,
Bas Raaymakers1,
and Martin Fast1
1Department of Radiotherapy, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands Keywords: Lung, Radiotherapy, 4D-MRI, Respiratory navigator Accurate characterization of internal anatomical motion is essential for correctly guiding free-breathing radiotherapy treatments on the MR-linacs. Respiratory-correlated 4D-MRI can potentially provide this crucial information during each treatment session. We acquired a 1D respiratory navigator (1D-RNAV) interleaved with simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) images, yielding a concurrent 2D navigator (2D-RNAV). Respiratory-correlated 4D-MRIs were obtained with the 1D and 2D internal navigator surrogate signals, and the amount of missing anatomical data was quantified. Using the 1D-RNAV signal yielded fewer missing data in respiratory-correlated 4D-MRIs. Improving breathing regularity using biofeedback did not substantially influence the choice of navigator. |
| 15:45 |
0725.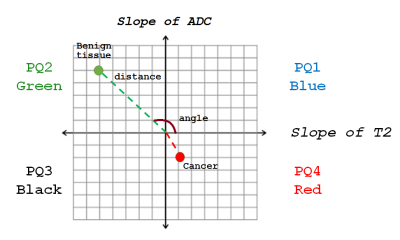 |
Four Quadrant Vector Mapping of Hybrid Multidimensional MRI
data for the diagnosis of prostate cancer
Aritrick Chatterjee1,2,
Xiaobing Fan1,
Aytekin Oto1,
and Gregory Karczmar1
1University of Chicago, CHICAGO, IL, United States, 2Sanford J. Grossman Center of Excellence in Prostate Imaging and Image Guided Therapy, Chicago, IL, United States Keywords: Prostate, Cancer This study introduces a new quantitative mapping technique referred to as “Four Quadrant Vector Mapping” of HM-MRI data, where each image voxel is represented as a vector within a 2D plot with components ‘∆T2/∆b’ and ‘∆ADC/∆TE’ with associated spatial coordinates and quadrant, distance and angle. Measured metrics provides effective cancer markers, with cancers associated with high PQ4, lower PQ2, and higher vector angle, and lower amplitude. Quadrant mapping parameters show promise for determining cancer aggressiveness as they are moderately correlated with Gleason score. Four quadrant mapping could be combined with the compartmental analysis of HM-MRI data to increase diagnostic accuracy. |
| 15:45 |
0726.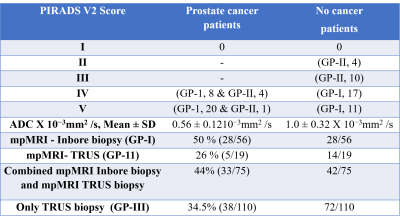 |
Detection rate of prostate cancer using mpMRI-Inbore
targeted prostate biopsy, mpMRI-TRUS guided biopsy and TRUS
guided biopsy
Sujeet Kumar Mewar1,
Sanjay Sharma2,
Ekta Dhamijia3,
Sanjay Thulkar3,
S. Datta Gupta4,
Sridhar Panaiyadiyan5,
Naranamangalam R. Jagannathan6,
Rajeev Kumar5,
and Virendra Kumar 1
1Department of N.M.R., All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India, 2Department of Radio-diagnosis , RPC, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India, 3Department of Radio-diagnosis, IRCH, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India, 4Department of Pathology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India, 5Department of Urology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India, 6Department of Radiology, Present address. Chettinad Academy of Research and Education, Kelambakkam., Tamil Nadu, India Keywords: Prostate, MR-Guided Interventions The present study demonstrated the comparison of detection rate of PCa between the three groups of patients recruited based on PSA > 4 ng/ml and abnormal DRE. The PCa detection rate of mpMRI-Inbore biopsy (Group I) was found 50 % while for mpMRI-TRUS guided biopsy (Group II) 26 %. The combined detection rate of techniques with and without mpMRI was also calculated and found 44 %, for mpMRI-Inbore biopsy and mpMRI-TRUS guided biopsy, while 34.5 %, in TRUS guided biopsy (Group III). Study shows that there is a significant advantage of mpMRI Inbore biopsy compared to TRUS guided prostate biopsy. |
| 15:45 |
0727.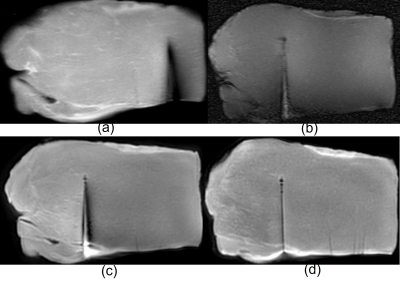 |
Reduction of cryoneedle artifacts due to cryoneedle-RF coil
interaction during MRI-guided cryoablation
Aiming Lu1,
Guruprasad Krishnamoorthy1,2,
Jacinta G Browne1,
Scott M Thompson1,
Daniel A Adamo1,
and David A Woodrum1
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States, 2Philips Healthcare, Rochester, MN, United States Keywords: Pelvis, Artifacts, intervention MRI-guided cryoablation is a widely used minimal invasive treatment that uses extreme cold to destroy localized diseased tissues. The cryoneedles used are expected to introduce little metal artifacts by themselves in the MRI images. However, severe artifacts along the cryoneedle shaft are sometimes observed during MRI guided cryoablations in practice, which can not only complicate the cryoablation procedures, but also potentially cause complications and negatively affect treatment outcome. This work demonstrated that the artifacts are likely due to coupling of the cryoneedles and the RF coils, and can be minimized by proper positioning of the cryoneedles, RF coils and patients. |
| 15:45 |
0728.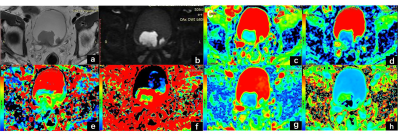 |
Combined IVIM and DKI MRI in pre-operative assessment of
bladder cancer with different stages and grades
Fang Wang1,
Xinghua Xu1,
Guangtai Wu1,
Lingyu Chang1,
Dumin Li1,
Weiqiang Dou2,
Dmytro Pylypenko2,
Dexin Yu1,
and Qing Wang1
1Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China Keywords: Urogenital, Bladder This study aimed to determine the feasibility of intravoxel-incoherent-motion(IVIM) and diffusion-kurtosis-imaging (DKI) parameters in differentiating tumor stages and grades of bladder cancers preoperatively. The IVIM-related parameter (true-diffusion-coefficient) and DKI-related parameters (mean-diffusivity; mean-kurtosis) were significantly higher in non–muscle-invasive than muscle-invasive bladder cancers, and in low-grade than high-grade ones (all p <0.05). Robust diagnostic efficacies were separately confirmed with high AUCs for IVIM and DKI in staging and grading bladder cancers, and the optimal efficacy was obtained with combined IVIM and DKI models. Therefore, combined IVIM and DKI might be considered effective in differentiating the stages and grades of bladder cancers. |
| 15:45 |
0729.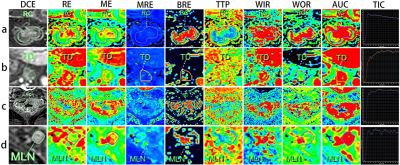 |
Diagnostic performance of DCE-MRI Parameters in
Distinguishing Tumor Deposits from Metastatic Lymph Nodes in
Rectal Cancer
Qiaoyu Xu1,
Hongliang Sun2,
Yanyan Xu2,
Juan Wang2,
and Tongyin Zhang2
1Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China Keywords: Pelvis, Cancer This study aimed to investigate the usefulness of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) derived apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) derived semi-quantitative parameters in distinguishing TD from MLN before surgical resection in RC patients. TD has some specific morphological features, including relatively larger size, lower short- to long-axis ratio, irregular shape and ill-defined border on T2-weighted MR images in rectal cancer. The combination of ADC values and parameters of DCE-MRI can help to improve the diagnostic efficiency of TD in rectal cancer. |
| 15:45 |
0730.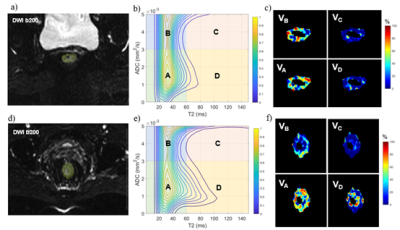 |
Diffusion-relaxation correlation spectroscopic imaging for
evaluating response to neoadjuvant therapy in locally
advanced rectal cancer
Xixi Zhao1,
Wentao Hu2,
Honglei Hu1,
Chuyao Chen1,
Yongming Dai2,
and Yikai Xu1
1Department of Medical Imaging Center, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China Keywords: Digestive, Cancer Different treatment strategies should be applied to locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) patients achieving different response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT). The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic performance of diffusion-relaxation correlation spectroscopic imaging (DR-CSI) in discriminating the pathological complete response (pCR) to nCRT in LARC. Compared to non-pCR group, pCR group showed significantly decreased average DR-CSI VD. ROC curve analysis indicated that the VD has better diagnostic performance in distinguishing pCR from non-pCR patients than traditional ADC and T2 value. |
| 15:45 |
0731.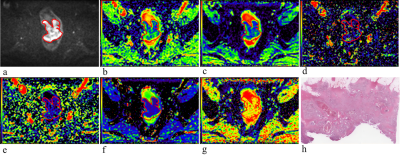 |
Value of multiple mathematical models of advanced zoomed DWI
for the evaluation of tumor-stroma ratio in rectal cancer
Lijuan Wan1,
Hongmei Zhang1,
Yumeng Zhu2,
Yueluan Jiang3,
and Guang Yang4
1National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2Beijing No.4 High School International Campus, Beijing, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China, 4Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China Keywords: Pelvis, Cancer, Tumor microenvironment Tumor-stroma ratio (TSR) can reflect the relationship between tumor cells and tumor microenvironment. Evaluation of the TSR timely and accurately is important because of its role in predicting prognosis and making individualized treatment plans. Diffusion parameters obtained from multiple mathematical models of DWI can reflect microscopic characteristics of tumors. Multi b-value DWI with the advanced zoomed DWI technology can provide a higher-spatial-resolution with less artifacts. This study aimed to investigate the value of zoomed multi b-value DWI for predicting TSR in rectal cancer. The results suggested that distributed diffusion coefficient (DDC) is a promising indicator to identify high TSR group. |
| 15:45 |
0732.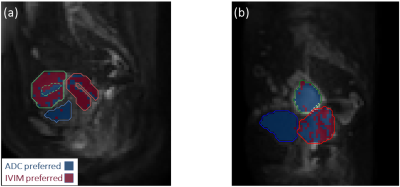 |
Evaluating intra-voxel incoherent motion in the uterine
cervix: healthy volunteer repeatability and therapy-induced
changes in tumours
Anubhav Datta1,2,
Damien J. McHugh1,3,
Michael J. Dubec1,3,
David L. Buckley3,4,
Ross Little1,
Michael Berks1,
Susan Cheung1,
Catharine West1,
Ananya Choudhury1,5,
Peter Hoskin1,5,6,
and James P. B. O'Connor1,2,7
1Division of Cancer Sciences, The University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom, 2Clinical Radiology, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, United Kingdom, 3Christie Medical Physics and Engineering, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, United Kingdom, 4School of Medicine, University of Leeds, Leeds, United Kingdom, 5Clinical Oncology, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, United Kingdom, 6Clinical Oncology, Mount Vernon Cancer Centre, Northwood, United Kingdom, 7Division of Radiotherapy and Imaging, Institute of Cancer Research, London, London, United Kingdom Keywords: Uterus, Cancer There is a need for robust imaging biomarkers which can be used to assess early tumour response to therapy. Intra-voxel incoherent motion (IVIM) can provide information about tumour microstructure and microvasculature, but requires technical and biological validation. This work evaluates IVIM repeatability in the uterine cervix of healthy volunteers, assesses the sensitivity of IVIM parameters to therapy in patients with uterine cervical cancer, and evaluates model suitability through a model comparison framework. |
| 15:45 |
0733.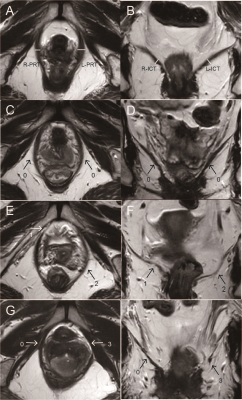 |
Pelvic organs prolapse recurrence after surgery using static
and dynamic MRI
Cheng Zhang1,
Yujiao Zhao2,
Cong You1,
Zhiwei Shen3,
and Wen Shen2
1The First Central Clinical College of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China, 2Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, School of Medicine, Nankai University, Tianjin, China, 3Philips healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Pelvis, Pelvis, Static-Dynamic MR; pelvic organs prolapse; levator ani muscle; pelvic floor reconstruction surgery; recurrent risk As high as 54% is the anatomical recurrence rate following hysterectomy with anterior and posterior vaginal wall restoration for pelvic organ prolapse (POP). The levator ani muscle (LAM) is the primary pelvic floor support system. Using static and dynamic MRI, we investigated the association between the morphology and function of LAM and the postoperative recurrence of POP. Risk factors for the recurrence of POP included the thickness and injury of the LAM at rest, the H line, the M line, and the size of the levator hiatus at rest and strain, as well as the variation of the levator hiatus during the Valsalva maneuver. |
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.